오늘의 개요
오늘은
AVL tree 자료구조 공부!
기록하는 것도 나름 중요한 것 같다. 이해가 더 잘되는 느낌
Tree 자료구조 개요
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AVL_tree
트리는 스택이나 큐와 같은 선형 구조가 아닌 비선형 자료구조이다. 트리는 계층적 관계(Hierarchical Relationship)을 표현하는 자료구조이다. 이 트리라는 자료구조는 표현에 집중한다. 무엇인가를 저장하고 꺼내야 한다는 사고에서 벗어나 트리라는 자료구조를 바라보자.
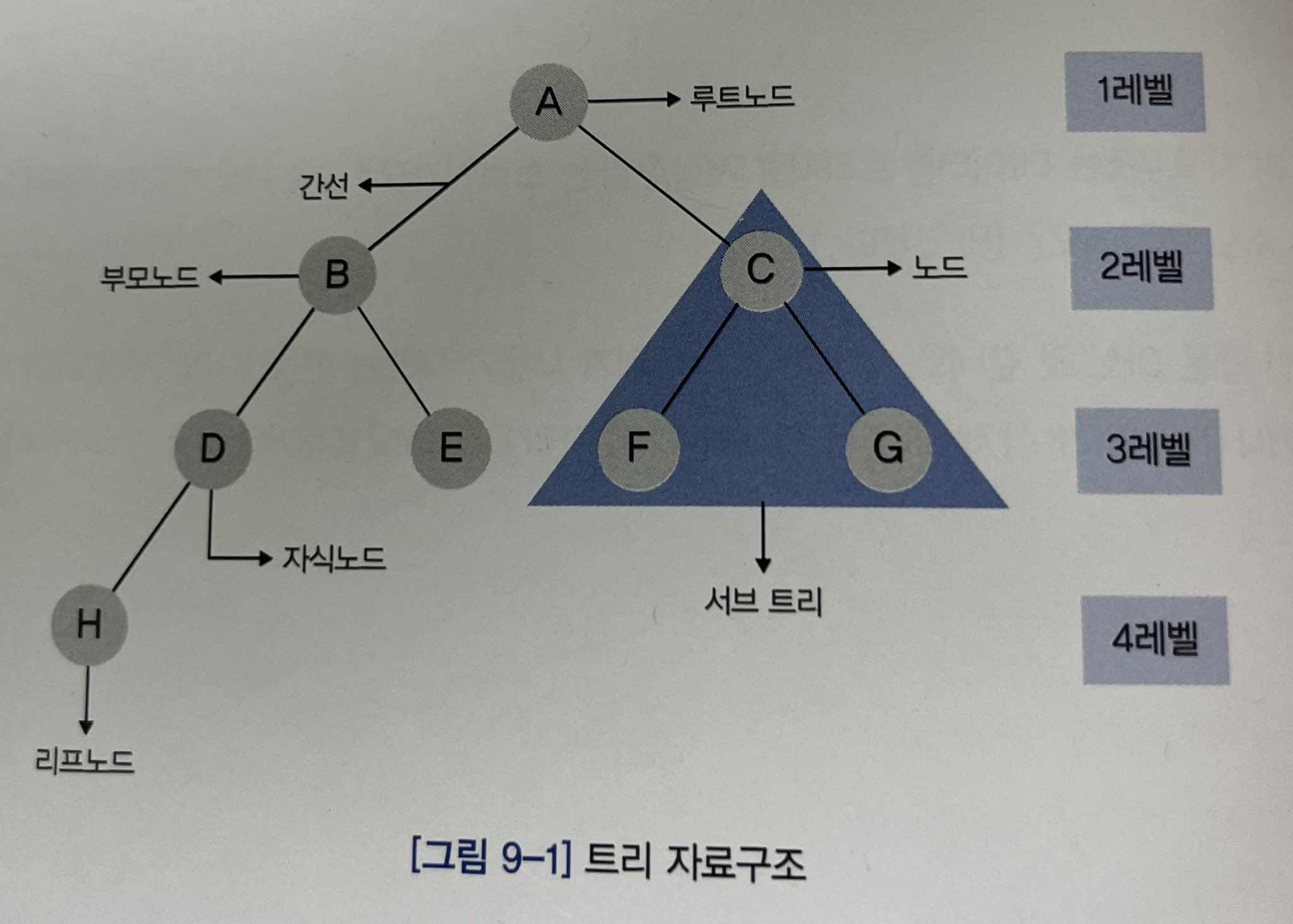
트리를 구성하고 있는 구성요소들(용어)
Node (노드) : 트리를 구성하고 있는 각각의 요소를 의미한다.
Edge (간선) : 트리를 구성하기 위해 노드와 노드를 연결하는 선을 의미한다.
Root Node (루트 노드) : 트리 구조에서 최상위에 있는 노드를 의미한다.
Terminal Node ( = leaf Node, 단말 노드) : 하위에 다른 노드가 연결되어 있지 않은 노드를 의미한다.
Internal Node (내부노드, 비단말 노드) : 단말 노드를 제외한 모든 노드로 루트 노드를 포함한다.
Binary Tree (이진 트리)
루트 노드를 중심으로 두 개의 서브 트리(큰 트리에 속하는 작은 트리)로 나뉘어 진다. 또한 나뉘어진 두 서브 트리도 모두 이진 트리어야 한다. 재귀적인 정의라 맞는듯 하면서도 이해가 쉽지 않을 듯하다. 한 가지 덧붙이자면 공집합도 이진 트리로 포함시켜야 한다. 그래야 재귀적으로 조건을 확인해갔을 때, leaf node 에 다다랐을 때, 정의가 만족되기 때문이다. 자연스럽게 노드가 하나 뿐인 것도 이진 트리 정의에 만족하게 된다.
트리에서는 각 층별로 숫자를 매겨서 이를 트리의 Level(레벨)이라고 한다. 레벨의 값은 0 부터 시작하고 따라서 루트 노드의 레벨은 0 이다. 그리고 트리의 최고 레벨을 가리켜 해당 트리의 height(높이)라고 한다.
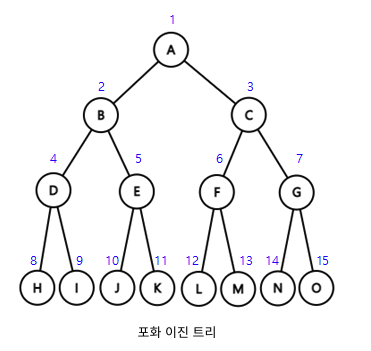
Perfect Binary Tree (포화 이진 트리), Complete Binary Tree (완전 이진 트리), Full Binary Tree (정 이진 트리)
모든 레벨이 꽉 찬 이진 트리를 가리켜 포화 이진 트리라고 한다. 위에서 아래로, 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 순서대로 차곡차곡 채워진 이진 트리를 가리켜 완전 이진 트리라고 한다. 모든 노드가 0개 혹은 2개의 자식 노드만을 갖는 이진 트리를 가리켜 정 이진 트리라고 한다. 배열로 구성된 Binary Tree는 노드의 개수가 n 개이고 root가 0이 아닌 1에서 시작할 때, i 번째 노드에 대해서 parent(i) = i/2 , left_child(i) = 2i , right_child(i) = 2i + 1 의 index 값을 갖는다.
BST (Binary Search Tree)
효율적인 탐색을 위해서는 어떻게 찾을까만 고민해서는 안된다. 그보다는 효율적인 탐색을 위한 저장방법이 무엇일까를 고민해야 한다. 이진 탐색 트리는 이진 트리의 일종이다. 단 이진 탐색 트리에는 데이터를 저장하는 규칙이 있다. 그리고 그 규칙은 특정 데이터의 위치를 찾는데 사용할 수 있다.
규칙 1. 이진 탐색 트리의 노드에 저장된 키는 유일하다.
규칙 2. 부모의 키가 왼쪽 자식 노드의 키보다 크다.
규칙 3. 부모의 키가 오른쪽 자식 노드의 키보다 작다.
규칙 4. 왼쪽과 오른쪽 서브트리도 이진 탐색 트리이다.
이진 탐색 트리의 탐색 연산은 O(log n)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다. 사실 정확히 말하면 O(h)라고 표현하는 것이 맞다. 트리의 높이를 하나씩 더해갈수록 추가할 수 있는 노드의 수가 두 배씩 증가하기 때문이다. 하지만 이러한 이진 탐색 트리는 Skewed Tree(편향 트리)가 될 수 있다.
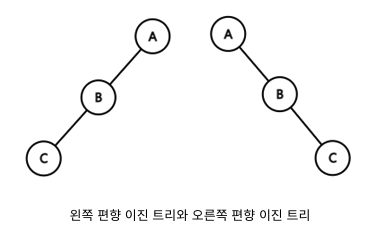
저장 순서에 따라 계속 한 쪽으로만 노드가 추가되는 경우가 발생하기 때문이다. 이럴 경우 성능에 영향을 미치게 되며, 탐색의 Worst Case 가 되고 시간 복잡도는 O(n)이 된다.
배열보다 많은 메모리를 사용하며 데이터를 저장했지만 탐색에 필요한 시간 복잡도가 같게 되는 비효율적인 상황이 발생한다. 이를 해결하기 위해 Rebalancing 기법이 등장하였다. 균형을 잡기 위한 트리 구조의 재조정을 Rebalancing이라 한다. 이 기법을 구현한 트리에는 여러 종류가 존재하는데 그 중에서 Red-Black Tree를 많이 쓴다고 한다.
다른 개발자분에게 자료 구조 관련 여쭤보니까 조언해주신 바로는 이렇게 자료구조 많이 쓴다고 함!
->
표준 라이브러리
선형 자료 구조
1. 동적 배열
2. Deque
비선형 자료 구조
3. 해시테이블 (HashMap, 딕셔너리, HashSet 이런식으로 부르는 애들)
4. 순서 트리 (TreeMap, TreeSet, ordered_map ...)
AVL Tree
참고 사이트
참고 사이트 2
https://www.programiz.com/dsa/avl-tree
강의영상 필기하면서 공부할 것임. 영어로~
AVL tree is a self-balancing Binary Search Tree (BST) where the difference between heights of left and right subtrees cannot be more than one for all nodes.
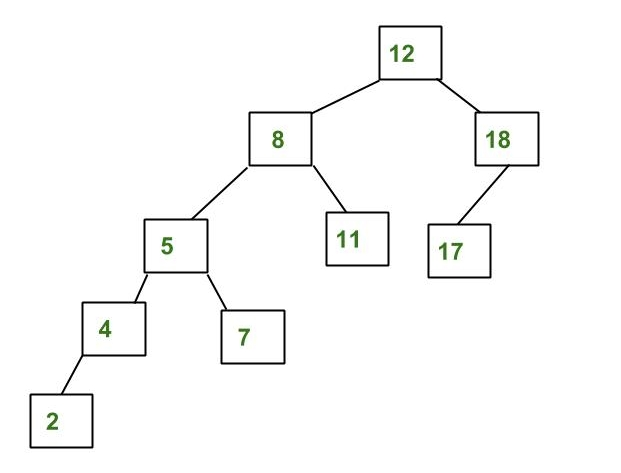
The above tree is not AVL because differences between heights of left and right subtrees for 8 and 12 is greater than 1.
Why AVL Trees?
Most of the BST operations (e.g., search, max, min, insert, delete.. etc) take O(h) time where h is the height of the BST.
-> cf ) BST operation : Binary Search Tree https://www.programiz.com/dsa/binary-search-tree
The cost of these operations may become O(n) for a skewed Binary tree.
If we make sure that height of the tree remains O(log n) after every insertion and deletion, then we can guarantee an upper bound of O(log n) for all these operations. The height of an AVL tree is always O(log n) where n is the number of nodes in the tree
The height of an AVL tree is always O(Logn) where n is the number of nodes in the tree
Insertion
-
Inserting a node, v, into an AVL tree changes the heights of some of the nodes in T.
-
The only nodes whose heights can increases are the ancestors of node v.
-
If insertion causes T to become
unbalanced, then some ancestor of v would have a height-imbalance. -
We travel up the tree from v until we find the first node x such that its grandparent z is unbalanced.
Which are the nodes whose heights could change?
-> It could only be the ancestors of this particular node.
-> Not because it is written here but you should also understand why it is only ancestors.
-> Because it is only in the ancestors of that node whose subtree has changed as result of this insertion process
For any other node its sub tree has not changed it remains the same as before.
So the ancestors of this node, their heights might change.
And change means it will only increase.
If the insertion causes the tree to become imbalanced of unbalanced, then some ancestor of this node v is the culprit and it is the place where one or more ancestors would have a height balance problem.
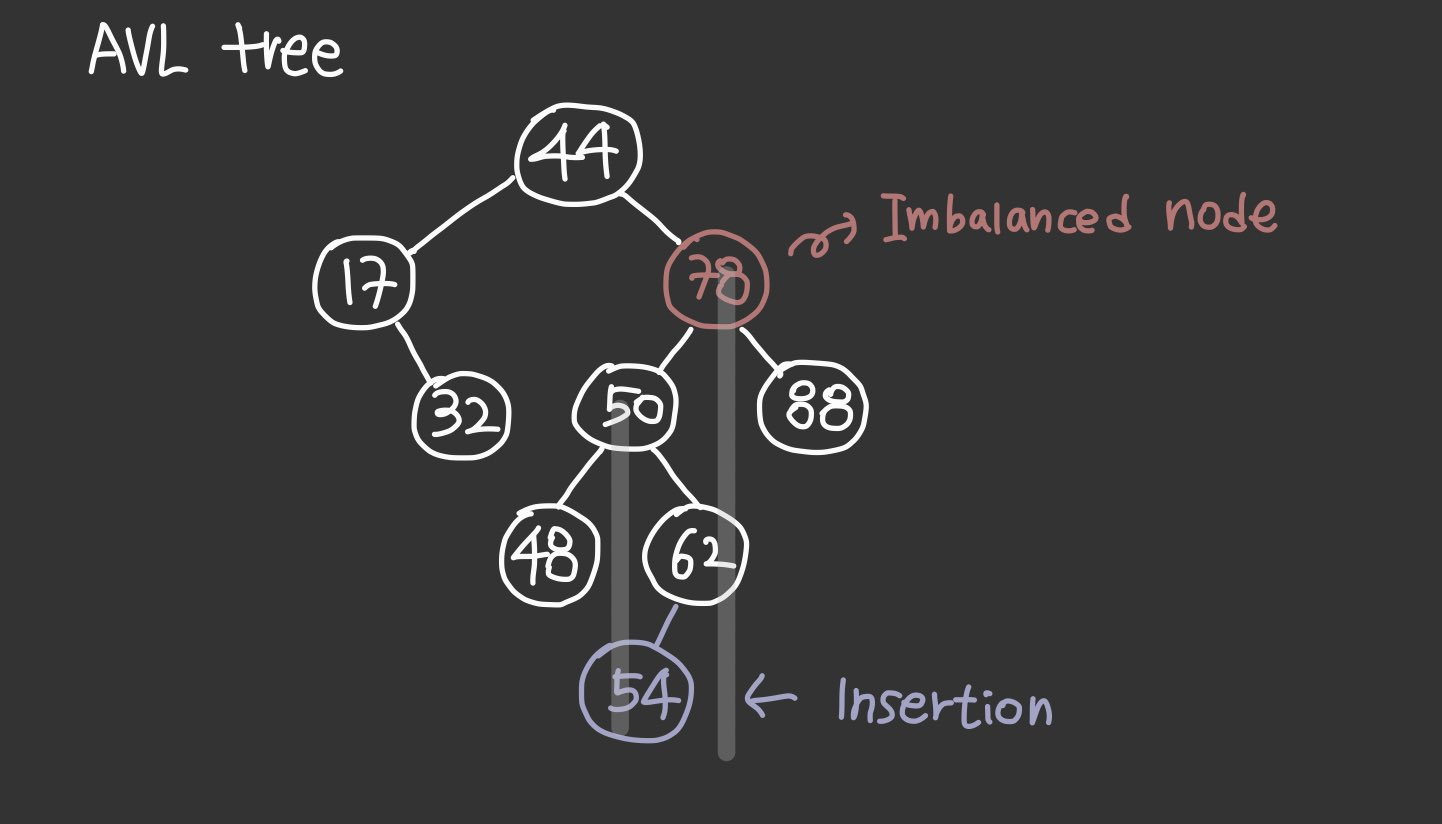
- To rebalance the subtree rooted at z, we must perform a
rotation

z: the first place where the imbalace happens
y: x's child
x: the grandchild(child's child) of z
Rotations


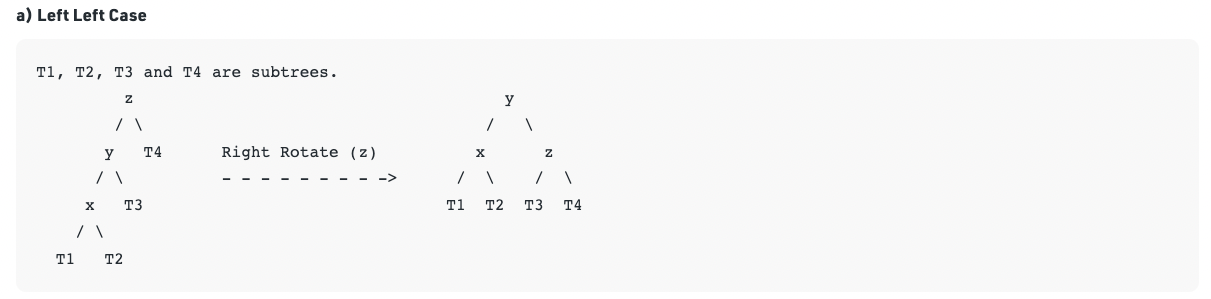
y is left child of z and x is left child of y (Left Left Case)
y is left child of z and x is right child of y (Left Right Case)
y is right child of z and x is right child of y (Right Right Case)
y is right child of z and x is left child of y (Right Left Case)
- Rotation is a way of locally reorganizing a BST.
- Let u, v be two nodes such that u = parent(v)
- Keys(T1) < key(v) < keys(T2) < key(u) < keys(T3)

Single Rotation: Left Left Case
y is left child of z and x is left child of y (Left Left Case)
Insertion (1): Node 'x'
- Insertion happens in subtree T1.
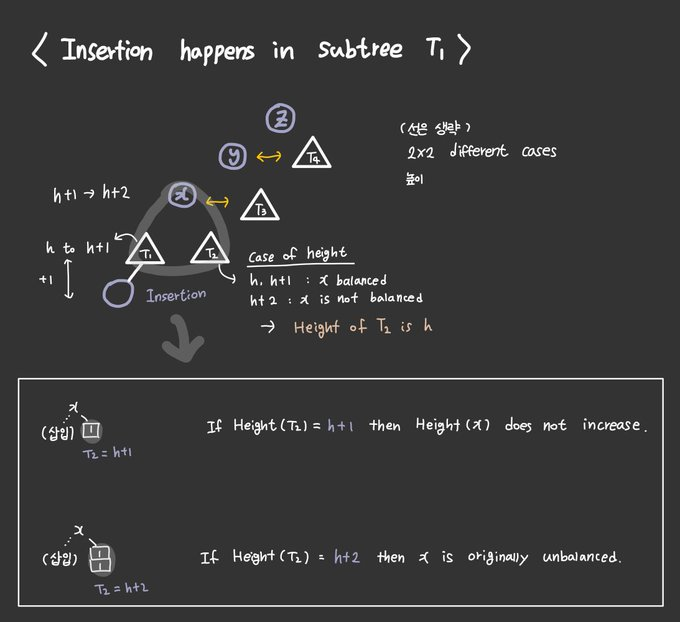
Note that z is imbalanced, y, x is balanced
- Height(T1) increases from
htoh+1. - Since x remains balanced ~ Height(T2) is
horh+1orh+2.
-> If Height(T2) = h + 2 thenxis originally unbalanced.
-> If Height(T2) = h + 1 then Height(x) does not increase. - Hence Height(T2) = h
(h = maximum depth 으로 이해하고 root에서부터 세는 높이인줄 알았는데 내가 보는 강의에서는 아래에서 높이 세시는듯... 참고)
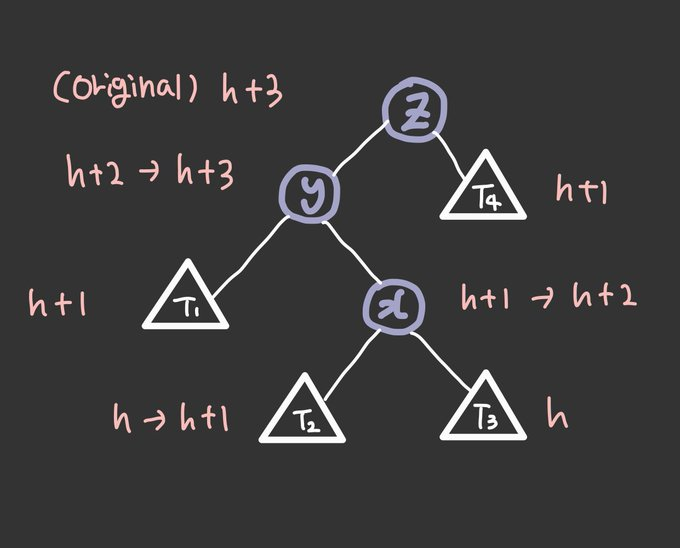
Insertion (2): Node 'y'

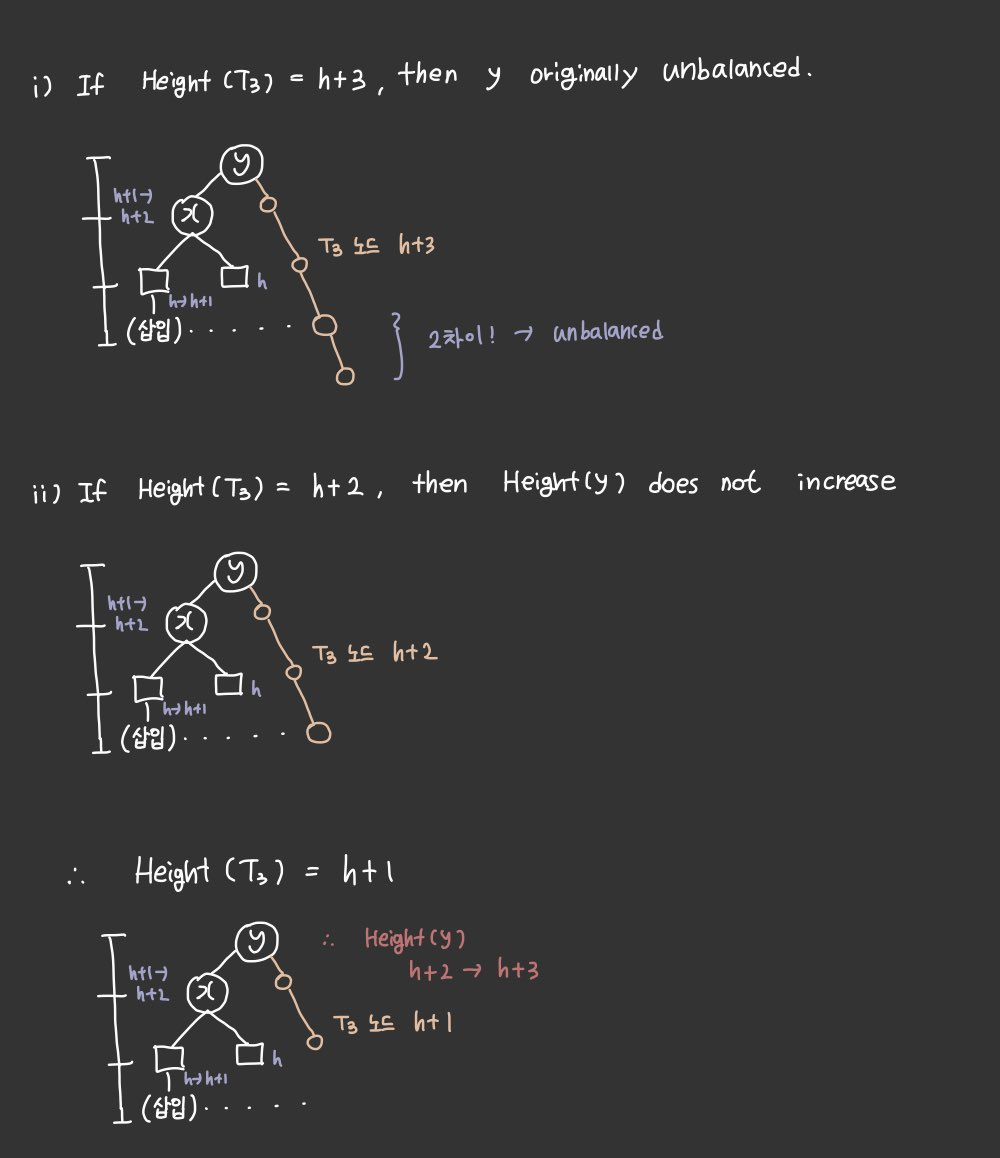
The height of y is from h + 2 to h + 3
Insertion (3): Node 'z'
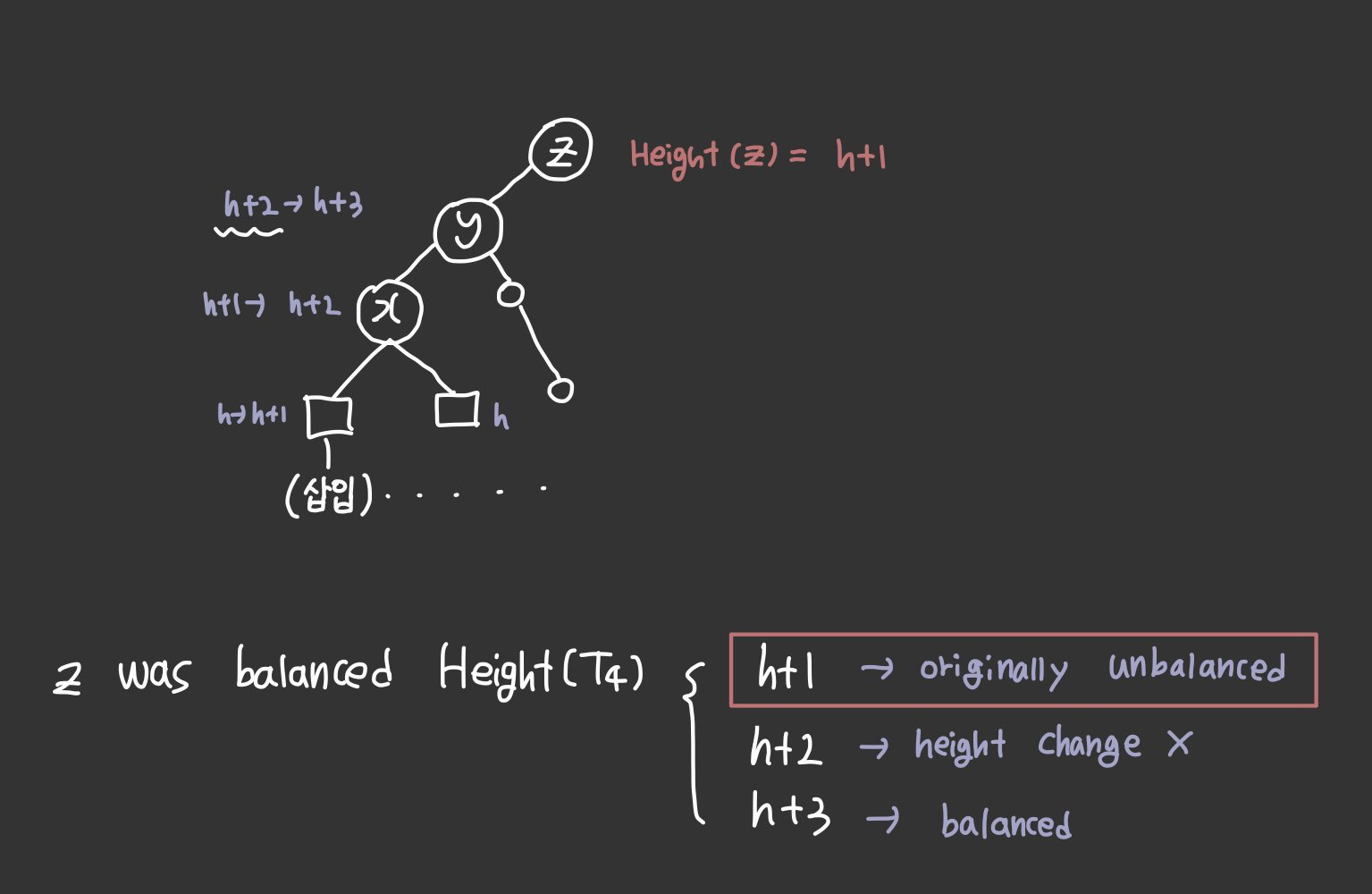
The new height of y is h + 3.
So what should the height T4 of be? (child node of z)
Since z was balanced, height of T4 is h + 1 or h + 2 or h + 3
Note that z is imbalanced
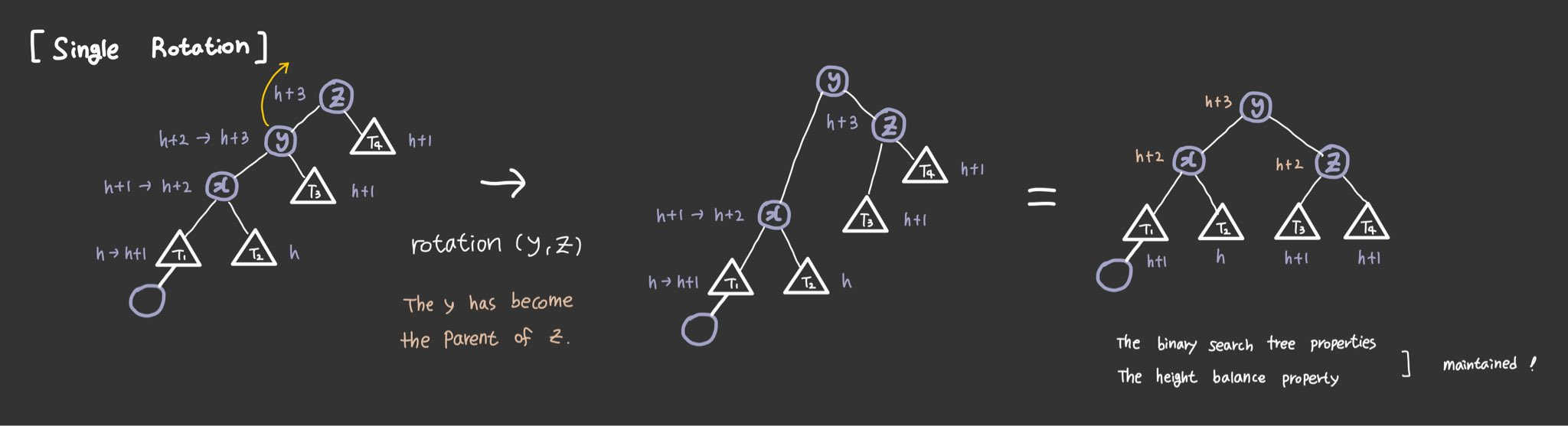
The height of the sub tree remains the same after rotation.
Hence no further rotations required.
Why is this important?
Because now It do not have to go up further.
any ancestor of this, its height would not change any more because whatever was the original height of this h + 3 of this node is the new height of this sub tree
After the insertion, moving up to find the first place where there was an imbalanced.
And The rotation to be done, It doesnt have to go up any further.
middle key ~ y, (x < y < z )
because they were all in a line.
z was the top, y was its left child so it means y is less than z.
And x was its left child, so x is less than y is less than z.
So after the rotation we ended up making y as the root.
The middle key we ended up making the root.
(주의: 모든 트리에서 미들키를 위로 올리는 것 아님! 다른 회전 쓰는 트리 있음!)
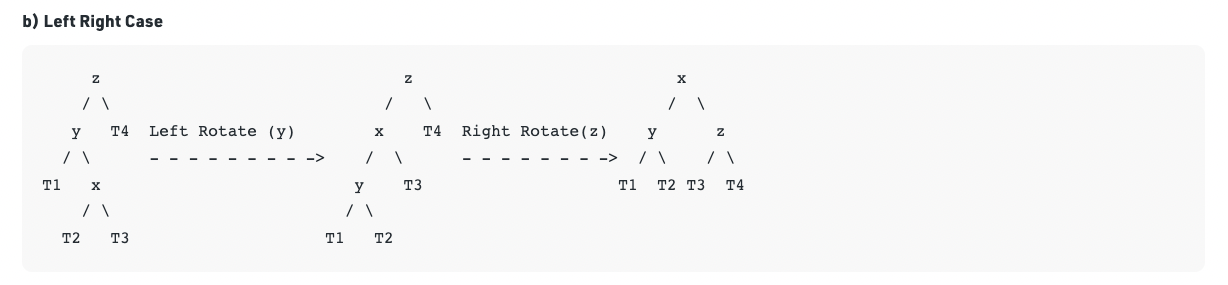
Double rotation: Left Right Case
y is left child of z and x is right child of y (Left Right Case)
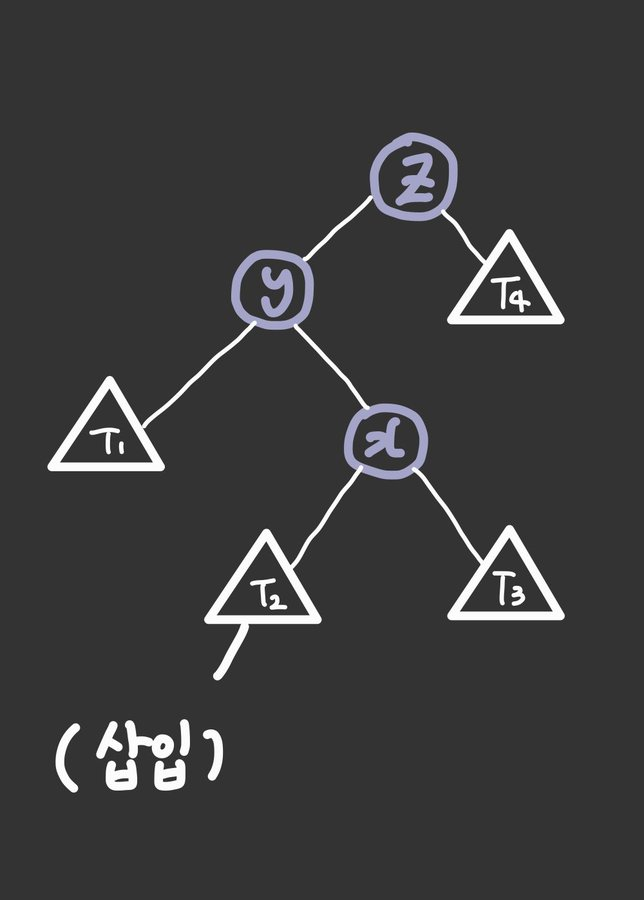
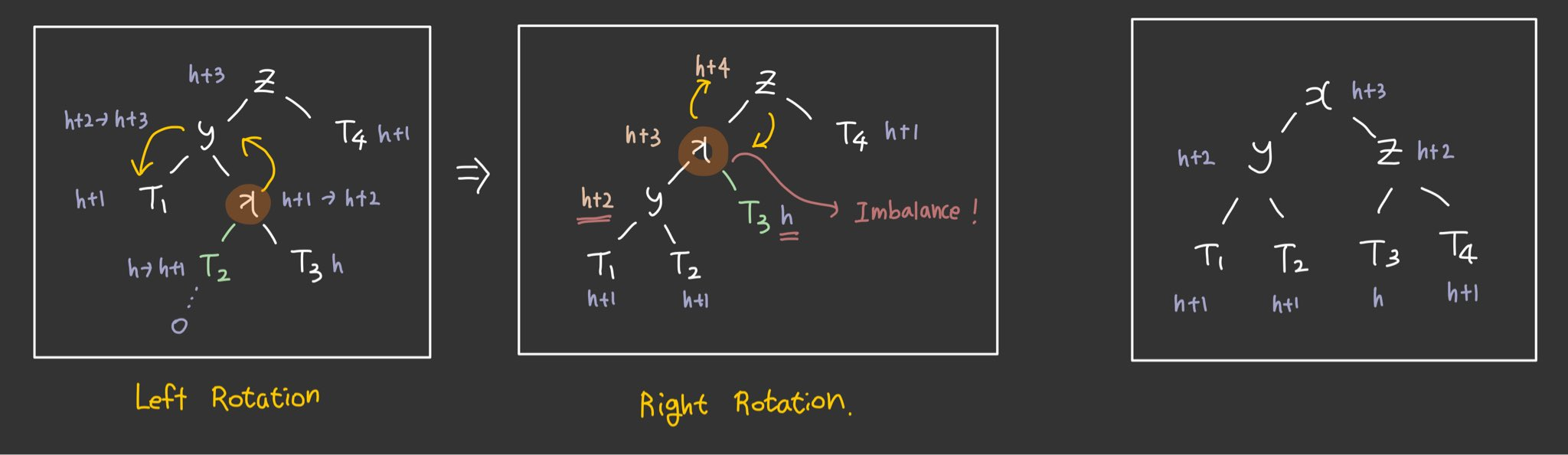
잠깐.. 이해가 안가는 부분 Recap !
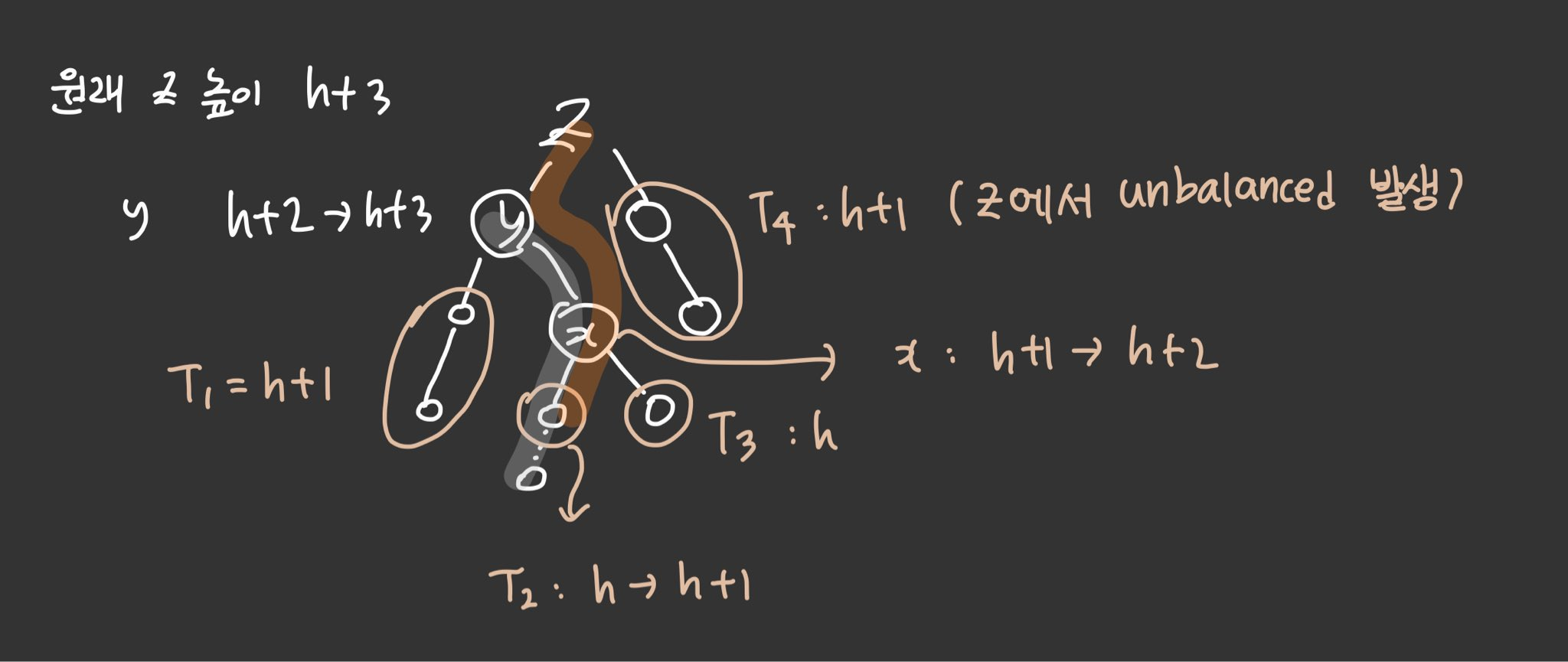
높이 관련 설명이 너무 이해가 안가서 한참 헤매었다.
그림과 함께 한글로.. 설명하자면
일단 높이라는게 영상에서 설명하시는 분이 좀 헷갈리게 해둬서 대충 추상적으로 이해함.
나는 서브 노드 자신 h + 달려있는 노드 수 숫자 만큼 표현한다고 생각했다.
T2에 하나 삽입한다고 했을 때, (간선이 점선으로 그려져 있음)
-
T2의 높이는 h -> h + 1
-
T3
인자를 추가해도 이진트리 구조(+2 이상 레벨 차이 안남)를 만족하는 T3는 h, h + 1, h + 2의 경우의 수를 둘 수 있다.
h + 2인 경우, originally unbalanced라서 제끼고, h + 1인 경우, 인자를 삽입해도 높이에 변화가 없기 때문에 제낀다. 그러면 T3의 높이는 h이다. -
T1, 위와 같이 경우의 수에 대해 똑같이 적용해보면 T1은 h + 1만큼의 높이를 가진다.
-
T4,
z에서 unbalanced가 발생하기 때문에 그림을 자세히 살펴본다면 h + 1만큼이라는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. -
x, y, z는 각 노드의 최대 길이의 노드 갯수를 세어보면 쉽게 높이의 변화를 파악할 수 있다.
자세한 설명은 위 single rotation 부분에 나와있다.
다시 강의 필기로..
The middle key is x (y < x < z)
(트리 값을 보면 왼쪽이 작은 값, 오른쪽이 큰 값)
The final tree has the same height as the original tree.
Hence we need not go further up the tree.
The middle key ended up being at the top.
Because we want to be able to split the thing uniformly.
- Why was the height imbalance happening?
Because x was the middle key, it was coming way down.
When I kind of split uniformly the heights reduced and there is and there is a height balanced.
- How much time does the double rotation take?
constant time.
Recap
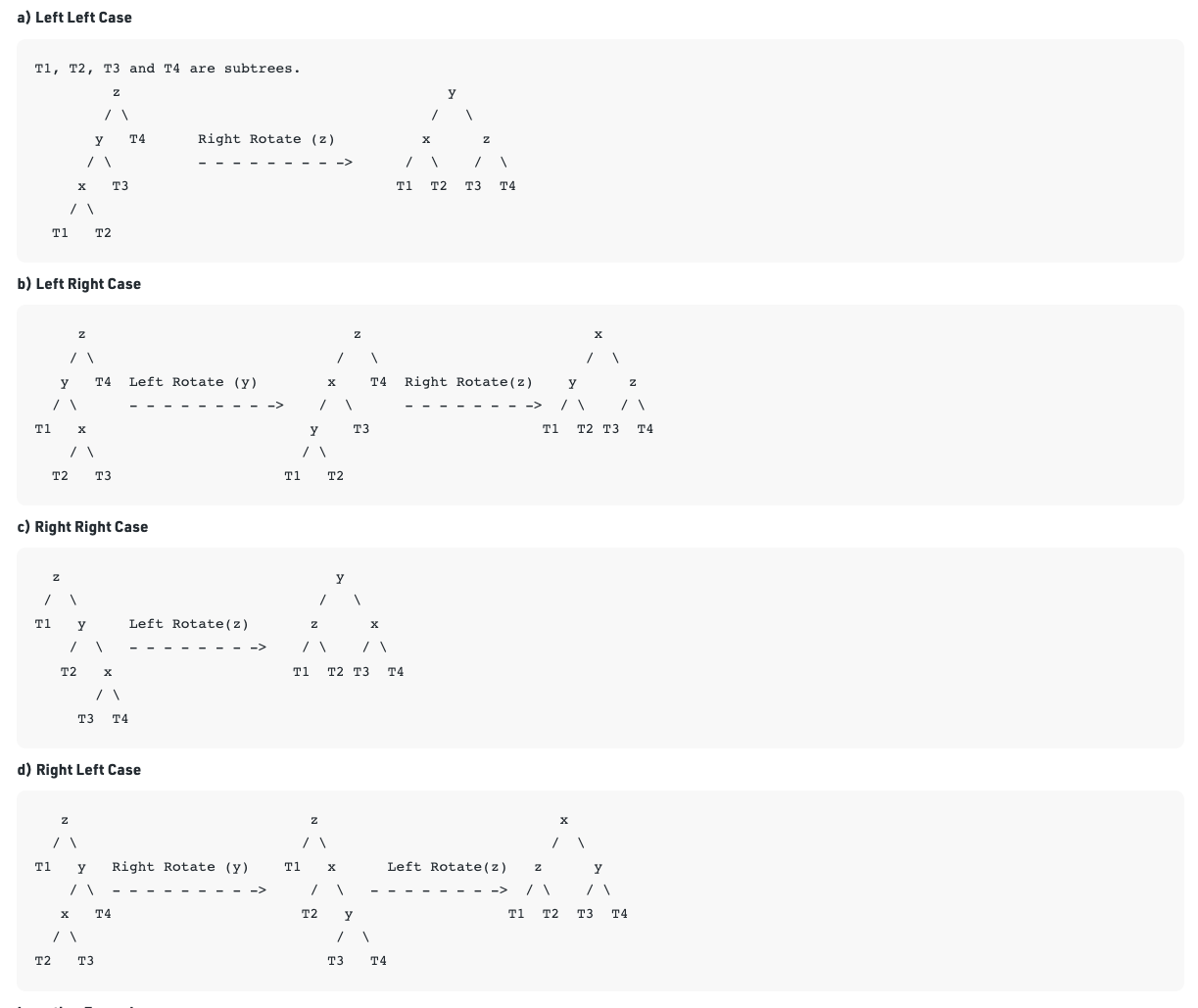
- The four ways to rotate nodes in an AVL tree.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AVL_tree
보면서 재정리!
Simple Rotation: (ex. Right-Right situation)
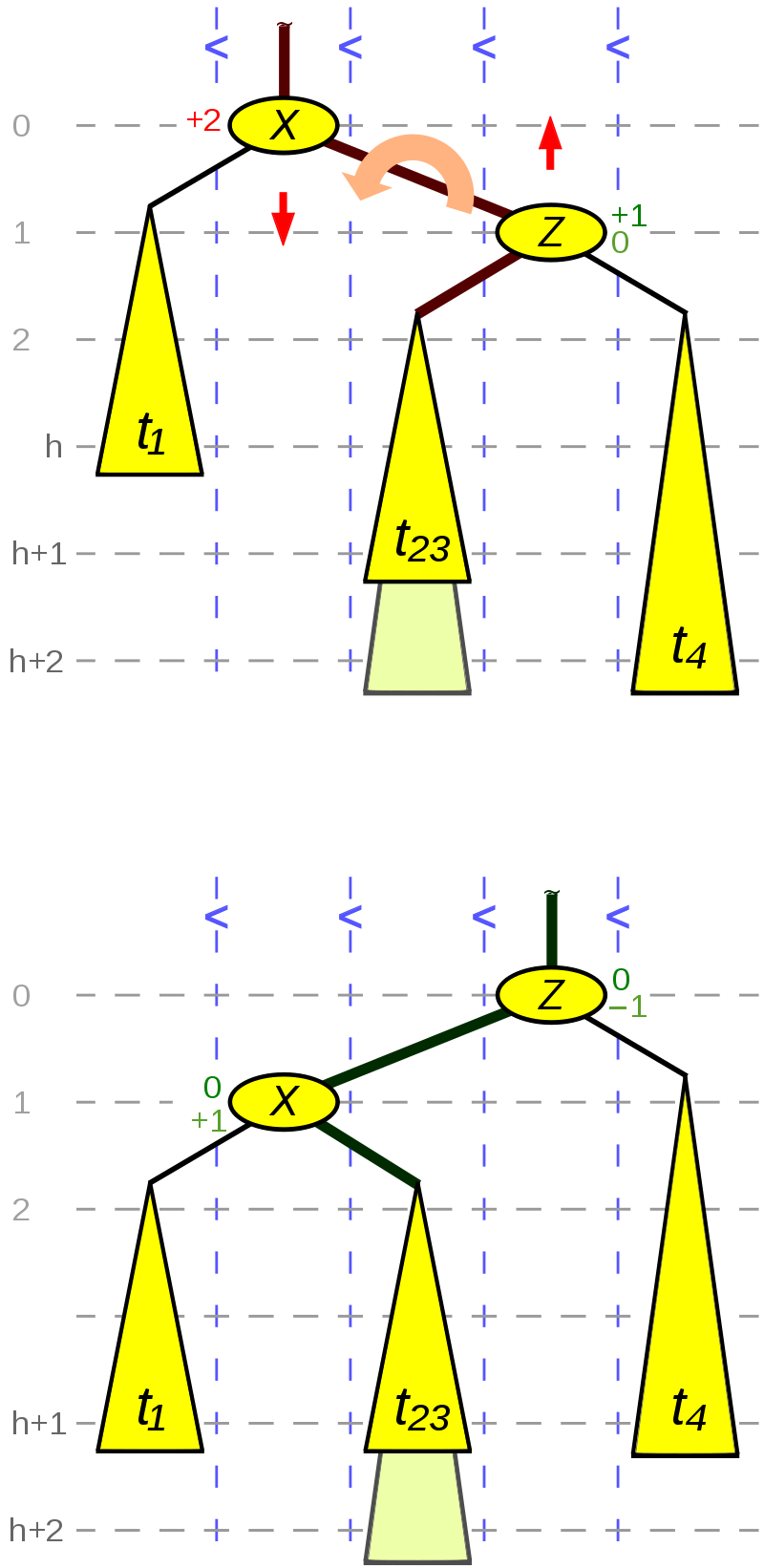
This picture figure 1 shows a Right Right situation.
In its upper half, node X has two child trees with a balance factor of +2.
Moreover, the inner child t23 of Z (i.e., left child when Z is right child resp.
Right child when Z is left child) is not higher than its sibling t4. This can happen by a height increase of subtree t4 or by a height decrease of subtree t1. In the latter case, also the pale situation where t23 has the same height as t4 may occur.
The result of the left rotation is shown in the lower half of the figure. Three links (thick edges in Picture) and two balance factors are to be updated.
As the figure shows, before an insertion, the leaf layer was at level h+1, temporarily at level h+2 and after the rotation again at level h+1. In case of a deletion, the leaf layer was at level h+2, where it is again, when t23 and t4 were of same height. Otherwise the leaf layer reaches level h+1, so that the height of the rotated tree decreases.
Double Rotation (ex. Right-Left situation)
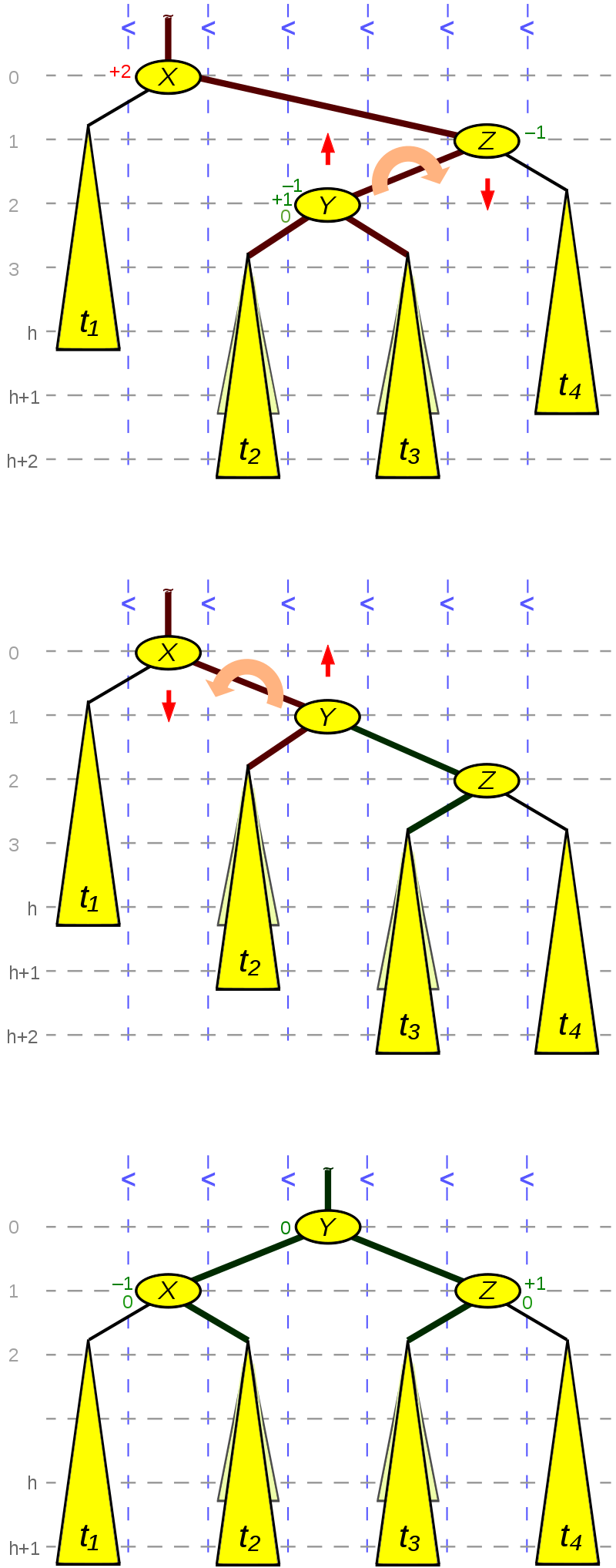
This picture figure 2 shows a Right Left situation.
In its upper third, node X has two child trees with a balance factor of +2. But unlike figure 2, the inner child Y of Z is higher than its sibling t4. This can happen by the insertion of Y itself or a height increase of one of its subtrees t2 or t3 (with the consequence that they are of different height) or by a height decrease of subtree t1. In the latter case, it may also occur that t2 and t3 are of the same height.
The result of the first, the right, rotation is shown in the middle third of the figure. (With respect to the balance factors, this rotation is not of the same kind as the other AVL single rotations, because the height difference between Y and t4 is only 1.) The result of the final left rotation is shown in the lower third of the figure. Five links (thick edges in figure 2) and three balance factors are to be updated.
As the figure shows, before an insertion, the leaf layer was at level h+1, temporarily at level h+2 and after the double rotation again at level h+1. In case of a deletion, the leaf layer was at level h+2 and after the double rotation it is at level h+1, so that the height of the rotated tree decreases.
자바스크립트로 구현
<script>
// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree
class Node {
constructor(d) {
this.key = d;
this.height = 1;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class AVLTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
// A utility function to get
// the height of the tree
height(N) {
if (N == null) return 0;
return N.height;
}
// A utility function to get
// maximum of two integers
max(a, b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
// A utility function to right
// rotate subtree rooted with y
// See the diagram given above.
rightRotate(y) {
var x = y.left;
var T2 = x.right;
// Perform rotation
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
// Update heights
y.height = this.max(this.height(y.left),
this.height(y.right)) + 1;
x.height = this.max(this.height(x.left),
this.height(x.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return x;
}
// A utility function to left
// rotate subtree rooted with x
// See the diagram given above.
leftRotate(x) {
var y = x.right;
var T2 = y.left;
// Perform rotation
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
// Update heights
x.height = this.max(this.height(x.left),
this.height(x.right)) + 1;
y.height = this.max(this.height(y.left),
this.height(y.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return y;
}
// Get Balance factor of node N
getBalance(N) {
if (N == null) return 0;
return this.height(N.left) - this.height(N.right);
}
insert(node, key) {
/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */
if (node == null) return new Node(key);
if (key < node.key)
node.left = this.insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = this.insert(node.right, key);
// Duplicate keys not allowed
else return node;
/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */
node.height =
1 + this.max(this.height(node.left),
this.height(node.right));
/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor
node to check whether this node became
unbalanced */
var balance = this.getBalance(node);
// If this node becomes unbalanced, then there
// are 4 cases Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return this.rightRotate(node);
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return this.leftRotate(node);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) {
node.left = this.leftRotate(node.left);
return this.rightRotate(node);
}
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) {
node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right);
return this.leftRotate(node);
}
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// A utility function to print preorder traversal
// of the tree.
// The function also prints height of every node
preOrder(node) {
if (node != null) {
document.write(node.key + " ");
this.preOrder(node.left);
this.preOrder(node.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
var tree = new AVLTree();
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25);
/* The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50
*/
document.write(
"Preorder traversal of the " + "constructed AVL tree is <br>"
);
tree.preOrder(tree.root);
</script>
내일 공부할 것:
부동소수점 오차,
Switch와 if문의 차이, slice(1, 0)과 shift()의 차이
큐 알고리즘 문제풀이 (걍 shift() 써서 풀어야지 생각중.. 그러다 시간초과 막히면 클래스 쓸 생각)
프로그래머스 1단계 문제 복습이나 못푼 것 풀어야지.
그리고 운영체제 공부!
https://github.com/JaeYeopHan/Interview_Question_for_Beginner 에 나와있는 OS랑 같이 운영체제 복습 자꾸 미뤄져서 각잡고 복습할 예정.
