JavaScript, 백준 온라인, 알고리즘 공부
백준 2941번 Node.js 문제풀이
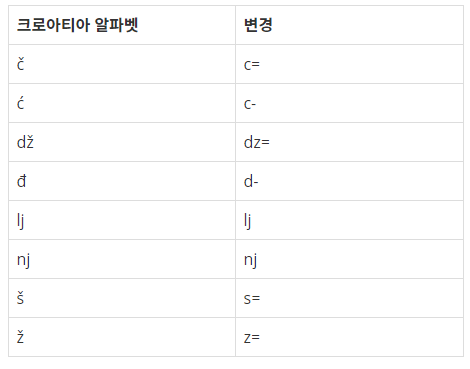
크로아티아 알파벳
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2941
본인이 제출한 답안 1
const fs = require("fs");
const input = (
process.platform === "linux"
? fs.readFileSync("/dev/stdin").toString()
: `c=c=`
)
.trim()
.split("");
let croatiaWordCount = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
let liftWord = input[i - 1];
let nowWord = input[i];
let rightWord = input[i + 1];
let rrWord = input[i + 2];
if (nowWord === "c") {
if (rightWord === "=" || rightWord === "-") {
croatiaWordCount++;
i++;
continue;
}
}
if (nowWord === "d") {
if (rightWord === "-") {
croatiaWordCount++;
i++;
continue;
}
if (rightWord === "z" && rrWord === "=") {
croatiaWordCount++;
i += 2;
continue;
}
}
if (nowWord === "l" || nowWord === "n") {
if (rightWord === "j") {
croatiaWordCount++;
i++;
continue;
}
}
if (nowWord === "s") {
if (rightWord === "=") {
croatiaWordCount++;
i++;
continue;
}
}
if (nowWord === "z") {
if (liftWord !== "d" && rightWord === "=") {
croatiaWordCount++;
i++;
continue;
}
}
croatiaWordCount++;
}
console.log(croatiaWordCount);
본인이 제출한 답안 2
const fs = require("fs");
const input = (
process.platform === "linux"
? fs.readFileSync("/dev/stdin").toString()
: `c=c=`
)
.trim()
.split("");
let croatiaWordCount = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
let nowWord = input[i];
let rightWord = input[i + 1];
let liftWord = input[i - 1];
let rrWord = input[i + 2];
if (nowWord === "c") {
if (rightWord === "=" || rightWord === "-") {
croatiaWordCount--;
}
}
if (nowWord === "d") {
if (rightWord === "-") {
croatiaWordCount--;
}
if (rightWord === "z" && rrWord === "=") {
croatiaWordCount -= 2;
}
}
if (nowWord === "l" || nowWord === "n") {
if (rightWord === "j") {
croatiaWordCount--;
}
}
if (nowWord === "s") {
if (rightWord === "=") {
croatiaWordCount--;
}
}
if (nowWord === "z") {
if (liftWord !== "d" && rightWord === "=") {
croatiaWordCount--;
}
}
croatiaWordCount++;
}
console.log(croatiaWordCount);
풀이과정 소감
- 출력하게 되는건 크로아티아 알파벳 (이하
C알파벳이라고 하겠다)의 갯수다. 따라서 주어진 입력 문자열을 순회하면서C알파벳을 인식하면 바로 카운터를 올리는게 무난한 방법이다. 그런데 이 정도 생각까지 하면 이미 카운드에 같이 넣었던 나머지C알파벳하고 남은 보통 알파벳은 카운트를 어떻게 처리할지가 문제다.
-
보통알파벳까지 순회시키면서 카운트에 넣는건 굉장히 비효울적이다. 대신
답안 1처럼 배열의 요소 하나하나 모두 카운트는 하고C알파벳을 카운트 할 때는 나머지 알파벳의 순회를 막기위해i++ori += 2와continue 문을 조합시는 방법이 더 효율적이다.답안 2인 경우 순회하는 배열의 갯수는 모두 카운트에 넣고 거기에C알파벳는 해당요소의 길이 갯수만큼 카운트를 빼버리는 방법이다.
- 답안 두가지를 비교해보면
답안 1이 직관적으로 읽기 쉬운 코드로 보이고답안 2는 코드가 좀 더 짫다.
메모리나 성능은 두 답안 모두 비슷한 수준이다.
백준에서 공개된 또 다른 답안
const fs = require("fs");
const input = (
process.platform === "linux"
? fs.readFileSync("/dev/stdin").toString()
: `ljes=njak`
).trim();
let croatia = ["c=", "c-", "dz=", "d-", "lj", "nj", "s=", "z="];
function solution(input) {
for (let alphabet of croatia) {
input = input.split(alphabet).join("Q");
}
return input.length; // return input일 경우 QeQQak를 반환한다.
}
console.log(solution(input));
-
정말 아주 간결한 코드다. 문제풀이의 핵심은
input.split(alphabet).join("Q")에 있는데
split(alphabet)는 input배열 중에C알파벳으로 교체할 알파벳이 있으면join("Q")으로 변경하고 그렇지 않으면 변화가 없는 효과가 있다. 결과적으로QeQQak를 반환하는데C알파벳을 한 글자 아무거나 변환한 덕분에 단어의 갯수를 의미있게 만들게된다. -
C알파벳의 갯수를 구하는게 목적이라join("Q")에서 'Q'가 아닌 다른 문자도 상관없다. join없이 실행할 경우 콘솔창에서TypeError: input.split is not a function라는 오류 메세지를 볼 수있다.
즉.split().join()을 같이 써야 효과가 있다. 매우 유용해서 반드시 기억해 두어도 좋을 조합이다.

input.split(alphabet).join("Q").. 미쳤네요 @_@