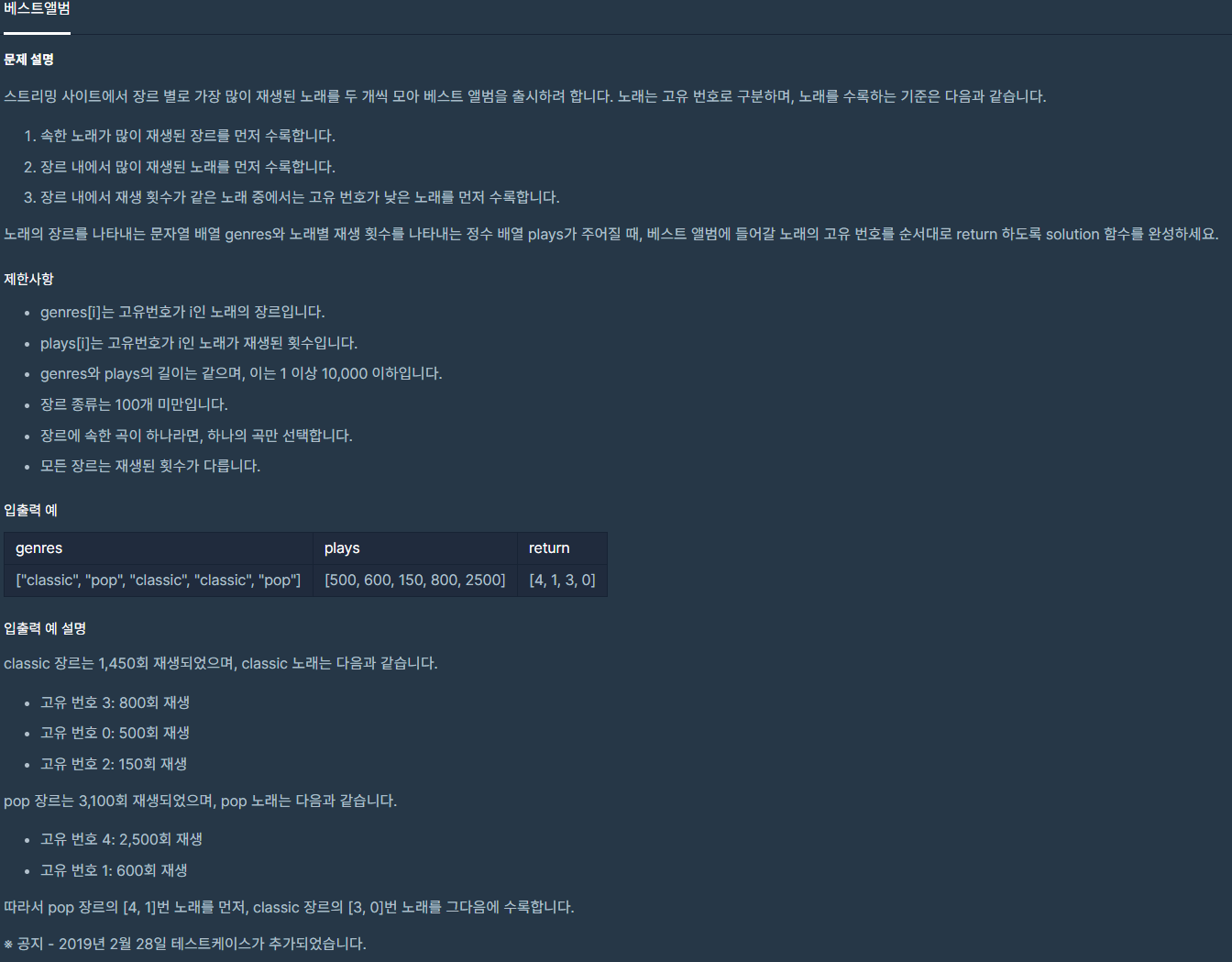
문제 주소
풀이
-
정렬하기 쉽게 Music 클래스를 만들어서 관리한다.
-
장르 별 합을 가지고 정렬하기 때문에 HashMap 으로 각 장르별 재생된 노래 횟수의 합을 저장한다.
hashMap.put(genres[i], hashMap.getOrDefault(genres[i], 0) + plays[i]);
-
인풋 장르 배열가지고는 재생된 횟수를 알수 없기 때문에 ArrayList를 하나 만들어서 재생 횟수를 기준으로 내림차순 장르 배열을 만든다.
genresSorted.sort((o1, o2) -> hashMap.get(o2).compareTo(hashMap.get(o1)));
-
정렬한 장르 배열로 Music을 뽑아내서 list에 추가하고 재생한 횟수를 내림차순으로 정렬한다.
-
베스트 앨범은 1 ~ 2개를 가지기 때문에 체크하고 result에 추가해준다.
전체 코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public static int[] solution(String[] genres, int[] plays) {
HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
// HashMap 으로 장르 당 노래별 재생 횟수의 합을 저장한다.
for (int i = 0; i < genres.length; i++) {
hashMap.put(genres[i], hashMap.getOrDefault(genres[i], 0) + plays[i]);
}
// HashMap 에서는 정렬이 안되므로 key 를 뽑아내 배열을 만들고 재생 횟수 기준으로 내림차순한다.
// (o1,o2) -> hashMap.get(o2).compareTo(hashMap.get(o1));
ArrayList<String> genresSorted = new ArrayList<>(hashMap.keySet());
genresSorted.sort((o1, o2) -> hashMap.get(o2).compareTo(hashMap.get(o1)));
// 정렬된 key 리스트로 장르를 뽑아내고 많이 들은 횟수로 정렬한다.
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (String genre : genresSorted) {
ArrayList<Music> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < genres.length; i++) {
if (genres[i].equals(genre)) {
list.add(new Music(genre, plays[i], i));
}
}
// 재생된 횟수 내림차순 정렬
list.sort((o1, o2) -> o2.play - o1.play);
// 장르에 속한 곡 처음 1개는 저장하고 2개면 2개까지 저장
result.add(list.get(0).idx);
if (list.size() != 1) {
result.add(list.get(1).idx);
}
}
// print result
int[] answer = new int[result.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
answer[i] = result.get(i);
}
return answer;
}
static class Music {
String genre;
int play;
int idx;
public Music(String genre, int play, int idx) {
this.genre = genre;
this.play = play;
this.idx = idx;
}
}
}