*본 내용은 [Do it! 자바 프로그래밍 입문] 책과 강의를 보고 공부하면서 요점 정리한 내용입니다.
◼ 상속
✔ 상속이란?
클래스를 정의할 때 이미 구현된 클래스를 상속(inheritance) 받아서 속성이나 기능이 확장되는 클래스를 구현함
-
상속하는 클래스: 상위 클래스, parent class, base class, super class
-
상속받는 클래스: 하위 클래스, child class, derived class, subclass
-
클래스 상속 문법
class B extends A { // A: 상위 클래스, B: 하위 클래스 } -
상위 클래스는 하위 클래스보다 일반적인 의미를 가짐
하위 클래스는 상위 클래스보다 구체적인 의미를 가짐

- extends 뒤에는 단 하나의 class만 사용할 수 있음. 자바는 single inheritance만을 지원함
✔ 상속과 합성
상속은 '코드의 재사용'을 의미하는 것이 아닌 '일반적인 개념에서 구체적인 개념으로 구체화하는 것'을 의미한다. (IS-A 관계)
코드를 재사용하는 방법 2가지로 상속과 합성이 있다.
다음 예시에서 원의 point를 나타내는 방법으로 상속이 아닌 합성을 사용한다. 원과 point의 관계는 상속 관계가 아니라 point를 단지 활용만 하는 관계(HAS-A 관계)이므로 상속이 아닌 합성을 사용하는 것이다.
Point.java
package inheritance;
public class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}Circle.java
package inheritance;
public class Circle { // public class Circle extends Point { (X)
private Point point; // HAS-A 관계
private int radius;
public Circle() {
point = new Point();
}
}
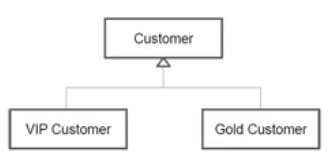
✔ 실습 - 상속을 활용한 고객관리 프로그램
고객의 정보를 활용하여 고객 맞춤 서비스를 구현
고객의 등급에 따라 차별화된 할인율과 포인트를 지급
등급에 따른 클래스를 따로 구현하는 것이 아닌 일반적인 클래스를 먼저 구현하고 그보다 기능이 많은 클래스는 상속을 활용하여 구현함
- Customer 클래스 속성
| 멤버 변수 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| customerID | 고객 아이디 |
| customerName | 고객 이름 |
| customerGrade | 고객 등급 - 기본 생성자에서 지정되는 기본 등급은 SILVER입니다. |
| bonusPoint | 고객의 보너스 포인트 - 고객이 제품을 구매할 경우 누적되는 보너스 포인트입니다. |
| bonusRatio | 보너스 포인트 적립 비율 - 고객이 제품을 구매할 때 구매 금액의 일정 비율이 보너스 포인트로 적립됩니다. 이때 계산되는 적립 비율입니다. - 기본 생성자에서 지정되는 적립 비율은 1%입니다. 즉 10,000원짜리를 사면 100원이 적립됩니다. |
- Customer 클래스 메서드
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Customer() | 기본 생성자입니다. 고객 한 명이 새로 생성되면 customerGrade는 SILVER이고, bonusRatio는 1%로 지정합니다. |
| calcPrice(int price) | 제품에 대해 지불해야 하는 금액을 계산하여 반환합니다. 할인되지 않는 경우 가격을 그대로 반환합니다. 그리고 가격에 대해 보너스 포인트 비율을 적용하여 보너스 포인트를 적립합니다. |
| showCustomerInfo() | 고객 정보를 출력합니다. 고객 이름과 등급, 현재 적립된 포인트를 보여 줍니다. |
- 새로운 고객 등급 추가하기
∙ 단골고객에 대한 혜택이 필요함
∙ 우수 고객을 관리하기 위해 다음과 같은 혜택을 줌
∙ 고객 등급: VIP
∙ 제품 구매 할인율: 10%
∙ 보너스 포인트: 5%
∙ 담당 전문 상담원 배정
Customer.java
package inheritance;
public class Customer {
protected int customerID;
protected String customerName;
protected String customerGrade;
int bonusPoint;
double bonusRatio;
public Customer()
{
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
}
public Customer(int customerID, String customerName){
this.customerID = customerID;
this.customerName = customerName;
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
}
public int calcPrice(int price){
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price;
}
public String showCustomerInfo(){
return customerName + " 님의 등급은 " + customerGrade + "이며, 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + "입니다.";
}
public int getCustomerID() {
return customerID;
}
public void setCustomerID(int customerID) {
this.customerID = customerID;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getCustomerGrade() {
return customerGrade;
}
public void setCustomerGrade(String customerGrade) {
this.customerGrade = customerGrade;
}
}VIPCustomer.java
package inheritance;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
private int agentID;
private double saleRatio;
public VIPCustomer()
{
customerGrade = "VIP";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
saleRatio = 0.1;
}
public VIPCustomer(int customerID, String customerName, int agentID){
super(customerID, customerName);
customerGrade = "VIP";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
saleRatio = 0.1;
this.agentID = agentID;
}
public int calcPrice(int price){
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price - (int)(price * saleRatio);
}
public int getAgentID(){
return agentID;
}
}CustomerTest1.java
package inheritance;
public class CustomerTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customerLee = new Customer();
customerLee.setCustomerID(10100);
customerLee.setCustomerName("Lee");
VIPCustomer customerKim = new VIPCustomer();
customerKim.setCustomerID(10101);
customerKim.setCustomerName("Kim");
System.out.println(customerLee.showCustomerInfo());
System.out.println(customerKim.showCustomerInfo());
}
}✔ protected 접근 제한자
외부 클래스에서는 private처럼, 상속 관계에서만 public처럼 사용할 수 있는 접근 제한자이다.
protected는 패키지가 달라도 상속관계에서는 public처럼 사용할 수 있다.
(cf. bonusRatio처럼 default일 때는 패키지가 다르면 접근 불가능하다.)
Customer.java
package inheritance;
public class Customer {
protected int customerID;
protected String customerName;
protected String customerGrade;
int bonusPoint;
double bonusRatio;
...VIPCustomer.java
package inheritance;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
private int agentID;
private double saleRatio;
public VIPCustomer()
{
customerGrade = "VIP"; //Customer.java에서 customerGrade를 private로 선언하면 이 코드가 오류가 나게 된다.
bonusRatio = 0.05;
saleRatio = 0.1;
}
...✔ 접근 제한자 가시성
| 외부 클래스 | 하위 클래스 | 동일 패키지 | 내부 클래스 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| public | O | O | O | O |
| protected | X | O | O | O |
| 선언되지 않음 (default) | X | X | O | O |
| private | X | X | X | O |
- private < default < protected < public
◼ 상속에서 클래스 생성과 형 변환
✔ 상속에서 클래스 생성 과정
- 하위 클래스가 생성될 때 상위 클래스가 먼저 생성된다.
상위 클래스의 생성자가 호출되고 하위 클래스의 생성자가 호출 된다. - 아무것도 없는 경우 컴파일러는 상위 클래스 기본 생성자를 호출하기 위한 super()를 코드에 넣어 준다.
- super() 호출되는 생성자는 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자이다.
만약 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자가 없는 경우 (매개변수가 있는 생성자만 존재하는 경우) 하위 클래스는 명시적으로 상위 클래스로 호출해야 함
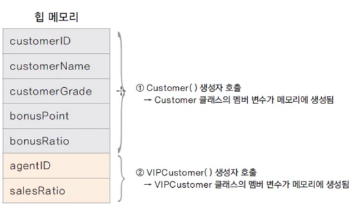
✔ 상속에서의 메모리 상태
상위 클래스의 인스턴스가 먼저 생성이 되고, 하위 클래스의 인스턴스가 생성된다.
private 이라고 생성이 안되는 것이 아닌 접근만 못하는 것이다.
✔ super 예약어
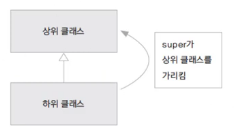
this가 자기 자신의 인스턴스의 주소를 가지는 것처럼 super는 하위 클래스가 상위 클래스에 대한 주소를 가지게 된다.
하위 클래스가 상위 클래스에 접근할 때 사용할 수 있다.
VIPCustomer.java
package inheritance;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
...
public VIPCustomer()
{
// super(); // 프리컴파일 단계에서 이 코드가 자동으로 들어간다.
// super 예약어로 인해 default 생성자 호출됨(Customer())
customerGrade = "VIP";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
saleRatio = 0.1;
}
public VIPCustomer(int customerID, String customerName, int agentID){
super(customerID, customerName);
// Customer(int customerID, String customerName) 이용하고 싶으면 직접 super 호출
customerGrade = "VIP";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
saleRatio = 0.1;
this.agentID = agentID;
}
... ※ 참고) 모든 클래스는 Object 클래스에게 상속받는다. 상위 클래스인 Customer 클래스도 Object클래스에게 상속 받으므로 Customer()에서 자동으로 super(); 호출됨
✔ 상위 클래스로의 묵시적 형변환(업캐스팅)
- 상위 클래스형으로 변수를 선언하고 하위 클래스 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있다.
- 하위 클래스는 상위 클래스의 타입을 내포하고 있으므로 상위 클래스로 묵시적 형변환이 가능하다.
- 예시) Customer으로 변수를 선언하고 VIPCustomer로 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있다.

✔ 형 변환에서의 메모리
Customer vc = new VIPCustomer();에서 vc가 가리키는 것은?
VIPCustomer() 생성자의 호출로 인스턴스는 모두 생성되었지만 타입이 Customer이므로 접근할 수 있는 변수나 메서드는 Customer의 변수와 메서드이다.
메모리는 VIPCustomer 영역까지 생성됐지만 타입이 Customer이므로 VIPCustomer 멤버 변수는 볼 수 없다.
◼ 메서드 오버라이딩(overriding)
✔ 메서드 오버라이딩(overriding)
-
상위 클래스에 정의 된 메서드 중 하위 클래스와 기능이 맞지 않거나 추가 기능이 필요한 경우 같은 이름과 매개변수로 '하위 클래스'에서 재정의한다.
-
VIPCustomer 클래스의 calcPrice() 메서드 재정의
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price + bonusRatio;
return price = (int)(price * saleRatio);
} // 보너스 포인트 적립하고 할인률을 적용한 가격을 반환✔ 묵시적 형 변환과 재정의된 메서드 호출
Customer vc = new VIPCustomer();
vc.calcPrice(10000);
위 코드에서 calcPrice()메서드는 어느 메서드가 호출될 것인가?
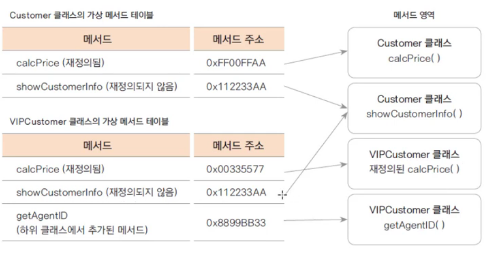
✔ 가상 메서드(virtual method)
-
프로그램에서 어떤 객체의 변수나 메서드의 참조는 그 타입에 따라 이루어진다.
가상 메서드의 경우는 타입과 상관없이 실제 생성된 인스턴스의 메서드가 호출되는 원리이다. -
Customer vc = new VIPCustomer();
vc.calcPrice(10000);
vc의 타입은 Customer지만, 실제 생성된 인스턴스인 VIPCustomer 클래스의 calcPrice()메서드가 호출된다. -
c++은 가상 메서드인 것도 았고 아닌 것도 잇지만, 자바는 모든 메서드가 가상메서드이다.
-
가상 메서드로 다형성이 구현된다.
◼ 다형성(polymorphism)
✔ 다형성(polymorphism)
-
하나의 코드가 여러가지 자료형으로 구현되어 실행되는 것,
코드 한 줄이 다양한 구현 나타낼 수 있는 것을 다형성이라고 한다. -
정보은닉, 상속과 더불어 객체지향 프로그래밍의 가장 큰 특징 중 하나이다.
-
객체지향 프로그래밍의 유연성, 재활용성, 유지보수성에 기본이 되는 특징이다.
✔ 다형성 구현하기
하나의 클래스를 상속받은 여러 클래스가 있는 경우, 각 클래스마다 같은 이름의 서로 다른 메서드를 재정의 한다.
상위 클래스 타입으로 선언된 하나의 변수가 여러 인스턴스에 대입되어 다양한 구현이 실행될 수 있다.
AnimalTest.java
package inheritance;
class Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("동물이 움직입니다.");
}
}
class Human extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("사람이 두 발로 걷습니다.");
}
}
class Tiger extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("호랑이가 네 발로 뜁니다.");
}
}
class Eagle extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("독수리가 하늘을 납니다.");
}
}
public class AnimalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnimalTest test = new AnimalTest();
test.moveAnimal(new Human());
test.moveAnimal(new Tiger());
test.moveAnimal(new Eagle());
//매개변수로 Human()을 넣는 것은 다음과 같다
//Animal animal = new Human();
}
public void moveAnimal(Animal animal) {
animal.move(); // 다형성을 나타내는 코드
}
}실행 결과
결과가 다양하게 출력된다.
사람이 두 발로 걷습니다.
호랑이가 네 발로 뜁니다.
독수리가 하늘을 납니다.✔ 애노테이션(Annotation)
마우스 우클릭 > source > override > 재정의 하고 싶은 메서드를 선택하면 메서드를 재정의 할 수 있다.
이 때 애노테이션을 사용한다. 애노테이션은 영어로는 주석이라는 의미로 @ 기호와 함께 사용하며 @애노테이션 이름으로 표현한다.
자바에서 제공하는 애노테이션은 컴파일러에게 특정한 정보를 제공해 주는 역할을 한다. 예를 들어 @Override는 이 메서드가 재정의된 메서드임을 컴파일러에게 알린다. 만약 메서드의 선언부가 다르다면 컴파일 오류가 발생해 프로그래머의 실수를 막아준다.
[표준 애노테이션]
| 애노테이션 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| @Override | 재정의된 메서드라는 정보 제공 |
| @FunctionalInterface | 함수형 인터페이스라는 정보 제공 |
| @Deprecated | 이후 버전에서 사용되지 않을 수 있는 변수, 메서드에 사용됨 |
| @SuppressWarnings | 특정 경고가 나타나지 않도록 함 |
✔ 고객관리 프로그램에서 다형성 활용하기
일반 고객과 VIP 고객의 중간 등급의 고객을 생성하고자 한다.
5명의 고객을 ArrayList에 생성하여 저장한 다음 각 고객이 물건을 샀을 때의 가격과 보너스 포인트를 계산.
VIPCustomer.java 추가된 부분
package witharraylist;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
...
@Override
public String showCustomerInfo() {
return super.showCustomerInfo() + "담당 상담원 아이디는 " + agentID + "입니다.";
}
}GoldCustomer.java
package witharraylist;
public class GoldCustomer extends Customer{
double saleRatio;
public GoldCustomer(int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
customerGrade = "Gold";
bonusRatio = 0.02;
saleRatio = 0.1;
}
@Override
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price - (int)(price * saleRatio);
}
}CustomerTest.java
package witharraylist;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Customer> customerList = new ArrayList<Customer>();
Customer customerLee = new Customer(10010, "이순신");
Customer customerShin = new Customer(10011, "신사임당");
GoldCustomer customerHong = new GoldCustomer(10012, "홍길동");
GoldCustomer customerYul = new GoldCustomer(10013, "이율곡");
VIPCustomer customerKim = new VIPCustomer(10014, "김유신", 12345);
customerList.add(customerLee);
customerList.add(customerShin);
customerList.add(customerHong);
customerList.add(customerYul);
customerList.add(customerKim);
System.out.println("====== 고객정보 출력 ======");
for(Customer customer : customerList) {
System.out.println(customer.showCustomerInfo());
}
System.out.println("====== 할인율과 보너스 포인트 결과 ======");
int price = 10000;
for(Customer customer : customerList) {
int cost = customer.calcPrice(price);
System.out.println(customer.getCustomerName() + "님이 " + cost + "를 지불하셨습니다.");
System.out.println(customer.showCustomerInfo());
}
}
}실행 결과
====== 고객정보 출력 ======
이순신 님의 등급은 SILVER이며, 보너스 포인트는 0입니다.
신사임당 님의 등급은 SILVER이며, 보너스 포인트는 0입니다.
홍길동 님의 등급은 Gold이며, 보너스 포인트는 0입니다.
이율곡 님의 등급은 Gold이며, 보너스 포인트는 0입니다.
김유신 님의 등급은 VIP이며, 보너스 포인트는 0입니다.담당 상담원 아이디는 12345입니다.
====== 할인율과 보너스 포인트 결과 ======
이순신님이 10000를 지불하셨습니다.
이순신 님의 등급은 SILVER이며, 보너스 포인트는 100입니다.
신사임당님이 10000를 지불하셨습니다.
신사임당 님의 등급은 SILVER이며, 보너스 포인트는 100입니다.
홍길동님이 9000를 지불하셨습니다.
홍길동 님의 등급은 Gold이며, 보너스 포인트는 200입니다.
이율곡님이 9000를 지불하셨습니다.
이율곡 님의 등급은 Gold이며, 보너스 포인트는 200입니다.
김유신님이 9000를 지불하셨습니다.
김유신 님의 등급은 VIP이며, 보너스 포인트는 500입니다.담당 상담원 아이디는 12345입니다.✔ IS-A 관계, HAS-A 관계
[상속을 언제 사용할까?]
- 여러 클래스를 생성하지 않고 하나의 클래스에 공통적인 요소를 모으고 나머지 클래스는 이를 상속받은 다음 각각 필요한 특성과 메서드를 구현하고자 할 때 사용하는 방법이다.
만약 하나의 클래스에 여러 특성을 한꺼번에 구현하고자 하면, 많은 if문이 생길 수 있다.
if(customerGrade == "VIP") { // 할인해주고, 적립도 많이 해주고
}
else if(customerGrade == "GOLD") { // 할인해주고, 적립은 적당히
}
else if(customerGrade == "SILVER") { // 적립만 해준다
}- 상속을 항상 사용해야하는 것은 아니다.
상속을 이용하게 되면 클래스간 종속적인 관계가 만들어지므로 이 점을 유의하고 사용해야 한다.
[IS-A 관계, HAS-A 관계]
-
IS-A 관계(is a relationship : inheritance)
일반적인(general) 개념과 구체적인(specific) 개념과의 관계
상위 클래스: 일반적인 개념 클래스(예: 포유류)
하위 클래스: 구체적인 개념 클래스(예: 사람, 원숭이, 고래...)
단순히 코드를 재사용하는 목적으로 사용하지 않는다. -
HAS-A 관계(composition)
한 클래스가 다른 클래스를 소유한 관계
코드 재사용의 한 방법이다.
Student가Subject를 포함한 관계
class Student {
Subject majorSubject;
}◼ 다운 캐스팅 - instanceif
✔ 다운 캐스팅 - instanceif
원래 형으로 복귀하고 싶을 때 사용한다.
이미 업 캐스팅을 했는데 다운 캐스팅을 한다는 것은 좋은 방법은 아니다. 먼저 오버라이딩으로 해결하고 안 되면 다운캐스팅으로 해결해보자.
하위 클래스가 상위 클래스로 형변환되는 것은 묵시적으로 이루어진다.
하지만 다시 원래 자료형인 하위 클래스로 형 변환하려면 명시적으로 다운캐스팅을 해야 한다.
이때 원래 인스턴스의 타입을 체크하는 예약어가 instanceof이다.
AnimalTest.java
package inheritance;
class Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("동물이 움직입니다.");
}
}
class Human extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("사람이 두 발로 걷습니다.");
}
public void readBook() {
System.out.println("사람이 책을 읽습니다.");
}
}
class Tiger extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("호랑이가 네 발로 뜁니다.");
}
public void hunting() {
System.out.println("호랑이가 사냥을 합니다.");
}
}
class Eagle extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("독수리가 하늘을 납니다.");
}
public void flying() {
System.out.println("독수리가 하늘을 날아갑니다.");
}
}
public class AnimalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnimalTest test = new AnimalTest();
test.moveAnimal(new Human());
test.moveAnimal(new Tiger());
test.moveAnimal(new Eagle());
}
public void moveAnimal(Animal animal) {
animal.move();
//****** 다운 캐스팅 ******//
//Human human = (human)animal;
//human.readBook();
//오류 발생
//인스턴스가 human인지 체크하고 human으로 바꾸기
if( animal instanceof Human ) {
Human human = (Human)animal;
human.readBook();
}
else if( animal instanceof Tiger ) {
Tiger tiger = (Tiger)animal;
tiger.hunting();
}
else if( animal instanceof Eagle ) {
Eagle eagle = (Eagle)animal;
eagle.flying();
}
else {
System.out.println("지원되지 않는 기능입니다.");
}
}
}실행 결과
사람이 두 발로 걷습니다.
사람이 책을 읽습니다.
호랑이가 네 발로 뜁니다.
호랑이가 사냥을 합니다.
독수리가 하늘을 납니다.
독수리가 하늘을 날아갑니다.