자료구조와 알고리즘 A+ 기원 3.
1. Stack
: 삽입한 순서와 반대의 순서로 삭제가 가능한 Data Structure
-> [LIFO] Last In First Out 후입선출
2. Stack ADT
- push: stack에 새로운 요소 추가 =add
- pop: 빈 stack이 아니라면, 가장 위의 요소 삭제 = remove, pull -> stack에 변화 O
- peek: 빈 stack이 아니라면, 가장 위의 요소를 가져오기 -> stack에 변화 X
- isEmpty: 빈 stack인지 check
- clear: stack의 모든 요소 삭제
Java에서 stack은 java.util.package에 포함되어 있다!
이때 java.util.*으로 대부분 많이 사용한다.
3. Stack 사용
import java.util.*;
public class ToyStack{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> toys = new Stack<>();
// 이때 <>안의 type은 반복하지 않는다.
toys.push("red YOYO");
toys.push("Black COOKIE MAN");
toys.peek(); // 제일 위에 있는 요소를 보여주기만 함
toys.size(); // stack 크기 반환
toys.pop(); // 제일 위에 있는 요소를 아예 stack에서 꺼냄
toys.toString(); // stack을 list 형태로 반환 (내부 열람 가능)
}
}4. Linked Stack
- Linked Stack의 형태
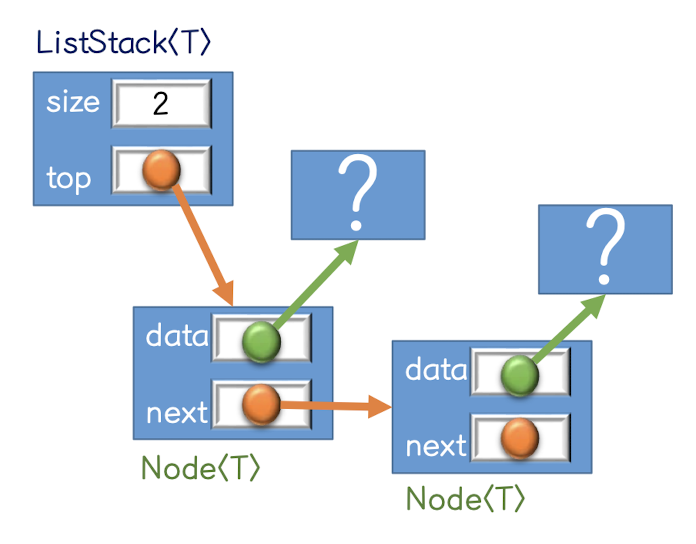
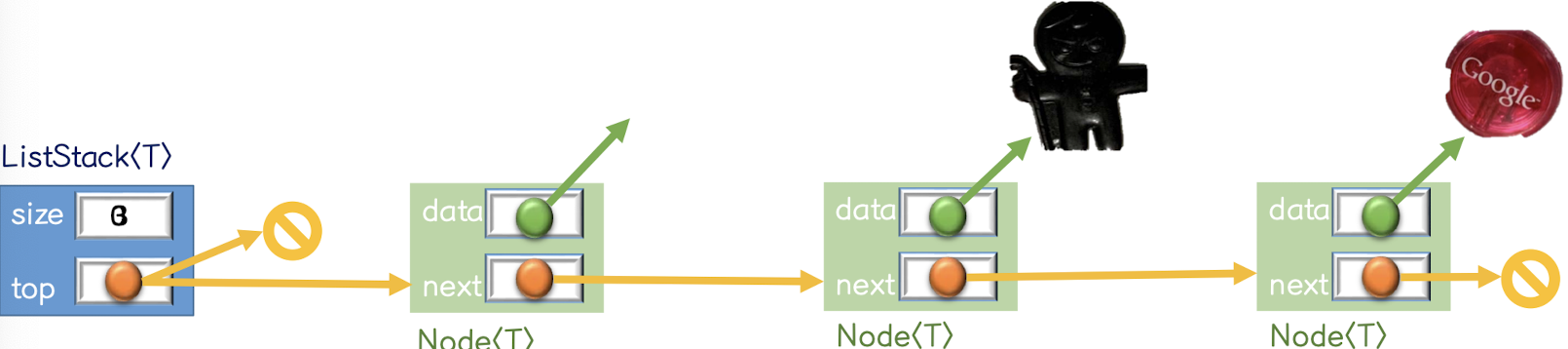
(실제 사용은 이런 식)
public class LinkedStack<T> implements StackInterface<T> {
private Node<T> top;
private int size;
public LinkedStack() {
top = null;
size = 0;
}
public void push(T newEntry) {
top = new Node(newEntry, top);
size++;
}
public T pop() {
T result = peek();
if(top!=null) {
top = top.next;
size--;
}
return result;
}
public T peek() {
T result = null;
if(top!=null) result = top.data;
return result;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top==null;
}
public void clear() {
top = null;
size = 0;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public String toString() {
String result = "LinkedStack [size=" + size + "]: ";
if(top == null) result += null;
else {
for(Node<T> p = top; p != null ; p = p.next)
result+= p.data + "\t";
}
return result;
}
private class Node<T> {
private T data;
private Node<T> next;
private Node(T x, Node<T> n) {
data = x; next = n;
}
}
}5. Array Stack
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayStack<T> implements StackInterface<T> {
private T[] item; // stack 배열
private int top;
private boolean integrityOK;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 50;
private static final int MAX_CAPACITY = 10000;
public ArrayStack() {
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
public ArrayStack(int initialCapacity) {
integrityOK = false;
if(initialCapacity < MAX_CAPACITY) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] tempItem = (T[]) new Object[initialCapacity];
item = tempItem;
top = -1;
integrityOK=true;
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Attempt to create a stack whose "
+ "capacity exceeds allowed maximum.");
}
public void push(T newEntry) {
checkIntegrity();
ensureCapacity();
item[++top]=newEntry;
}
public T pop() {
if(isEmpty()) return null;
else {
T result = item[top];
item[top] = null;
top--;
return result;
}
}
public T peek() {
if(isEmpty()) return null;
else return item[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top<0;
}
public void clear() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] tempItem = (T[]) new Object[item.length];
item = tempItem;
top = -1;
}
public int size() {
return top+1;
}
private boolean isFull() {
return top >= item.length-1;
}
private void checkIntegrity() {
if(!integrityOK) throw new SecurityException("ArrayBag object is corrupt");
}
private void ensureCapacity() {
if(top == item.length -1) {
int newLength = 2*item.length;
if(newLength < MAX_CAPACITY) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] tempItem = (T[]) new Object[newLength];
item= Arrays.copyOf(item, newLength);
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Attempt to increse the size of a stack whose "
+ "capacity exceeds allowed maximum.");
}
}
public String toString() {
String s = "ArrayStack ["+(top + 1)+"]: " ;
for(int i = 0 ; i <= top ; i++)
s += item[i] +"\t";
return s;
}
}

