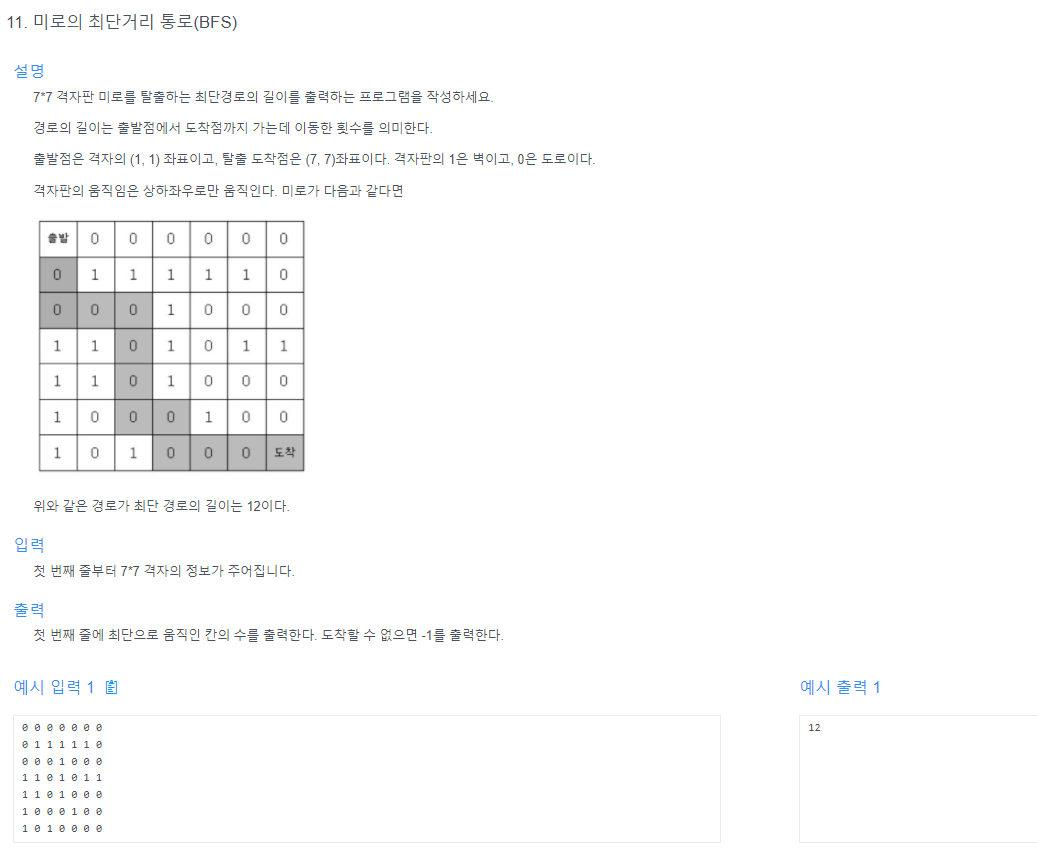
문제
풀이
- dfs의 한 루트만 끝까지 파고 드는 것에 반해 Queue에 branch(열린 곳)를 모두 담고 순차적으로 모든 가지들을 한 단계씩 점진하여 최적의 경로를 구한다.
- dfs : 재귀
- bfs : queue
전체 코드
package inflearn;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class I0811 {
static int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int[] dy = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[][] board, dis;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
board = new int[8][8];
dis = new int[8][8];
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 7; j++) {
board[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
bfs();
if (dis[7][7] == 0) System.out.println(-1);
else System.out.println(dis[7][7]);
}
static void bfs() {
Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Point(1, 1));
board[1][1] = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point p = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = p.getX() + dx[i];
int ny = p.getY() + dy[i];
if (nx >= 1 && ny >= 1 && nx <= 7 && ny <= 7) {
if (board[nx][ny] == 0) {
board[nx][ny] = 1;
queue.offer(new Point(nx, ny));
dis[nx][ny] = dis[p.getX()][p.getY()] + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
class Point {
private final int x;
private final int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
}

