Spring MVC 패턴을 작업하다 보면, @Controller, @Service, @Repository, @Configuration등 어노테이션을 작성할텐데 기본적으로 @Component을 가지고 있다.
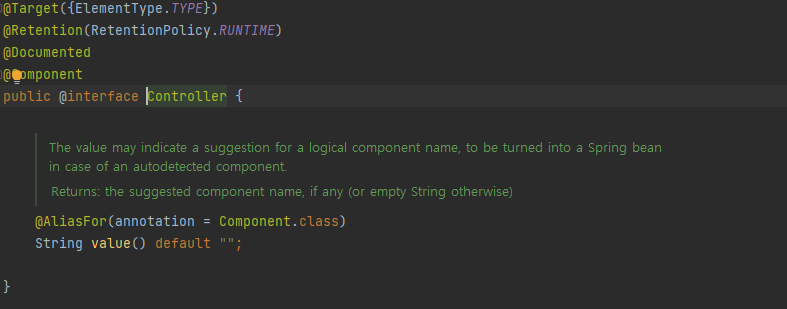
@Component가 붙은 모든 클래스를 @ComponentScan을 통해 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
그런데 작업이나, 오픈 소스를 참고하다보면 @Configuration 및 @Component를 사용하여 빈으로 등록하는데 무슨 차이가 있는지 궁금해서 검색해봤다.
(외부 라이브러리엔 Configuration, 내부 Class엔 Component)
우선 코드를 통해 결과값부터 확인하자
//공용 객체
public class SingletonBean {
}
/**
* @Configuration
*/
@Configuration
public class ConfigurationTest {
@Bean
public SingletonBean singletonBeanConfiguration(){
return new SingletonBean();
}
}
/**
* @Component
*/
@Component
public class ComponentTest {
@Bean
public SingletonBean singletonBeanComponent(){
return new SingletonBean();
}
}
/**
* @Configuration
*/
@Test
void configuration(){
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigurationTest.class);
ConfigurationTest bean = ac.getBean(ConfigurationTest.class);
ConfigurationTest bean2 = ac.getBean(ConfigurationTest.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean = ac.getBean(ConfigurationTest.class).singletonBeanConfiguration();
SingletonBean singletonBean2 = ac.getBean(ConfigurationTest.class).singletonBeanConfiguration();
System.out.println("bean = " + bean);
System.out.println("bean2 = " + bean2);
System.out.println("singletonBean = " + singletonBean);
System.out.println("singletonBean2 = " + singletonBean2);
//-------출력 결과------
bean = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.ConfigurationTest$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$4765d44@6622fc65
bean2 = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.ConfigurationTest$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$4765d44@6622fc65
singletonBean = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.SingletonBean@a43ce46
singletonBean2 = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.SingletonBean@a43ce46
}
/**
* @Component
*/
@Test
void component(){
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ComponentTest.class);
ComponentTest bean = ac.getBean(ComponentTest.class);
ComponentTest bean2 = ac.getBean(ComponentTest.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean = ac.getBean(ComponentTest.class).singletonBeanComponent();
SingletonBean singletonBean2 = ac.getBean(ComponentTest.class).singletonBeanComponent();
System.out.println("bean = " + bean);
System.out.println("bean2 = " + bean2);
System.out.println("singletonBean = " + singletonBean);
System.out.println("singletonBean2 = " + singletonBean2);
//-------출력 결과------
bean = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.ComponentTest@2766ca9d
bean2 = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.ComponentTest@2766ca9d
singletonBean = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.SingletonBean@4fad9bb2
singletonBean2 = com.server.TourServer.Tour.Singleton.SingletonBean@517d4a0d
}분명 싱글톤으로 빈을 등록한거 같은데 결과가 완전 다르다.
우선 Configuration에 등록 된 빈은 스프링 CGLIB라는 바이트코드 조작 라이브러리를 사용하여 ConfigurationTest 클래스를 상속받은 임의의 다른 클래스를 만들고, 그 다른 클래스를 스프링 빈으로 등록 한 것이다.
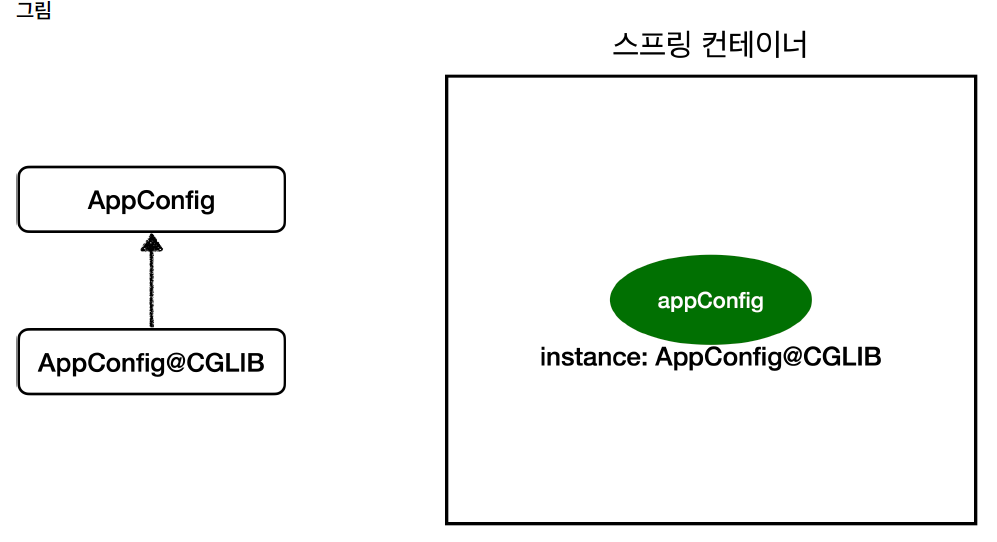
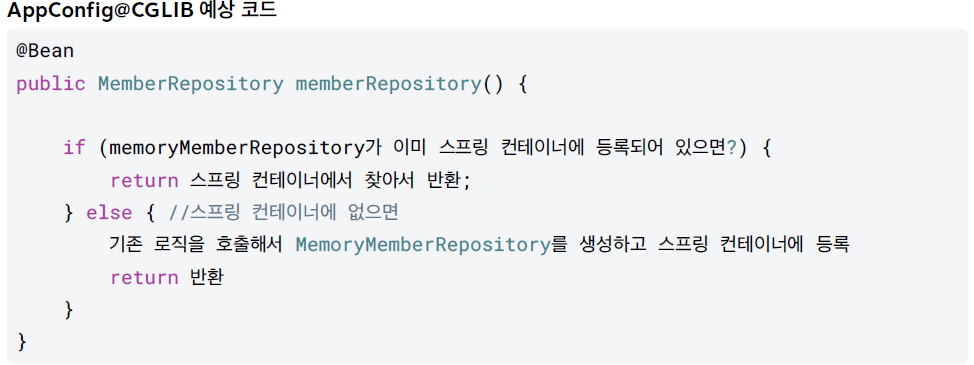
참조 : 스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편 김영한
그래서 new SingletonBean()을 새롭게 생성하여도 이미 등록이 되어있기때문에 스프링 컨테이너에서 반환을 하는 것이다.
그러면 Component에서 SingletonBean 객체가 서로 다르게 출력이 될까? 이유는 메서드 호출 방식 때문이다
해당 빈을 Spring 컨테이너에서 관리한다. 그러나 직접 메서드를 호출하여 빈을 생성하는 경우, Spring이 아닌 자바 메서드 호출에 의해 객체가 생성되므로 매번 새로운 인스턴스가 반환된다.
결국 CGLIB 프록시가 적용되어있지 않기 때문에 단순히 자바 메서드 호출이 이루어져 새로운 객체가 생성 되는거다
아래는 해결 방안이다
@Component
public class SingletonBean {
}
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ComponentTest {
private final SingletonBean singletonBean;
public SingletonBean singletonBeanComponent(){
return singletonBean;
}
}
@Test
void component(){
ComponentTest bean = componentTest;
SingletonBean singletonBean = componentTest.singletonBeanComponent();
SingletonBean singletonBean2 = componentTest.singletonBeanComponent();
System.out.println("bean = " + bean);
System.out.println("singletonBean = " + singletonBean);
System.out.println("singletonBean2 = " + singletonBean2);
}SingletonBean도 빈 으로 등록하여 의존성 주입하여 사용하면 싱글톤이 된다!
결국 외부라이브러리에 @Configuration을 해야하는지는 다른 문제 이다.
@Configuration : 스프링 설정 정보에서 사용
Configuration으로 등록했기 때문에 설정 클래스를 명확히 하고, 코드의 유지보수성과 관리성을 높일 수 있어서 사용하는 것이다.
- 내가 실험한 결과 외부라이브러리 read-only 파일이지만 @Component를 사용하더라도 빈으로 등록가능하고 싱글톤으로 사용 가능하다.
@Component
public class RestTemplateConfig {
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory();
requestFactory.setConnectTimeout(5000);
requestFactory.setReadTimeout(5000);
restTemplate.setRequestFactory(requestFactory);
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RestTemplateService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
}