출처
해당 게시글은 [Java] 어서와! 자료구조 알고리즘은 처음이지?https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/13577를 간략히 요약한 게시글이며 모든 출처는 해당강의에 있습니다
문제

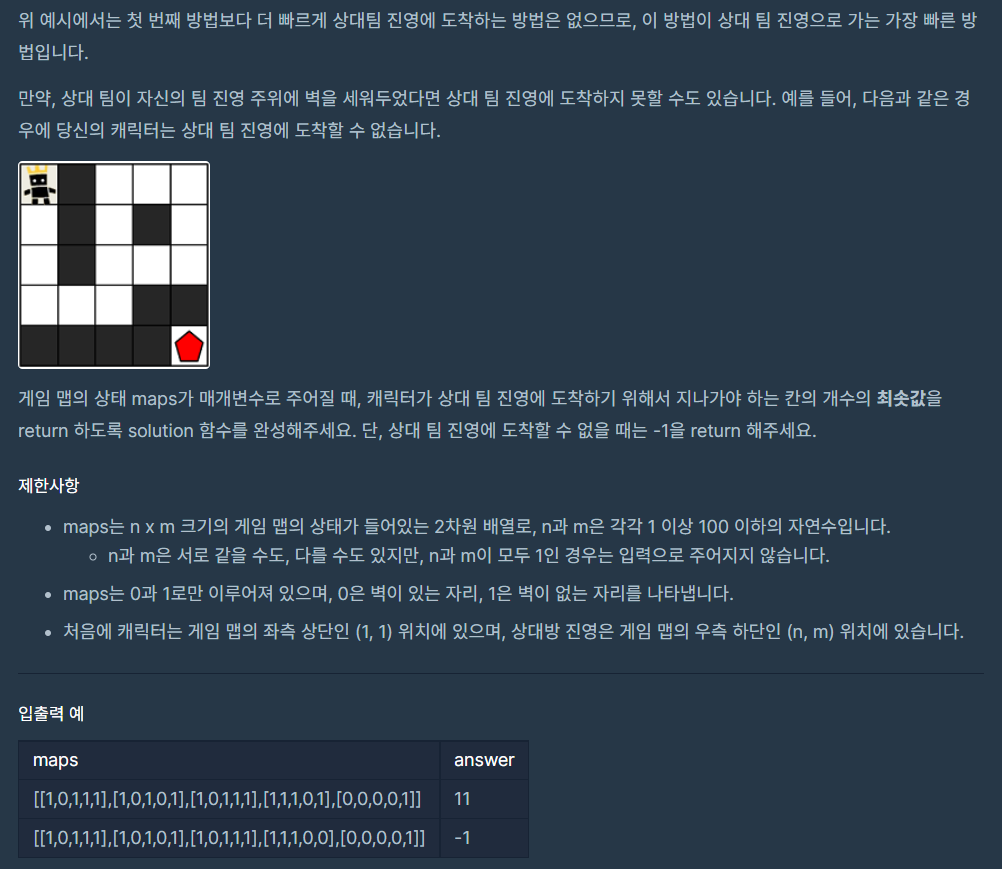
문제 분석
플레이어가 목적지 까지 가는 최단 거리를 구하는 문제입니다. 그래프를 따라 최단 거리를 이동해야 하므로 항상 최단거리가 보장되는 BFS를 사용합니다.
풀이
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
class Player{
int row;
int col;
int dir;
int count;
Player(int row, int col, int dir, int count){
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.dir = dir;
this.count = count;
}
}
class Solution {
public int solution(int[][] maps) {
int answer = 0;
//맵 테두리에 벽을 침
int[][] graph = new int[maps.length+2][maps[0].length+2];
for(int i = 0; i < maps.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < maps[0].length; j++){
graph[i+1][j+1] = maps[i][j];
}
}
//방문 여부
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[graph.length][graph[0].length];
//BFS
Queue<Player> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Player(1,1,1,1));
visited[1][1] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Player player = queue.poll();
if(player.row == maps.length && player.col == maps[0].length)
return player.count;
for(int dir = player.dir; dir < 4; dir++){
int nextRow = player.row;
int nextCol = player.col;
switch(dir){
case 0:
nextRow--;
break;
case 1:
nextCol++;
break;
case 2:
nextRow++;
break;
case 3:
nextCol--;
break;
}
if(graph[nextRow][nextCol] == 1 && visited[nextRow][nextCol] == false){
visited[nextRow][nextCol] = true;
queue.offer(new Player(nextRow,nextCol,0,player.count+1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}- 외곽에 0이라는 벽을 모두 쳤습니다.
map의 행과 열이 각각 2씩 추가된(외벽을 친)Graph를 만들어 탐색을 수행하였습니다. dir라는 방향이라는 변수를두어 0일때up, 1일때left, 2일때down, 3일때right한칸 이동을 수행하였습니다.- 다음 노드로 이동할때 현재
count+ 1하여 이동하였습니다.(강의에서steps)
강의의 풀이
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
//위치 정보 클래스
class Location{
int x, y;
Location(int x, int y){ this.x=x; this.y=y;}
boolean equals(Location other){
return this.x == other.x && this.y == other.y;
}
Location left(){ return new Location(x-1, y);}
Location right(){ return new Location(x+1, y);}
Location up(){ return new Location(x, y-1);}
Location down(){ return new Location(x, y+1);}
}
//플레이어 이동 정보 클래스
class Position{
int steps;
Location location;
Position(Location l, int s){ location = l; steps = s; }
}
public int solution(int[][] maps) {
final int mapSizeX = maps.length;
final int mapSizeY = maps[0].length;
final Location target = new Location(mapSizeX-1, mapSizeY-1); //목적지
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[mapSizeX][mapSizeY];
Queue<Position> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Position(new Location(0,0), 1));
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Position now = queue.poll();
//맵 밖
if(now.location.x < 0) continue;
if(now.location.x >= mapSizeX) continue;
if(now.location.y < 0) continue;
if(now.location.y >= mapSizeY) continue;
//벽
if(maps[now.location.x][now.location.y] == 0) continue;
//이미 방문
if(visited[now.location.x][now.location.y]) continue;
visited[now.location.x][now.location.y] = true;
//목적지 도착
if(now.location.equals(target)) return now.steps;
//다음 위치 이동
queue.offer(new Position(now.location.left(), now.steps+1));
queue.offer(new Position(now.location.right(), now.steps+1));
queue.offer(new Position(now.location.up(), now.steps+1));
queue.offer(new Position(now.location.down(), now.steps+1));
}
//경로 막힘
return -1;
}
}기본적인 원리는 BFS로 제가한 방식과 동일하지만, 외벽을 치지 않았고, x와 y를 변수로 저장한 것에 반해 클래스를 새로 만들어 위치만 따로 저장하였습니다.
또 이동하기 전에 판단을 먼저 한 제가 한 풀이에 반해 이동 후 판단을 하는 차이점이 있었습니다.
