- It is difficult to understand in what situations each of inheritance, interface, and abstract class should be used. In particular, I know that interface is a feature that is only available in Java.
- In actual programming, there are few clear situations like the Animal class, but how to apply it is too vague.
- abstract class, ⇒ template method pattern
-event-us?? ⇒ Participant (participation code, authentication method). ⇒ Non-member participants (e-mail, nickname, mobile phone), member participants (e-mail)
- I want to know exactly what the difference is when casting. I want to know what exactly is the difference between Animal animal = new Animal and Cat animal = new Animal and Animal animal = new Cat?
- When using upcasting, is there an appropriate example of a situation where you must use upcasting?
- Upcasting (going up)
- (Parent) Child c;
- Downcasting
- (Child) Parent p;
-Parent p = new Child(); - (Child) p;
- (Child) Parent p;
- Upcasting (going up)
- For example, when declaring Animal animal = new Cat(), etc., is there a clear situation, such as that an animal should never be declared as new Animal() and must use new cat()?
- Participant ⇒ member participant, non-member participant
- Participant
-Member Participant
-B
-NonMemberParticipant
-A - Participant p ??? Participant? member participant? Non-member participants?
- I want to use function A for non-member participants
- (NonMemberParticipant) p.A();
- I want to use function A for non-member participants
- Participant
3-Tier Architecture
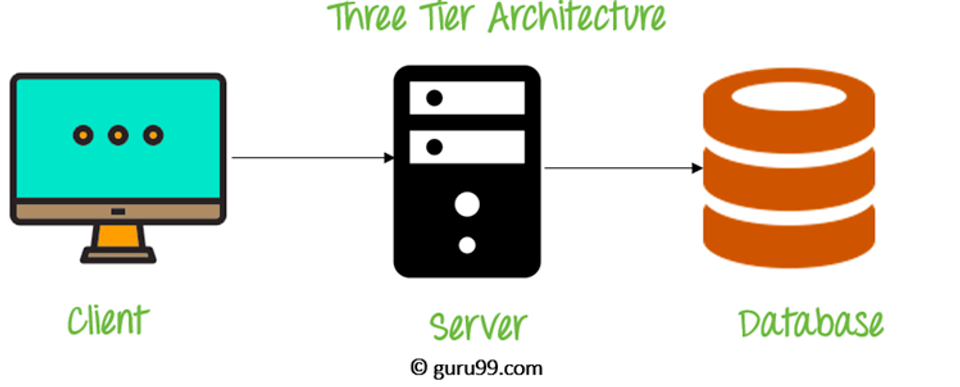
Presentation Tier
- The presentation layer is the user interface and communication layer of the application where end users interact with the application. Its main purpose is to display information and collect information from users. This top-level layer can run, for example, in a web browser, desktop application, or graphical user interface (GUI). The web presentation layer is usually developed using HTML, CSS and JavaScript. Desktop applications can be written in many different languages, depending on the platform.
- UI (User-Interface)
- wiki definition
- Means a communication medium between a person (user) and a computer system. This communication is aimed at ensuring efficient operation and user control over the device in question. A nearby touchscreen, mouse, etc. are good examples of physically seeing the UI.
- General web or app service
- browser
- Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Explorer, Whale, Edge
- app
- Android app
- IOS app
-
Application Tier
The application layer, also called the logic layer or middle layer, is the heart of the application. In this layer, the information gathered from the presentation layer is processed against other information from the data layer using business logic, a specific set of business rules. The application layer can also add, delete, or modify data in the data layer.
The application layer is typically developed using Python, Java, Perl, PHP, or Ruby and communicates with the data layer using API calls.
-
Data Tier
The data tier, also known as the database tier, data access tier, or backend, is where the information processed by the application is stored and managed. It is a relational database management system such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle, DB2, Informix or Microsoft SQL Server, or Cassandra,](https:/ /www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/relational-databases) CouchDB or [MongoDB](https://www.ibm.com/ It can be a NoSQL database server, such as cloud/learn/mongodb).
If you create a service with JAVA...?
https://enjoydevelop.tistory.com/22 - Scanner
- Layered-Architecture → Clean Architecture (Hexagonal Architecture)
- Consider the part of the cafe system that stores and displays the menu list.
- Presentation Tier (UI)
- browser
- Make a menu list inquiry request.
- The menu list that can be ordered is exposed.
- Save the menu.
- Make a menu list inquiry request.
- Java console
- Receives menu list inquiry request.
- The menu list that can be ordered is exposed.
- Save the menu.
- Receives menu list inquiry request.
- browser
- Application Tier
-Spring
- Search menu list
- Search the menu list stored in the Data Tier.
- The searched menu list is delivered to the Presentation Tier through the network.
- Network- Java
- Search menu list
- Search the menu list stored in the Data Tier.
- The searched menu is delivered to the Presentation Tier.
- just pass the value
- Search menu list
- Java
- Data Tier
-Spring
- Search the menu list stored in the DB through Query.
- RepositoryInterface → SpringMysqlDB
- Delivers the searched information to the Application Tier.- Java
- Retrieves the menu list stored in memory (Java function.. List, HashMap).
-RepositoryInterface
- DefaultMemoryDB → Get the value from the array - Delivers the searched information to the Application Tier.
- Retrieves the menu list stored in memory (Java function.. List, HashMap).
- Java
Reference
