[Paper Review] A Survey of Quantization Methods for Efficient Neural Network Inference (2021)
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.13630.pdf
A Survey of Quantization Methods for Efficient Neural Network Inference, Amir Gholami, Sehoon Kim, Zhen Dong, Zhewei Yao 2021
1. Quantization
1-1. Introduction
● Realizing pervasize deep learning model requires real=time inference, with low energy consumption and high accuracy, in resource-constrained environments.
● Moving from floating-point representations to low-precision fixed integer values represented in four bits or less holds the potential to reduce the memory footprint and latency by a factor of 16x; and, in fact, reductions of 4x to 8x are often realized in practice in these applications.
2. Basic concepts common to many applications of quantizatin
2-1. Risk minimization function to optimize
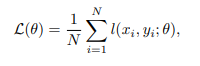
θ: trained parameters {W1, W2, …, WL} in fp precision
(x, y): input data, corresponding label
l(x, y; θ): loss function
hi: the input hidden activations of the ith layer
ai: corresponding output hidden activations
The goal is to reduce the precision of both the parameters θ,as wells as the intermediate activation maps (i.e., hi, ai) to low-precision, with minimal impact on the generalization power/accuracy of the mode.
2-2. Uniform and Non-uniforn quantization
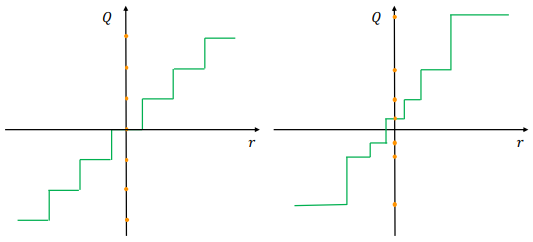
● Uniform quantization 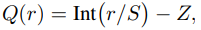
Q: quantization operator
r: real valued input (activation or weight)
S: real valued scaling factor
Z: integor zero point
The resulting quantized values (aka quantiation levels) are uniformly spaced. So This concept is currently de-facto method due to its simplicity, efficient mapping to hardware.
● Non-uniform quantization 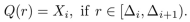
Quantizated values are not necessarily uniformly spaced, and typicaly difficult to deploy efficiently on general computation hardware (e.g. GPU, CPU).
2-3. Symmetric and Asymmetric Quantization
● A real valued scaling vector S:
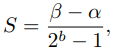
In oder for the scaling vector to be defined, the clipping range [α, β] should first be determined (=calibration)
● Calibration Method
- use min/max of the signal for both symmetric and asymmetric quantization (popular)
- use percentile (the i-th largest/smallest values are used as β/α)
- select α, β to minimize KL divergence between the real values and the quantized values
● Symmetric quantization, Asymmetric quantization
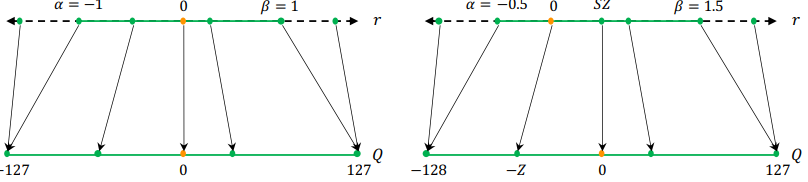
Symmetric quantization is easy to implement because an integer zeropoint Z becomes 0. However, The range could be skewed and not symmetric, accuracy might get low.
2-4. Range Calibration Algorithm: Static vs Dynamic Quantization
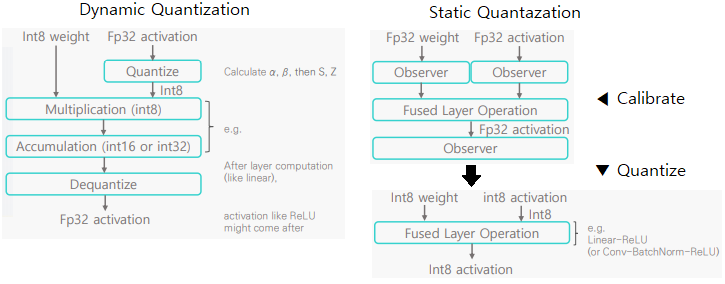
● With static quantization, the parameters are fized during inference, but the activation maps differ for each input sample (popular).
● With dynamic quantization, the clipping range is dynamically calculated for each activation map during runtime. So it has higher accuracy as the signal range, but overhead in computatino.
3. More unique to the quantization of NNs
● Quantization Granularity: granularity of how the clipping range [α, β] is calculated for the weights
● Layerwise and Channelwise quantization
- Layerwise quantization: the same clipping range is applied to all the filters that belong to the same layer
- Channelwise quantization: the same clipping ranges dedicate to same channels
- Groupwise quantization
4. Relationship between quantization and training
● Fine-tuning Methods: how to adjust parameters in NN after quantization
4.1. Quantization Aware Training (QAT): performed by retraining model
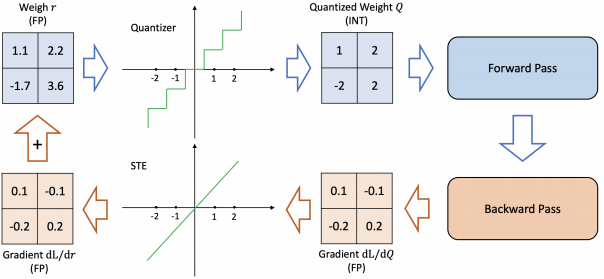
With QAT, the usual forward and backward pass are performed on the quantized model in floating point, but the model parameters are quantized after each gradient update.
Performing the backward pass with floating point is important, as accumulating the gradients in quantized precision can result in zero gradient or gradients that have high error, especially in low-precision.
● How to approximate the gradient of non-differentable quantization operator? STE and non-STE
- Straight Through Estimator (STE) ignores the rounding operation and approximate it iwht and identity function. Despite of computational cot of retraining, it is commonly used.
- non-STE requires a lot of tuning
▲ QAT using STE
4.2. Post Training Quantization(PTQ): performed with retraining the model(=static quantization)
PTQ model performs the quantization and adjustments of the weights without any fine-tuning or retraining.
So It can be applied in situations with limited data or unlabeled data, but it has lower accuracy compared to QAT
5. Advanced concept: quantization below 8 bits
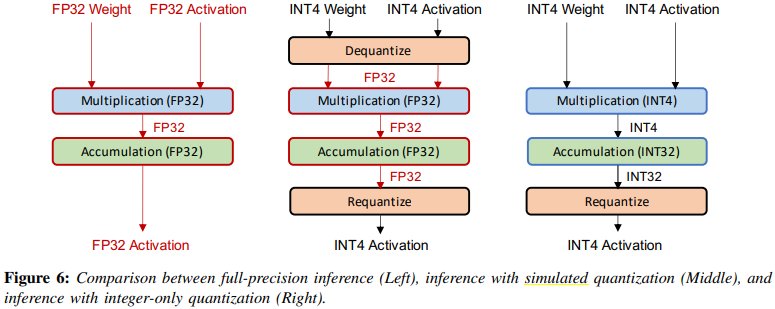
5.1. Simulated and Integer-only quantization
● Simulated quantization (fake quantization)
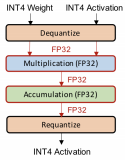
In this model, parameters are stored in low-precision, but the operations(e.g. matrix mul, convolutions) are carried out with floating point arithmetic.
Therefore, the quantized parameters need to be dequantized before the floating point operations as schematically shown
in Figure.
It has the benefit for problems that are bandwidth-bound(loading parameters from memory) rather than compute-cound, but has low-precision.
● Integer-only quantization (fixed-point quantization)
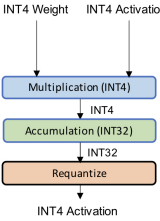
With Integer-only quantization, the entire inference carried out with integer arithmetic.
5.2. Dyadic quantization
Dyadic quantization is another clas of integer-only quatization that has scaling performed with dyadic numbers, rational numbers with integer values in their numerator and a power of 2 in the denominator. (Integer/2^n)
This case only requires integer addition, multiplication, bit shifting, but no division, that makes the addition logic simpler with higher efficiency.
5.3. Hardware aware quantization
The benefits from quantization is hardware-dependant, with many factors such as on-ceip memory, bandwidth, and cache hierachy affecting the quantization speed up.
So this approach uses simulated ahrdware latency and measures the actual deployment latency by directly deploying quantized operations in heardware.

Conducting a survey is the method to know the client's genuine feelings. Most of the big companies across the globe are conducting surveys to know their customer's experience. If the experience is bad, then they will work on it and improve their services. My favorite supermarket company Loblaws is also following the same method to know their customer's experience. They surveyed at https://storeopinion-ca.page. The winner of this store opinion survey will get a $1000 gift card for free.