https://www.tutorialspoint.com/rust/rust_ownership.htm
프로그램 메모리는 Stack 또는 Heap에 할당
Stack
스택은 후입선출
스택은 컴파일 타임에 크기가 알려진 데이터 값을 저장
모든 스칼라 유형은 크기가 고정이므로 스택에 저장할 수 있음
Heap
힙 메모리는 컴파일 시 크기를 알 수 없는 데이터 값을 저장
동적 데이터를 저장하는 데 사용
Ownership
Rust의 각 값에는 그 값의 소유자라고 하는 변수가 존재
Rust에 저장된 모든 데이터에는 관련된 소유자가 존재
- 각 데이터에는 한 번에 한 명의 소유자만 있을 수 있
- 변수는 항상 다른 메모리 위치를 가리킴
- 두 변수는 동일한 메모리 위치를 가리킬 수 없음
Transferring Ownership
- 한 변수의 값을 다른 변수에 할당
- 함수에 값 전달
- 함수에서 값을 반환
위와 같은 방법으로 소유권 이전
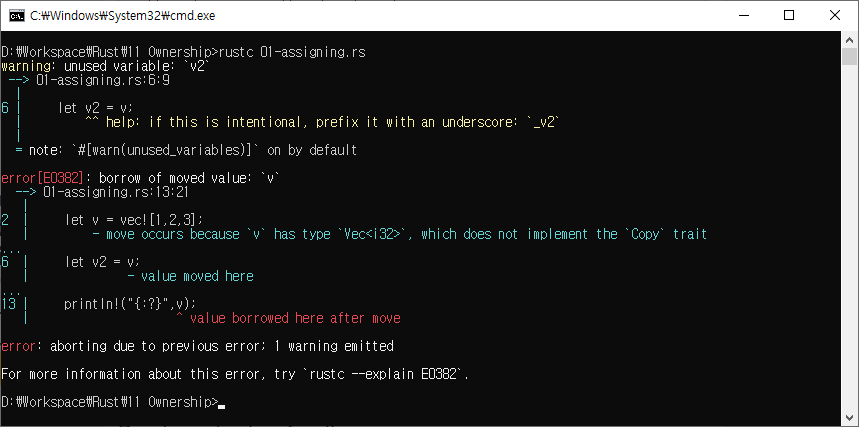
한 변수의 값을 다른 변수에 할당
Rust 핵심 포인트는 메모리 안전성
메모리 안전성은 누가 무엇을 언제 사용할 수 있는지에 대한 엄격한 제어를 통해 달성
fn main(){
let v = vec![1,2,3];
// vector v owns the object in heap
// only a single variable owns the heap memory at any given time
let v2 = v;
// here two variables owns heap value,
// two pointers to the same content is not allowed in rust
// Rust is very smart in terms of memory access ,so it detects a race condition
// as two variables point to same heap
// println!("{:?}",v); //Error
println!("{:?}",v2);
}

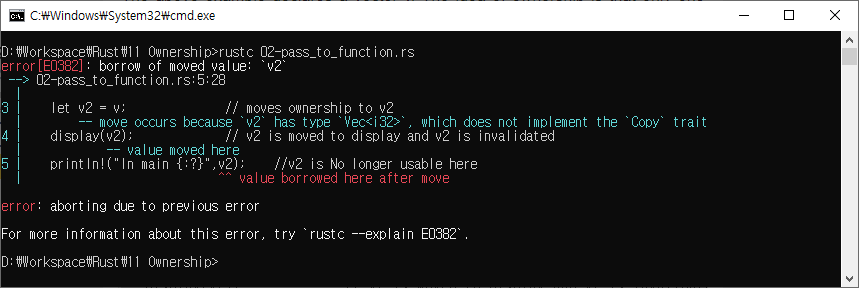
함수에 값 전달
값의 소유권은 힙에 있는 객체를 클로저나 함수에 전달할 때도 변경
fn main(){
let v = vec![1,2,3]; // vector v owns the object in heap
let v2 = v; // moves ownership to v2
display(v2); // v2 is moved to display and v2 is invalidated
println!("In main {:?}",v2); //v2 is No longer usable here
}
fn display(v:Vec<i32>){
println!("inside display {:?}",v);
}
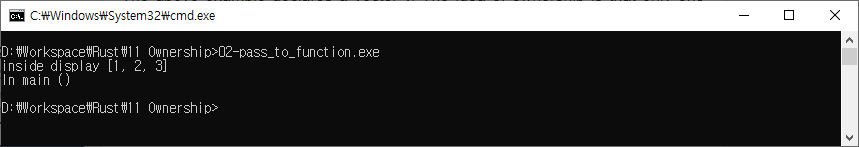
함수에서 값을 반환
fn main(){
let v = vec![1,2,3]; // vector v owns the object in heap
let v2 = v; // moves ownership to v2
let v3 = display(v2); // v2 is moved to display and v2 is invalidated
println!("In main {:?}",v3); //v2 is No longer usable here
}
fn display(v:Vec<i32>)->Vec<i32>{
// returning same vector
println!("inside display {:?}",v);
}
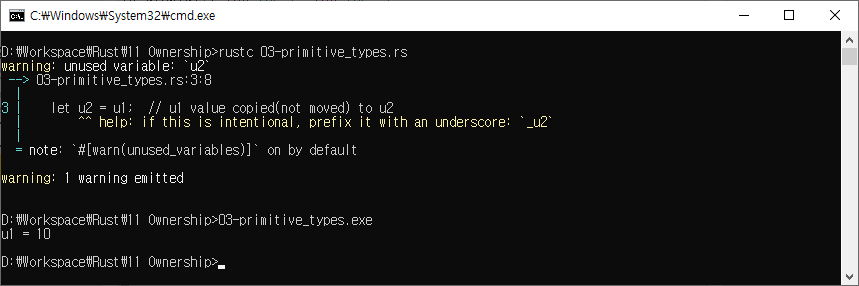
기본 형식의 소유권
기본 형식의 경우 한 변수의 내용이 다른 변수로 복사
소유권 이전이 발생하지 않음
기본 형식 변수가 개체보다 적은 리소스를 필요
fn main(){
let u1 = 10;
let u2 = u1; // u1 value copied(not moved) to u2
println!("u1 = {}",u1);
}