*본 내용은 [Do it! 자바 프로그래밍 입문] 책과 강의를 보고 공부하면서 요점 정리한 내용입니다.
◼ 예외 클래스
✔ 오류란 무엇인가요?
-
컴파일 오류(compile error)
프로그램 코드 작성 중 발생하는 문법적 오류 -
실행 오류(runtime error)
실행 중인 프로그램이 의도하지 않은 동작을 하거나(bug) 프로그램이 중지된느 오류
-실행 오류시 비정상 종료는 서비스 운영에 치명적
-
오류가 발생할 수 있는 경우에 로그(log)를 남겨 추후 이를 분석하여 원인을 찾아야 함
-
자바는 예외 처리를 통하여 프로그램의 비정상 종료를 막고 log를 남길 수 있음
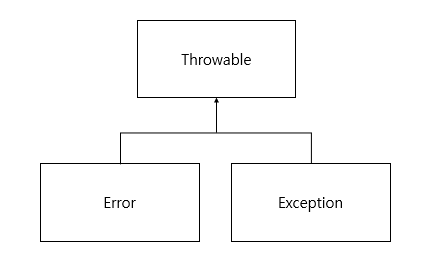
✔ 오류와 예외 클래스
-
시스템 오류(error)
가상 머신에서 발생, 프로그래머가 처리할 수 없음
동적 메모리 없는 경우, 스택 오버 플로우 등 -
예외(Exception)
프로그램에서 제어할 수 있는 오류
읽어 들어려는 파일이 존재하지 않는 경우, 네트웍 연결이 끊어진 경우
[클래스들]
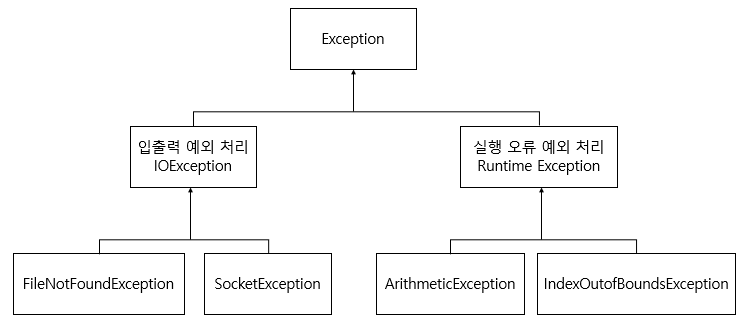
✔ 예외 클래스의 종류
- 모든 예외 클래스의 최상위 클래스는 Exception
- 다양한 예외 클래스가 제공 됨

◼ 예외 처리하기
✔ try-catch문
try {
예외가 발생할 수 있는 코드 부분
} catch(처리할 예외 타입 e) {
try 블록 안에서 예외가 발생했을 때 예외를 처리하는 부분
}ArrayExceptionTest.java
package exception;
public class ArrayExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
for(int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}실행 결과
1
2
3
4
5
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 5
at First/exception.ArrayExceptionTest.main(ArrayExceptionTest.java:9)
//end 출력되지 않음[try-catch 사용]
ArrayExceptionTest.java
package exception;
public class ArrayExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
try {
for(int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { // try{}과정 중에 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException오류가 발생하며
System.out.println(e); // catch{}안으로 들어옴
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
실행 결과
1
2
3
4
5
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 5
end
✔ try-catch-finally문
try {
예외가 발생할 수 있는 코드 부분
} catch(처리할 예외 타입 e) {
try 블록 안에서 예외가 발생했을 때 예외를 처리하는 부분
} finally {
항상 수행되는 부분
}- finally에서 프로그램 리소스를 정리함
- try{} 블럭이 실행되면 finally{} 블록은 항상 실행됨
- 리소스를 정리하는 코드를 각 블록에서 처리하지 않고 finally에서 처리함
- 자동으로 리소스 종료하기 위해 finally 사용
ArrayExceptionTest.java
package exception;
public class ArrayExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
try {
for(int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println(e);
return; // return 은 finally{}다음에 수행됨.
} finally { // try{} 수행된 다음 무조건 finally{} 수행됨
System.out.println("finally");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
실행 결과
1
2
3
4
5
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 5
finally
✔ try-with-resources문
- 리소스를 자동 해제하도록 제공해주는 구문
- 자바7부터 제공됨
- close()를 명시적으로 호출하지 않아도 try{}블록에서 열린 리소스는 정상적인 경우, 예외 발생한 경우 모두 자동해제 됨 --> finally를 부를 필요 없다
- 해당 리소스가 AutoCloseable을 구현해야 함
- FileInputStream의 경우 AutoCloseable을 구현하고 있음
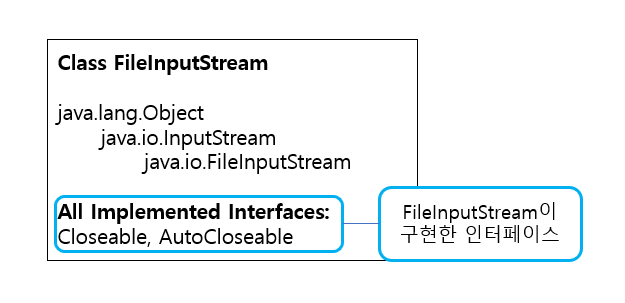
ExceptionTest.java
package exception;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("finally");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
실행 결과
finally
end[try-with-resources 사용]
ExceptionTest.java
package exception;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt")) {
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
실행 결과
end✔ AutoCloseable 인터페이스
- AutoCloseable 인터페이스 구현한 클래스 만들기
AutoCloseable이 구현된 클래스는 finally에서 close 구현하지 않아도 됨
AutoCloseObj.java
package exception;
public class AutoCloseObj implements AutoCloseable{
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
System.out.println("close()");
}
}
AutoCloseTest.java
package exception;
public class AutoCloseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(AutoCloseObj obj = new AutoCloseObj()){ // AutoCloseable 제공하는 obj 객체
throw new Exception(); // exception 강제적으로 발생 시킴
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("exception");
}
}
}
실행 결과
close()
exception
✔ 향상된 try-with-resources문
-
자바9에서 제공되는 구문
-
외부에 선언된 리소스도 변수만 사용 가능
-
자바9 이전
AutoCloseObj obj = new AutoCloseObj();
try (AutoCloseObj obj2 = obj) // 다른 참조 변수로 다시 선언해야 함
throw new Exception();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("예외 부분입니다");
}- 자바9 이후
AutoCloseObj obj = new AutoCloseObj();
try(obj) // 외부에서 선언한 변수를 그대로 쓸 수 있음
throw new Exception();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("예외 부분입니다");
}◼ 예외 처리 미루기
✔ 예외 처리 미루기
-
주의) throw: 예외 발생 시킴 vs throws: 예외 처리 미루기
-
throws를 사용하여 예외처리 미루기
-
메서드 선언부에 throws를 추가
-
예외가 발생한 메서드에서 예외처리를 하지 않고 이 메서드를 호출한 곳에서 예외처리를 한다는 의미
-
main()에서 throws를 사용하면 가상머신에서 처리 됨
-
예외 처리 미루기 예제
각 상황마다 예외처리하기
ThrowsException.java
package exception;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class ThrowsException {
public Class loadClass(String fileName, String className) throws FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
Class c = Class.forName(className);
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThrowsException ex = new ThrowsException();
try {
ex.loadClass("b.txt", "java.lang.String");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} catch (Exception e) { // 어떤 exception 핸들링 해야 할지 모를 때, 최상위 클래스 Exception 이용(주의: 맨아래에 작성)
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
실행 결과
end◼ 사용자 정의 예외
✔ 사용자 정의 예외
-
JDK에서 제공되는 예외 클래스 외에 사용자가 필요에 의해 예외 클래스를 정의하여 사용
-
기존 JDK 예외 클래스 중 가장 유사한 클래스에서 상속
-
기본적으로 Exception에서 상속해도 됨
public class IDFormatException extends Exception {
public IDFormatException(String message) { // message: 생성자의 매개변수로 예외 상황 메시지를 받음
super(message);
}
}- 사용자 정의 예외 예제
전달받은 아이디의 값이 null이거나 8자 이하 20자 이상인 경우 예외를 발생시킴
IDFormatException.java
package exception;
public class IDFormatException extends Exception {
public IDFormatException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
IDFormatTest.java
package exception;
public class IDFormatTest {
private String userID;
public String getUserID() {
return userID;
}
// 아이디에 대한 제약 조건 구현
public void setUserID(String userID) throws IDFormatException { // IDFormatException 예외를 setUserID()메서드가 호출 될 때 처리하도록 미룸
if(userID == null) {
throw new IDFormatException("아이디는 null일 수 없습니다.");
}
else if(userID.length() < 8 || userID.length() > 20) {
throw new IDFormatException("아이디는 8자 이상 20자 이하로 쓰세요.");
}
this.userID = userID;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
IDFormatTest idTest = new IDFormatTest();
String userID = null;
try {
idTest.setUserID(userID);
} catch (IDFormatException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
userID = "1234567";
try {
idTest.setUserID(userID);
} catch (IDFormatException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
실행 결과
exception.IDFormatException: 아이디는 null일 수 없습니다.
아이디는 8자 이상 20자 이하로 쓰세요.
