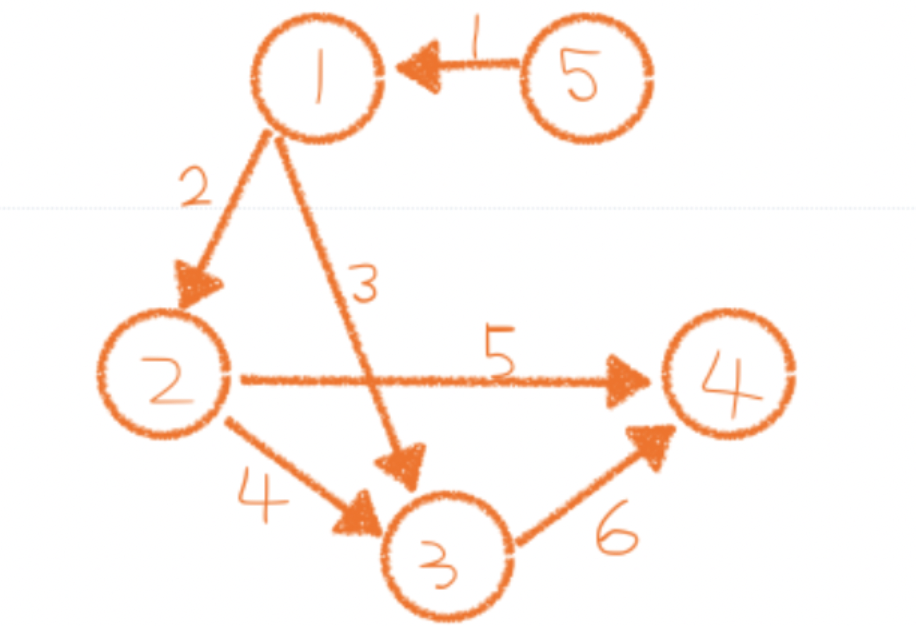
이 포스팅은 최단경로 알고리즘에 대한 이해가 필요합니다.
shortest path #1753
문제 원본 보러가기
깃헙 코드 보러가기
문제 설명
방향그래프가 주어지면 주어진 시작점에서 다른 모든 정점으로의 최단 경로를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오. 단, 모든 간선의 가중치는 10 이하의 자연수이다.
입력
- 첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 V와 간선의 개수 E가 주어진다.
- (1 ≤ V ≤ 20,000, 1 ≤ E ≤ 300,000)
- 모든 정점에는 1부터 V까지 번호가 매겨져 있다고 가정한다.
- 둘째 줄에는 시작 정점의 번호 K(1 ≤ K ≤ V)가 주어진다.
- 셋째 줄부터 E개의 줄에 걸쳐 각 간선을 나타내는 세 개의 정수 (u, v, w)가 순서대로 주어진다.
- 이는 u에서 v로 가는 가중치 w인 간선이 존재한다는 뜻이다.
- u와 v는 서로 다르며 w는 10 이하의 자연수이다.
- 서로 다른 두 정점 사이에 여러 개의 간선이 존재할 수도 있음에 유의한다.
출력
- 첫째 줄부터 V개의 줄에 걸쳐, i번째 줄에 i번 정점으로의 최단 경로의 경로값을 출력한다.
- 시작점 자신은 0으로 출력하고, 경로가 존재하지 않는 경우에는 INF를 출력하면 된다.
예제를 그림으로 표현
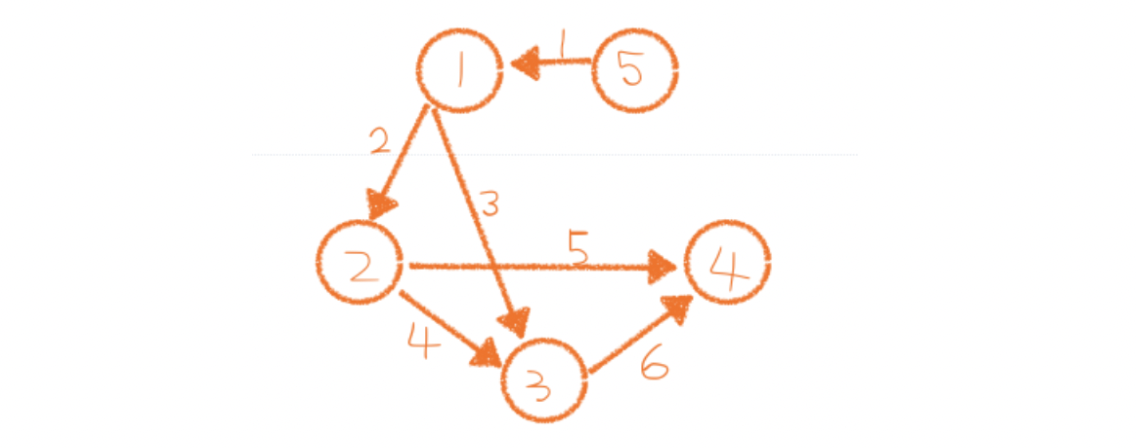
문제 접근 방식
- 첫번째 접근 : 연결 리스트로 그래프를 구현하고, 직접 연결된 경우 가중치를 출력하도록 작성
Edge클래스linkedNode: 간선의 도착 노드 번호를 저장하는 필드weight: 연결된 간선의 가중치를 저장하는 필드
Node클래스number: 노드의 번호를 저장하는 필드edgeList: 직접 연결된 간선들을 저장하는 리스트- 간선은 여러 개가 연결될 수 있으므로, 리스트로 구현
createNode(): 1번부터 N번까지의 노드들을 생성하는 메소드createLinking(): 간선을 만드는 메소드- 시작 노드, 도착 노드, 가중치를 매개 변수로 요구
printDistance(): 모든 노드로의 가중치를 출력하는 메소드- 시작 노드를 매개 변수로 요구
public class Main {
private static BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
private static List<Node> graph = new ArrayList<>();
private static int nodeCount;
private static int linkCount;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//System.out.println("정점의 개수와 간선의 개수를 입력");
String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
StringTokenizer st1 = new StringTokenizer(s);
nodeCount = Integer.parseInt(st1.nextToken());
linkCount = Integer.parseInt(st1.nextToken());
createNode(nodeCount);
// System.out.println("시작 노드를 입력");
String startNodeNum = bufferedReader.readLine();
for (int i = 0; i < linkCount; i++) {
// System.out.println("간선 정보 : 시작 노드, 끝 노드, 가중치를 입력");
String input = bufferedReader.readLine();
StringTokenizer st2 = new StringTokenizer(input);
int endInt = Integer.parseInt(end);
int weightInt = Integer.parseInt(weight);
createLinking(startInt, endInt, weightInt);
}
//시작 정점을 이용한 거리 출력문 필요
printDistance(Integer.parseInt(startNodeNum));
}
private static void createNode(int N) {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {//1번 노드부터 ~ N번 노드 까지 생성
graph.add(new Node(i));
}
}
private static void createLinking(int start, int end, int weight) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++)
if (graph.get(i).number == start)
graph.set(i, new Node(start, new Edge(end, weight)));
}
private static void printDistance(int startNodeNum) {
Node startNode = null;
for (Node n : graph) {
if (n.number == startNodeNum) {
startNode = n; //시작 노드 지정
}
}
//직접 연결되어 있을 경우
for (int i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++) {
if (i == startNodeNum) {
System.out.println("0");
} else if (startNode.edgeList.get(i).linkedNode == i) { //직접 연결이 된 경우
System.out.println(startNode.edgeList.get(i).weight);
} else { //연결이 안된 경우
System.out.println("INF");
}
}
}
}
class Node {
final int number;
List<Edge> edgeList = new ArrayList<>();
Node(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
Node(int number, Edge edge) {
this.number = number;
edgeList.add(edge);
}
}
class Edge {
int linkedNode; //연결된 상대 노드 번호를 저장
int weight; //간선의 가중치
Edge(int linkedNode, int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
this.linkedNode = linkedNode;
}
}
결과 제출 시, 시간 초과 발생!! → 다른 방식으로 접근 필요? :
Dijkstra
- 두번째 접근 : 시간 단축을 위해
Comparable인터페이스의compareTo()를 오버라이딩- 한 정점에서부터 모든 정점까지의 거리를 구하므로
dijkstra알고리즘으로 접근 - 초기
distance를 모두 MAX로 초기화하고, 새로운 거리가 더 작으면 교체한다.
- 한 정점에서부터 모든 정점까지의 거리를 구하므로
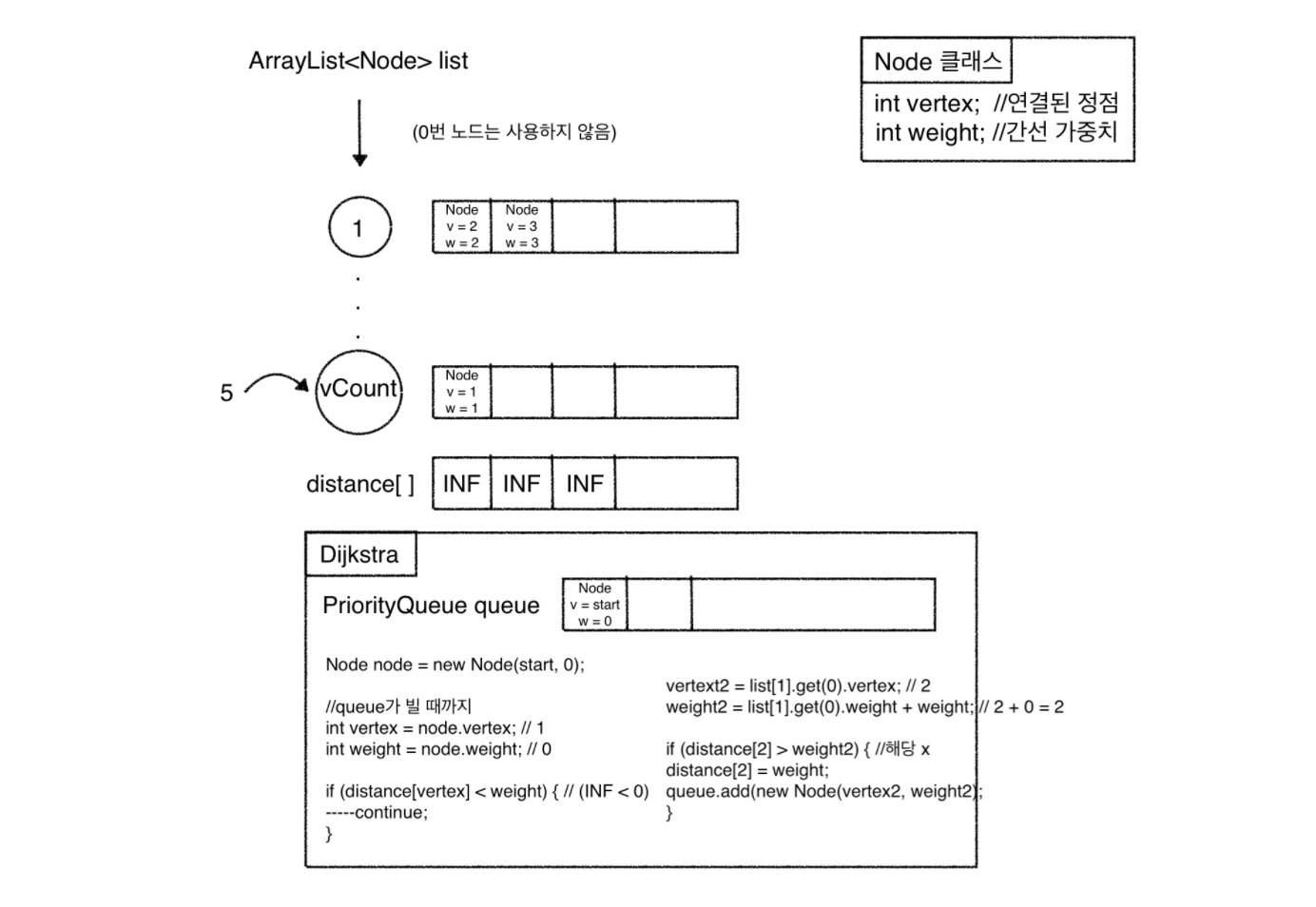
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<Node>[] list;
private static int vCount; //정점 개수
private static int eCount; //간선 개수
private static int start;
private static int[] distance;
private static int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//System.out.println("정점의 개수와 간선의 개수를 입력");
String s = br.readLine();
StringTokenizer st1 = new StringTokenizer(s);
vCount = Integer.parseInt(st1.nextToken());
eCount = Integer.parseInt(st1.nextToken());
// System.out.println("시작 노드를 입력");
start = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
list = new ArrayList[vCount + 1]; //정점 인접 리스트
distance = new int[vCount + 1]; //시작점과 다른 정점간의 최단경로
for (int i = 1; i <= vCount; i++)
list[i] = new ArrayList<>();
//초기화
Arrays.fill(distance, INF);
distance[start] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < eCount; i++) {
String str = br.readLine();
StringTokenizer st2 = new StringTokenizer(str);
int u = Integer.parseInt(st2.nextToken()); //출발
int v = Integer.parseInt(st2.nextToken()); //도착
int w = Integer.parseInt(st2.nextToken()); //가중치
list[u].add(new Node(v, w));
}
dijkstra();
for (int i = 1; i <= vCount; i++) {
if (distance[i] == INF) {
System.out.println("INF");
} else {
System.out.println(distance[i]);
}
}
}
private static void dijkstra() {
PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
queue.add(new Node(start, 0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
int vertex = node.vertex;
int weight = node.weight;
if (distance[vertex] < weight) { //지금께 더 가중치가 크면 갱신할 필요가 없다.
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list[vertex].size(); i++) {//해당 정점과 연결된 것들 탐색
int vertex2 = list[vertex].get(i).vertex;
int weight2 = list[vertex].get(i).weight + weight;
if (distance[vertex2] > weight2) { //지금께 더 최단경로라면 갱신해준다.
distance[vertex2] = weight2;
queue.add(new Node(vertex2, weight2));
}
}
}
}
private static class Node implements Comparable<Node> { //시간 단축으로 성능 개선
int vertex;
int weight;
Node(int vertex, int weight) {
this.vertex = vertex;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return weight - o.weight;
}
}
}