https://www.tutorialspoint.com/rust/rust_structure.htm
배열은 동종 값 모음을 나타내는 데 사용
유사하게, Structure는 다른 Structure를 포함하여 다른 유형의 데이터 항목을 결합할 수 있게 해주는 다른 사용자 정의 데이터 형식
Structure는 Key-Value Pair로 정의
구조체 선언
struct 키워드는 구조체를 선언하는 데 사용
structure는 정적 형식이므로 structure의 모든 필드는 데이터 형식이 지정되어야 함
structure 이름규칙은 변수의 이름규칙과 동일
structure 블록은 세미콜론으로 끝나야 함
struct Name_of_structure {
field1:data_type,
field2:data_type,
field3:data_type
};구조체 초기화
구조체를 선언한 후에는 각 필드에 값을 할당해야 함
특정 필드의 값에 접근하려면 점 표기법을 사용
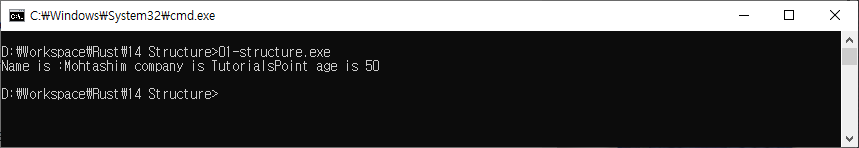
struct Employee {
name:String,
company:String,
age:u32
}
fn main() {
let emp1 = Employee {
company:String::from("TutorialsPoint"),
name:String::from("Mohtashim"),
age:50
};
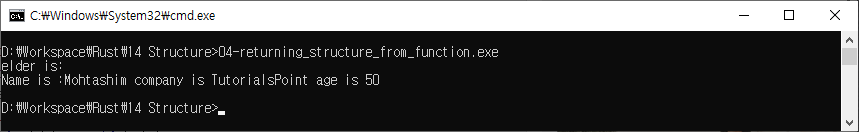
println!("Name is :{} company is {} age is {}",emp1.name,emp1.company,emp1.age);
}
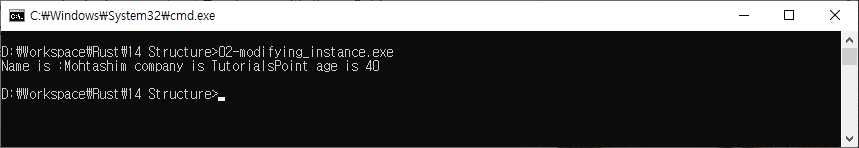
구조체 인스턴스 수정
인스턴스를 수정하려면 인스턴스 변수를 가변으로 설정 해야함
struct Employee {
name:String,
company:String,
age:u32
}
fn main() {
let mut emp1 = Employee {
company:String::from("TutorialsPoint"),
name:String::from("Mohtashim"),
age:50
};
emp1.age = 40;
println!("Name is :{} company is {} age is {}",emp1.name,emp1.company,emp1.age);
}
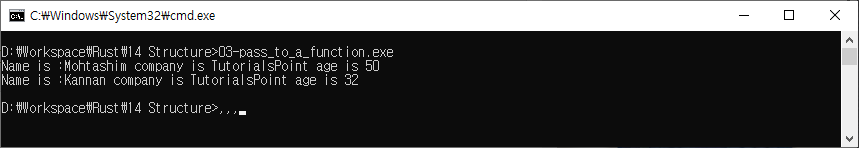
구조체를 함수에 전달
//declare a structure
struct Employee {
name:String,
company:String,
age:u32
}
fn main() {
//initialize a structure
let emp1 = Employee {
company:String::from("TutorialsPoint"),
name:String::from("Mohtashim"),
age:50
};
let emp2 = Employee{
company:String::from("TutorialsPoint"),
name:String::from("Kannan"),
age:32
};
//pass emp1 and emp2 to display()
display(emp1);
display(emp2);
}
// fetch values of specific structure fields using the
// operator and print it to the console
fn display( emp:Employee){
println!("Name is :{} company is {} age is {}",emp.name,emp.company,emp.age);
}
함수에서 구조체 반환
fn main() {
//initialize structure
let emp1 = Employee{
company:String::from("TutorialsPoint"),
name:String::from("Mohtashim"),
age:50
};
let emp2 = Employee {
company:String::from("TutorialsPoint"),
name:String::from("Kannan"),
age:32
};
let elder = who_is_elder(emp1,emp2);
println!("elder is:");
//prints details of the elder employee
display(elder);
}
//accepts instances of employee structure and compares their age
fn who_is_elder (emp1:Employee,emp2:Employee)->Employee {
if emp1.age>emp2.age {
return emp1;
} else {
return emp2;
}
}
//display name, comapny and age of the employee
fn display( emp:Employee) {
println!("Name is :{} company is {} age is {}",emp.name,emp.company,emp.age);
}
//declare a structure
struct Employee {
name:String,
company:String,
age:u32
}
Method in Structure
메서드는 프로그래밍 명령어의 논리적 그룹
fn 키워드로 메소드를 선언
메서드의 스코프는 structure 블록 내
메서드는 구조 블록 외부에서 선언
impl 키워드는 structure의 메서드를 정의
메서드의 첫 번째 매개변수는 항상 구조체의 호출 인스턴스를 나타내는 self
메서드는 구조의 데이터 멤버에서 작동
메서드를 호출하려면 먼저 structure를 인스턴스
메서드는 structure의 인스턴스를 사용하여 호출
struct My_struct {}
impl My_struct {
//set the method's context
fn method_name() {
//define a method
}
}//define dimensions of a rectangle
struct Rectangle {
width:u32, height:u32
}
//logic to calculate area of a rectangle
impl Rectangle {
fn area(&self)->u32 {
//use the . operator to fetch the value of a field via the self keyword
self.width * self.height
}
}
fn main() {
// instanatiate the structure
let small = Rectangle {
width:10,
height:20
};
//print the rectangle's area
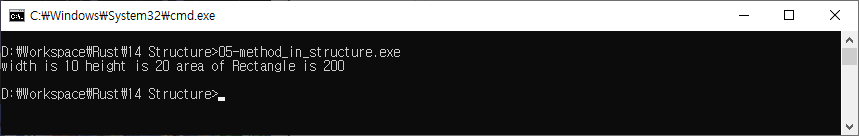
println!("width is {} height is {} area of Rectangle
is {}",small.width,small.height,small.area());
}
구조체의 정적 메서드
정적 메서드는 유틸리티 메서드로 사용할 수 있음
이러한 메서드는 구조가 인스턴스화되기 전에도 존재
정적 메서드는 구조의 이름을 사용하여 호출되며 인스턴스 없이 액세스
일반 메서드와 달리 정적 메서드는 &self 매개변수를 사용하지 않음
정적 메서드 선언
impl Structure_Name {
//static method that creates objects of the Point structure
fn method_name(param1: datatype, param2: datatype) -> return_type {
// logic goes here
}
}정적 메서드 호출
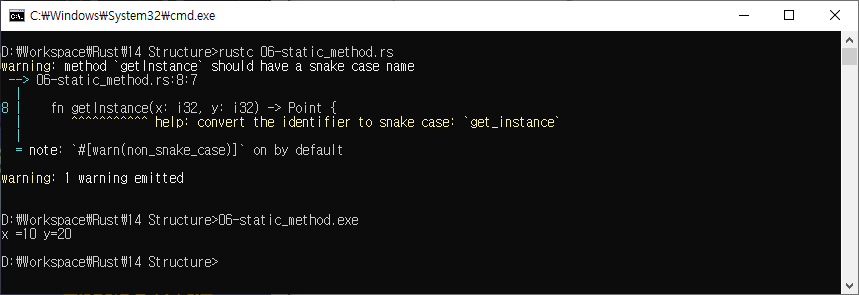
structure_name::method_name(v1,v2)getInstance 메서드를 Point 구조의 인스턴스를 만들고 반환하는 팩토리 클래스로 사용
//declare a structure
struct Point {
x: i32,
y: i32,
}
impl Point {
//static method that creates objects of the Point structure
fn getInstance(x: i32, y: i32) -> Point {
Point { x: x, y: y }
}
//display values of the structure's field
fn display(&self){
println!("x ={} y={}",self.x,self.y );
}
}
fn main(){
// Invoke the static method
let p1 = Point::getInstance(10,20);
p1.display();
}