모듈(module)
- 여러 기능(함수 등)들이 뭉쳐진 하나의 .py 파일
- 함수, 변수, 클래스 등을 담아 코드의 재사용성과 관리 효율을 높임
모듈을 사용하는 이유
- 코드의 분할 및 재사용
- 유지보수 용이성
- 네임스페이스 분리로 충돌 방지
hello.py
def greeting(name):
print(f"Hello, {name}!")
def introduce(name, age):
print(f"제 이름은 {name}이고, 나이는 {age}살 입니다.")# 모듈 불러오기(1) <-- 모듈 전체 불러오기
import hello
hello.greeting("Baek") # Hello, Baek!
# 모듈 불러오기(2) <-- 특정 함수만 불러오기
from hello import greeting
greeting("Dongyun") # Hello, Dongyun!
# 모듈 불러오기(3) <-- 모든 함수/변수 불러오기
from hello import * <-- *는 전체를 의미한다.
# introduce("Dongyun2", "26") # 제 이름은 Dongyun2이고, 나이는 26살 입니다.
# 모듈 불러오기(4) <-- 모듈에 별칭을 사용
import hello as h
h.greeting("dingdong") # Hello, dingdong!calc.py
def add(a, b):
return print(a + b)
def subtract(a, b):
return print(a - b)
def multiply(a, b):
return print(a * b)
def divide(a, b):
if b == 0:
print("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.")
return None
else:
return print(a / b)실습1. 계산기 모듈 만들어보기
import calc as calc
calc.add(100, 28) # 128
from calc import subtract
subtract(555, 55) # 500
import calc as m
m.multiply(77, 847821) # 65282217
import calc as c
c.divide(123876493296178326498, 0) # 0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.
import calc as n
n.divide(78346, 24) # 264.4166666666665결과

패키지
- 여러 모듈(.py파일)을 폴더 (디렉터리) 단위로 묶은 것
- 대규모 프로젝트, 라이브러리 제작 시 사용
# 패키지에서 모듈 불러오기(1)
from my_package import calc as c
c.add(10, 20) # 30
# 패키지에서 모듈 불러오기(2)
from my_package.calc import add
add(10, 20) # 30파이썬 표준 라이브러리
# math 모듈: 수학적 연산에 사용되는 모듈
# import math as m
# # 1. 올림/내림
# # ceil: 올림, 소수점 지정x
# m.ceil(3.14) # 4
# # floor: 내림, 소수점 지정x
# m.floor(3.14) # 3
# # round: 반올림 - 내장함수
# round(3.141592, 2) # 3.14
# # 2. 제곱, 제곱근
# # pow(x, y): 제곱 - x ^ y
# m.pow(2, 3) # 8.0
# # sqrt(x): 제곱근 반환
# m.sqrt(16) # 4.0
# # 3. 상수
# # pi: 원주율
# print(m.pi) # 3.141592653589793
# # 4. 수학계산 편의 기능
# print(m.factorial(3)) # 6
# # 최대 공약수
# print(m.gcd(12, 20)) # 4
# # 최소 공배수
# print(m.lcm(12, 20)) # 60실습 2-1. 실제 거리 계산: 좌표 두 점 사이 거리 구하기
# import math as a
# x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, input("변수값 입력(x1, y1, x2, y2) : ").split(", "))
# distance = a.sqrt(a.pow(int(x2-x1), 2) + a.pow(int(y2-y1), 2))
# print(distance)결과
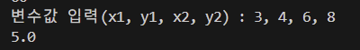
실습 2-2. 상품 나누기: 최소 공배수와 최대 공약수
# import math as a
# students = 18
# teachers = 24
# # 최대 공약수
# print(a.gcd(students, teachers))
# # 최소 공배수
# print(a.lcm(students, teachers))결과
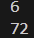
random 모듈
- 랜덤값(난수) 생성 시 사용
- 주요기능: 난수, 임의 선택, 섞기
import random1. 난수 생성
- random(): 0이상 1 미만의 float 난수 반환
print(random.random())- uniform(a, b): a 이상 b 이하의 실수 난수 반환
print(random.uniform(1, 10))- randint(a, b): a이상 b 이하의 정수 난수 반환
print(random.randint(1, 100))- randrange(Start, stop, step): 범위 안의 정수 난수 반환, 간격 지정 가능
print(random.randrange(0, 100, 5))2. 랜덤 선택
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "watermelon", "grape", "orange"]- choice(seq): 시퀀스에서 임의의 요소 1개 반환
print(random.choice(fruits))- choices(seq, k): 시퀀스에서 "중복허용" k개 요소 리스트를 반환
print(random.choices(fruits, k = 2))- 섞기/sample(seq, k): 시퀀스에서 "중복없이" k개 요소 리스트를 반환
print(random.sample(fruits, k = 2))- shuffle(seq): 시퀀스의 요소를 무작위로 섞음 -> 원본 시퀀스를 변경
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(random.shuffle(numbers))
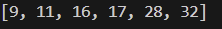
print(numbers)실습 3. 로도 번호 뽑기
num = []
for i in range(6):
num.append(random.randint(1, 46))
print(sorted(random.sample(num, k=6)))
# result = sorted(random.sample(range(1, 46), k=6))
# print(result)결과
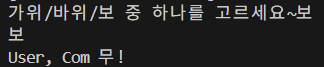
실습 4. 가위 바위 보 게임 만들기
game_set = ['가위', '바위', '보']
com_pick = random.choice(game_set)
user_pick = input("가위/바위/보 중 하나를 고르세요~")
if com_pick == '가위' and user_pick == '바위':
print("User 승!")
elif com_pick == '가위' and user_pick == '보':
print("Com 승!")
elif com_pick == '바위' and user_pick == '가위':
print("User 승!")
elif com_pick == '바위' and user_pick == '보':
print("Com 승!")
elif com_pick == '보' and user_pick == '가위':
print("User 승!")
elif com_pick == '보' and user_pick == '바위':
print("Com 승!")결과
이 코드는 너무 불필요하게 반복을 하니 while을 사용해서 효율을 높여보겠다.
elif com_pick == user_pick:
print("User, Com 무!")
while True:
com_pick = random.choice(game_set)
user_pick = input("가위/바위/보 중 하나를 고르세요~")
print("컴퓨터: ", com_pick)
# 승리 규칙 정의(key가 이기면 value를 이김)
win_rules = {'가위':'보', '바위':'가위', '보':'바위'}
if com_pick == user_pick:
print("무승부! 다시!\n")
continue # 다시 반복문 처음으로 돌아감
elif win_rules[user_pick] == com_pick:
print("User 승!")
break # 승패가 결정되면 반복문 종료
else:
print("Com 승!")
breakdatetime 모듈
- 날짜와 시간의 생성, 조작, 형식 변환과 같은 시간 관련 기능을 제공
- 주요기능: 현재 날짜/시간, 시간 차이 계산, 포멧 변환
import datetime- 날짜/시간 구하기
# 현재 날짜와 시간 구하기
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print(now)
# 오늘 날짜만 구하기
today = datetime.date.today()
print(today)- 날짜/시간 형식 변환
formatted = now.strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")
print(formatted)
parsed = datetime.datetime.strptime(formatted, "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")
print(parsed)- 날짜/시간 연산
dt = datetime.date(2025, 7, 7)
passed_time = today - dt
print(f"{passed_time}일이 지났습니다.")
# 4. 요일반환: weekday
# 0: 월요일 ~ 7: 일요일
days = ["월", "화", "수", "목", "금", "토", "일"]
day_num = today.weekday()
print(days[day_num])
# datetime 또는 date 객체에는 년/월/일 시간 등이 속성으로 들어있음
print(datetime.datetime.now().year)실습 5. 다음 생일까지 남은 날짜 계산하기
# bd = input("생일(MM-DD)을 입력하세요: ")
# bd = datetime.datetime.strptime(bd, '%m-%d').date()
# today = datetime.date.today()
# bd_this_year = datetime.date(today.year, bd.month, bd.day)
# if today > bd_this_year:
# next_bd = datetime.date(today.year + 1, bd.month, bd.day)
# else:
# next_bd = bd_this_year
# days = (next_bd - today).days
# print(f"다음 생일까지 {days}일이 남았습니다.")
# b_month, b_day = map(int, input.split("-"))
# today = datetime.date.today()
# # 올해 생일을 date 객체로 변환
# b_this_year = datetime.date(today.year, b_month, b_day)
# # 이하는 동일하므로 생략결과

calendar 모듈
- 날짜와 달력 관련 다양한 기능을 제공
- 주요기능: 달력(캘린더) 생성, 요일 계산, 윤년 판별
import calendar-
달력 조회
print(calendar.prmonth(2025, 9))
print(calendar.prcal(2025)) -
텍스트로 값을 반환
print(calendar.month(2025, 11)) -
요일 반환
print(calendar.weekday(2025, 11, 26))
time 모듈
- 시간의 측정, 지연, 변환과 같은 시간 관련 기능을 제공
- 주요기능: 현재 시간, 대기(sleep), 시간측정
import time- 시간 반환
# time()
# Unix 타임스탬프로 반환 (1970.1.1부터 경과 초)
print(time.time())
# ctime(): 현재 시간을 문자열로 반환
print(time.ctime())
print(time.ctime(0)) # 기준시로 반환 (1970.1.1)
# strftime(): 원하는 포맷의 문자열로 시간 객체 변환
lt = time.localtime()
formatted = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", lt)
print(formatted)
# strptime(): 문자열을 struct_time 객체로 변환
parsed = time.strptime(formatted, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print(parsed)- 시간 지연
# sleep(seconds) = 지정한 초만큼 프로그램이 일시 정지
time.sleep(1)
print("time sleep")
# 시간 측정하기
start = time.time()
for i in range(5):
print(i)
time.sleep(1)
end = time.time()
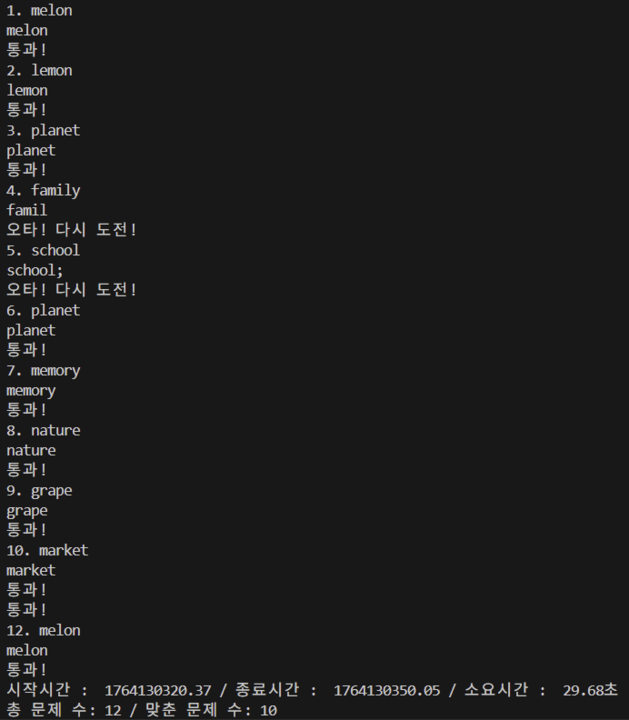
print(f"수행시간 : {end - start: .2f}초")실습 6. 타자 연습 게임 만들기
words = [
"apple", "banana", "orange", "grape", "lemon",
"peach", "melon", "cherry", "plum", "pear",
"school", "friend", "family", "flower", "garden",
"window", "bottle", "pencil", "summer", "winter",
"happy", "future", "travel", "animal", "market",
"doctor", "planet", "energy", "nature", "memory"
]
word_correct_count = 0
word_idx = 0
question_num = 0
input("시작하려면 엔터를 누르세요.")
print("시작!")
start = time.time()
time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime(start))
while word_correct_count < 2:
new_word = random.choice(words)
word_idx += 1
trial += 1
print(f"{word_idx}. {new_word}")
while True:
user_input = input()
if new_word == user_input:
print("통과!")
word_correct_count += 1
break # 맞추면 빠져나와서 다음 단어로 진행
else:
print("오타! 다시 도전!")
end = time.time()
time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime(end))
print(f"시작시간 : {start: .2f} / 종료시간 : {end: .2f} / 소요시간 : {end - start: .2f}초")
print(f"총 시도 수: {trial} / 맞춘 문제 수: {word_correct_count}")결과
sys 모듈
- 파이썬 인터프리터와 관련된 다양한 기능 제고
import sys파이썬 버전 정보
print(sys.version)운영체제 정보
print(sys.platform)프로그램 종료
# print("프로그램 시작")
# sys.exit() # 강제 종료
# print("실행되지 않는 코드")os 모듈
- 운영체제와 상호작용 할 수 있도록 도와주는 기능 제공
import os# getcwd(): 현재 작업 디렉토리 반환
print(os.getcwd())
# listdir(): 현재 폴더 내 파일, 디렉토리 목록 반환
print(os.listdir())
# 폴더 생성
folder_name = "sample_folder"
if not os.path.exists(folder_name):
os.mkdir(folder_name)
else:
print(f"{folder_name} 폴더가 이미 존재합니다.")
print(os.listdir())