리플렉션이란?
- 구체적인 클래스 타입을 알지 못해도 그 클래스의 메소드, 변수들에 접근할 수 있도록 해주는 자바 API
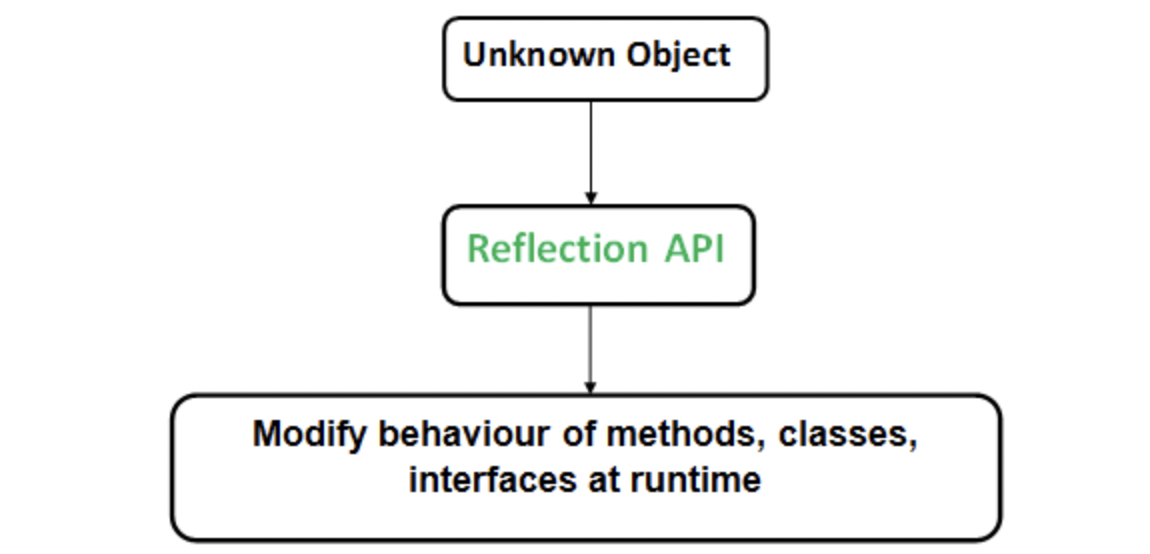
리플렉션은 언제 사용할까?
- 동적으로 클래스를 사용해야할 때
- 코드를 작성할 시점에는 어떤 타입의 클래스를 사용할지 모르지만, 런타임 시점에 지금 실행되고 있는 클래스를 가져와서 실행해야 하는 경우
- 프레임워크나 IDE에서 이런 동적인 바인딩을 이용한 기능을 제공한다.
- intelliJ의 자동완성 기능, 스프링의 어노테이션이 리플렉션을 이용한 기능이다.
사용 예제
- 실습을 위해 아래 클래스가 필요합니다.
public class Dog extends Animal{
private String myName = "뽀삐";
public String myCity = "서울";
public Dog() {
}
private Dog(String myName) {
this.myName = myName;
}
private void myName(String name){
System.out.println("myName : " + name);
}
private void myCity(String city){
System.out.println("myCity : " + city);
}
private void hello(){
System.out.println("hello~");
}
}Class 찾기
- Case 01 - class를 알고 있다는 전제
- 아래 코드를 보시면
Dog.class처럼 클래스 정보를 할당할 수 있습니다. - Class객체는 여러 메서드를 제공하고 있으며
getName()은 클래스의 이름을 리턴합니다.
- 아래 코드를 보시면
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Dog.class;
System.out.println("Class Name : " + cls.getName());
// Class Name : test.Dog 출력
}
}- Case 02 - class를 참조할 수 없고 이름만 알고 있는 상황이라면?
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
System.out.println("Class Name : " + cls.getName());
// Class Name : Dog 출력
}
}Constructor 찾기
- Case 01 - 인자가 없는 생성자 가져오기
getDeclaredConstructor()메서드에 아무런 내용을 작성하지 않으면 인자가 없는 기본 생성자를 가져올 수 있습니다.- 기본 생성자가 없고 오버로딩된 생성자만 있다면
java.lang.NoSuchMethodException예외를 발생시킵니다.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
Constructor constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor();
System.out.println("Constructor : " + constructor.getName());
// Constructor : Dog 출력
}
}- Case 02 - 인자가 있는 생성자 가져오기
getDeclaredConstructor(Param)에 인자를 넣으면 해당 타입과 일치하는 생성자를 찾습니다.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
Constructor constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println("Constructor : " + constructor.getName());
// Constructor : Dog 출력
}
}- Case 03 - 모든 생성자 가져오기
getDeclaredConstructor()메서드를 사용하면 클래스의private,public등의 모든 생성자를 리턴합니다.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
Constructor constructors[] = cls.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor item : constructors){
System.out.println("Get constructors : " + item);
// Get constructors : public test.Dog()
// Get constructors : public test.Dog(java.lang.String)
}
}
}- Case 04 -
public생성자만 가져오기getConstructor()메서드를 사용하면 클래스의public생성자를 리턴할 수 있습니다.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
**Constructor constructors[] = cls.getConstructors();**
for (Constructor item : constructors){
System.out.println("Get public constructors : " + item);
// Get public constructors : public Dog()
}
}
}Method 찾기
- Case 01 - 인자가 없는 메서드 가져오는 방법
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
**Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("hello", null);**
System.out.println("Method : " + method);
// Method : Method : private void Dog.hello()
}
}- Case 02 - 인자가 있는 메서드 가져오는 방법
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
**Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("myName", String.class);**
System.out.println("Method : " + method);
// Method : private void Dog.myName(java.lang.String)
}
}- Case 03 - 모든 메서드를 가져오는 방법
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
**Method methods[] = cls.getDeclaredMethods();**
for (Method item : methods) {
System.out.println("Method : " + item);
// Method : private void test.Dog.hello()
// Method : private void test.Dog.myName(java.lang.String)
// Method : private void test.Dog.myCity(java.lang.String)
}
}
}- Case 04 - 상속받은 메서드와
public메서드만 가져오는 방법
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
**Method methods[] = cls.getMethods();**
for (Method item : methods) {
System.out.println("Method : " + item);
}
}
}Field 찾기
- Case 01 - 필드의 이름을 알고 있을 경우
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("myName");
System.out.println(field);
// private java.lang.String Dog.myName
}
}- Case 02 - 모든 필드를 찾는 방법
- (단, 상속받은 객체의 정보는 찾지 않습니다.)
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class cls = Class.forName("Dog");
**Field fields[] = cls.getDeclaredFields();**
for (Field item : fields) {
System.out.println(item);
// private java.lang.String Dog.myName
// public java.lang.String Dog.myCity
}
}
}참고 자료
