REF
https://jiho-ml.com/weekly-nlp-34/
https://openmmlab.medium.com/dive-into-yolov8-how-does-this-state-of-the-art-model-work-10f18f74bab1
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py#L205
YOLO-World: Real-Time Open-Vocabulary Object Detection 리뷰
DEMO : https://huggingface.co/spaces/stevengrove/YOLO-World
PAPER : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.17270.pdf / https://www.semanticscholar.org/reader/37c112454a236ab91c9c6b5cc165a6c3251e9206
MODEL & CODE : https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World?tab=readme-ov-file
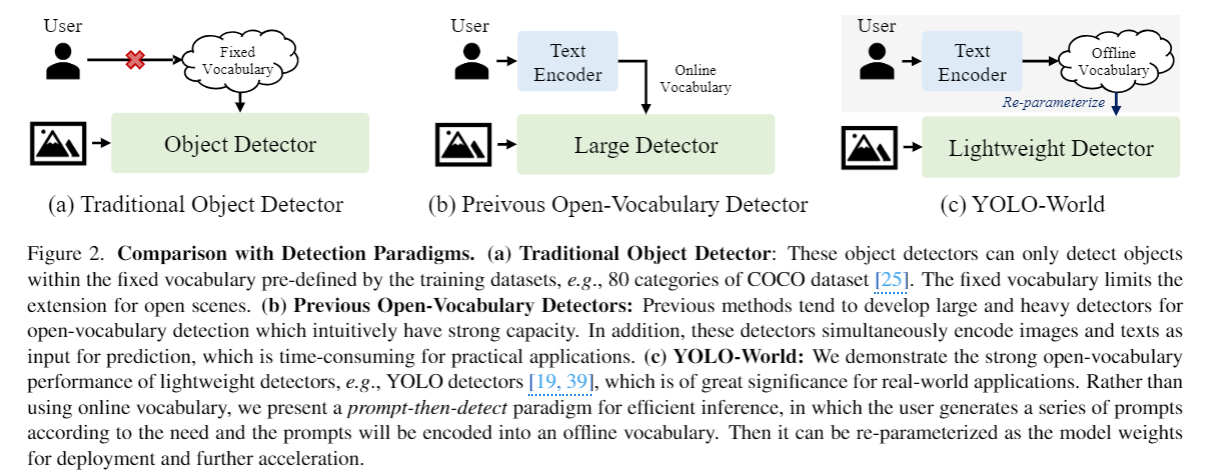
BACKGROUND
- yolo series - yolov8
- multi modal
- open valcabulary obejct detetion
- region-text matching
- clip, Glip, G-dino
- online / offline vocabulary
Related work
Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
to detect objects beyond the predefined categories 를 목적으로 한 연구 분야
초기 셋팅 : training detectors on the base classes and evaluating the novel (unknown) classes
novel object 에 대한 detector의 성능을 알아보려 했지만 제한된 데이터 셋으로 학습했기 때문에 여전히 일반화 성능 떨어짐
최근 연구 : grounding 멀티모달 학습을 함
-
GLIP - phrase grounding 을 기반으로 open-vocabulary detection을 위한 pretrained framework 제안하고 zero-shot 평가
-
Groungind DINO - grounded pre-training을 cross-modality fusion을 통해 detection transformers 에 통합
-
DETCLIP, DETCLIPv2, GLIPv2 와같은 연구 - large-scale image-text pairs로 학습된 pre-trained detectors사용, region-text matching 을 통한 image-text datasets 사용으로 일반화 성능 향상을 도모
그러나 이런 연구는 ATSS, DINO, SWIN-T 와 같은 매우 큰 백본을 사용하여 high computationl demands, deplyment 가 어려운 문제가 있음
→ YOLO-WORLD 제안 : aiming for efficient open-vocabulary object detection with real-time inference and easier downstream application deployment
Grounding 이란?
Grounding이란, 사람 사이에 효과적인 소통을 위해 필수적인 공통 된 이해와 기반을 다지는 과정을 뜻합니다.
예를 들면 “비가 오네"라는 말을 듣고 고개를 끄덕이거나 “빗물이 떨어진다”라고 의역을 하는 것도 grounding의 한 방법이죠. 다른 배우가 “싫어. 지금 화창한데?”라고 하면 함께 세계관을 형성하지 못하고 연극의 흐름을 깨겠죠. 반면 “우산이 없으니 편의점에서 사자."라고 대답하면 비가 오고 있다는 제안을 우산이 없다는 말로 수용하고 우산을 사야된다라는 정보를 제공하기 때문에 적절한 “Yes, and-”식 대사가 됩니다.
기냥 large scale 데이터로 학습한 pre-trained 모델 만든다는 말인듯 ??OD에서의 Grounding이란 객체의 위치를 추론하는 것을 말함
ABSTRACT
yolo 는 많이 쓰이고 있으나 미리 라벨링이 된 데이터로 지도 학습하는 모델은 open-senario 에서의 활용도가 떨어짐
이를 해결하기 위해 vision-language modeling 과 pretraining on large scale dataset을 통해 open vocabulary detection 수행
CONTRIBUTION
- On the challenging LVIS dataset, YOLO-World achieves 35.4 AP with 52.0 FPS on V100, which outperforms many state-of-the-art methods in terms of both accuracy and speed.
- Re-parameterizable Vision- Language Path Aggregation Network (RepVL-PAN)
- region-text contrastive loss to facilitate the interaction be- tween visual and linguistic information.
METHOD
3.1. Pre-training Formulation: Region-Text Pairs
기존 : YOLO series 는 각 카테고리 기준으로 라벨링된 bounding box 가 있는 instance annotations 학습
논문 : instance annotations → resgion-text pairs 로 refomulate
- 각 region B(bounding box)는 상응하는 text T 를 가짐
- T 는 category name, noun phrases, or object description 이 될 수 있음
- 이미지 I와 텍스트 T(명사 집합)를 모두 입력으로 채택하고 예측된 상자 와 해당 객체 임베딩을 출력
3.2. Model Architecture
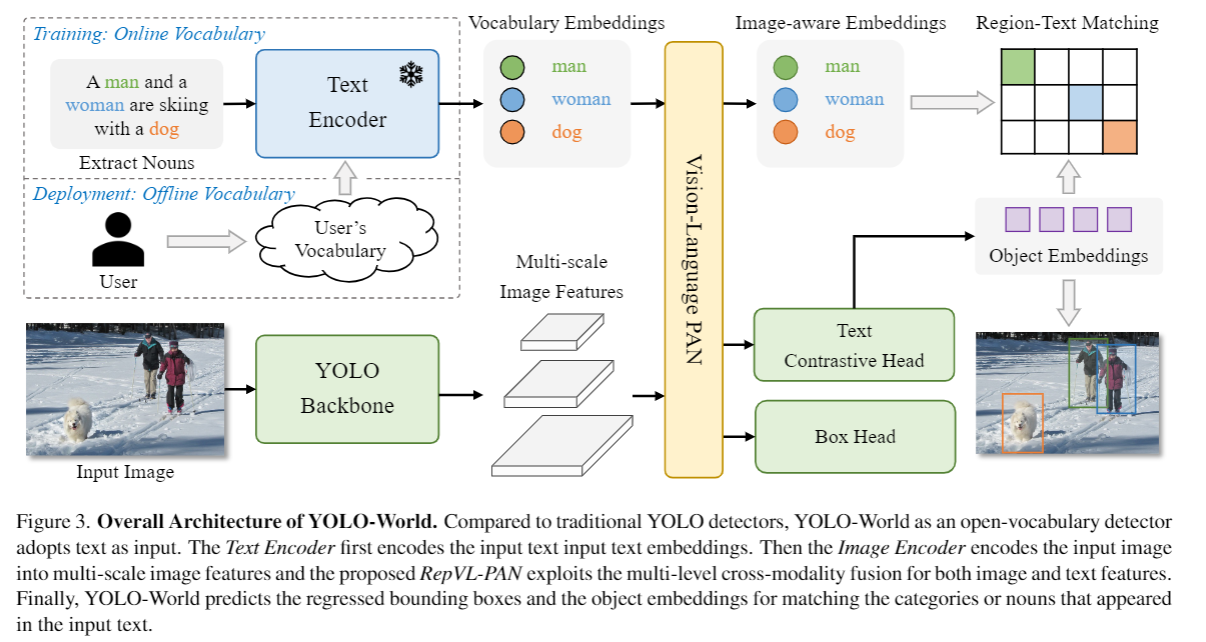
구성 : YOLO detector, a Text Encoder, and a Re-parameterizable Vision-Language Path Aggregation Network (RepVL-PAN)
처리 과정 :
먼저 text가 입력으로 들어오면, Text Encoder가 text를 embedding으로 만듬
YOLO detector에 있는 Image encoder가 입력 이미지를 multi scale features로 만듬
RepVL-PAN으로 image features 와 text embeddings을 fusion해서 text and image representation을 모두 활용
구성요소를 하나씩 보면
-
YOLO Detector
- YOLOv8 을 base 로 개발
- YOLOv8 :
- Darknet backbone as the image encoder
- a path aggregation network (PAN) for multi-scale feature pyramids,
- head for bounding box regression and object embeddings.
-
Text Encoder
- Transformer text encoder pre-trained by CLIP
- CLIP text encoder 가 text-only language encoder 보다 더 나은 visual-semantic capability
-
Text Contrastive Head
- yolov8 에서 사용한 decoupled head with two 3×3 convs 사용
- object-text similarity(classification head 에서 나온 obejct embedding e 와 text encoder에서 나온 text embedding t 의 유사도 )를 계산하는 text contrastive head 제안
- stabilizing the region-text training을 위해 obejct embedding e 와 text embedding t 에 L2-Norm 적용 후 affine transformation
-
Training with Online Vocabulary
- 학습하는 동안은 4개의 이미지를 포함하는 mosaic sample에 대해 online vocabulary T 를 구성함
- 모자이크 이미지에 포함된 모든 positive nouns를 샘플링하고 해당 데이터 셋에서 일부 negative nouns를 무작위로 샘플링
- 각 모자이크 샘플의 어휘는 최대 M개의 명사를 포함하며, M은 기본값으로 80개
-
Inference with Offline Vocabulary
- 효율성을 위해 offline voabulary 를 사용하여 prompt-then-detect strategy 제시
- 사용자가 캡션이나 카테고리를 포함하는 custom 프롬프트를 정의하면, text encoder로 offline vocabulary embedding을 포함하는 offline text embedding 생성
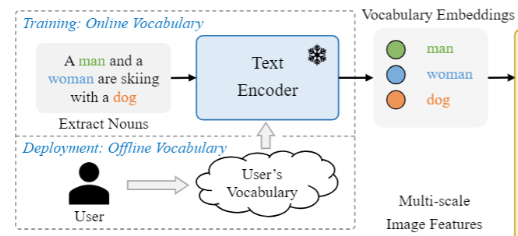
- 각 입력에 대한 계산을 피할 수 있으며 필요에 따라 어휘를 유연하게 조정 가능
3.3. Re-parameterizable Vision-Language PAN
yolov8 에서 사용된대로 csp network의 p3,p4,p5 layer에서 나온 image feature c3,c4,c5 사용
추론 시에는 offline vocabulary embeddings can be re-parameterized
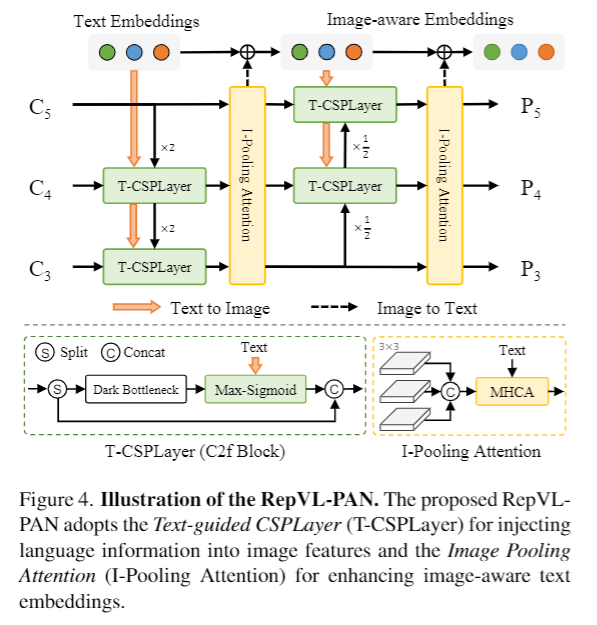
open-vocabulary capability 에서의 vision-semantic representation을 improve하고 image-text embedding 상호작용을 강화하기 위해 아래 모듈 제안
- Text-guided CSPLayer (T-CSPLayer)
- Image-Pooling Attention (I-Pooling Attention)
하나씩 자세히 보면
-
Text-guided CSPLayer (T-CSPLayer)
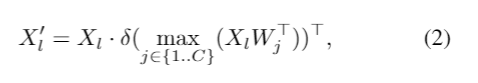
- yolov8 에서 사용된 CSP layer( c2f layer) 에서 concat 하기 전 - text embedding W와 image feature X 를 max-sigmoid attention을 거친 다음 concat
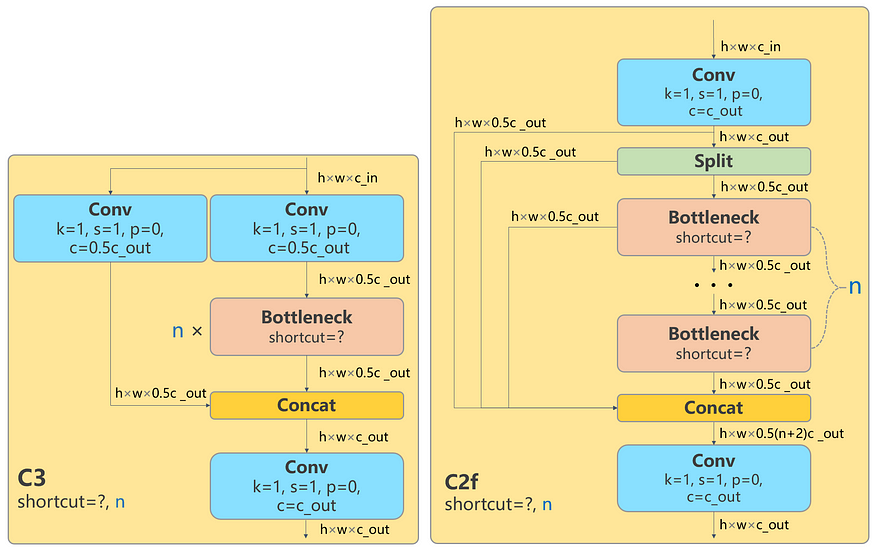
yolov5 의 c3 layer 와 yolov8 c2f layer
c3 : 3개의 convlayer로 구성된 csp bottleneck layer
c2f : 3개의 conv layer로 구성된 fast implementation csp bottleneck layer
c2f layer 는 skip connection 과 split 갯수가 늘어남
- yolov8 에서 사용된 CSP layer( c2f layer) 에서 concat 하기 전 - text embedding W와 image feature X 를 max-sigmoid attention을 거친 다음 concat
-
Image-Pooling Attention
- To enhance the text embed- dings with image-aware information, image feature 를 Image-Pooling Attention으로 aggregation

- c3, c4, c5 multi scale feature에 3x3 max pooling을 적용한 뒤 total of 27 patch tokens을 가진 embedding을 text embedding과 MHCA
- To enhance the text embed- dings with image-aware information, image feature 를 Image-Pooling Attention으로 aggregation
3.4. Pre-training Schemes
on large-scale detection, grounding, and image-text datasets.
Learning from Region-Text Contrastive Loss.
모자이크 샘플 이미지 I 와 텍스트 T가 주어지면 , YOLO-Worldsms K개의 object predictions와 Annotaions를 출력
yolov8 에서 사용한 TOOD의 task-aligned label assignment 를 사용하여 prediction 과 GT를 매칭하였고
text index를 classification label로 활용하려 각 positive prediction을 assign
Loss functions :
이 vocabulary를 기반으로 object-text (region-text) 간의 유사도와 object-text assignments간의 cross-entropy region-text contrastive loss L_con을 구성
bounding box regression을 위한 IOU loss , distributed focal loss 추가
최종 Loss:
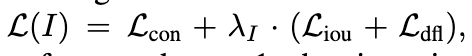
람다_I는 indicator factor : input Image가 detection 또는 grounding data면 1, image-text data면 0
image-text 데이터에서온 이미지면 contrastive loss 만 학습해서 멀모 데이터를 배우게 끔, detection 데이터면 검출 기능을 배우도록
image-text datasets은 noisy box 를 가지고 있다고 간주해서(수도 라벨링으로 생성했기 때문에) regression loss는 정확한 bounding box를 가졌을 때만 계산되도록 함
Pseudo Labeling with Image-Text Data.
pre-training을 할 때 image-text pairs 를 바로 사용하는게 아니라, region-text pair를 자동으로 생성하는 automatic labeling 기법을 제안함
수도 라벨링 3단계
-
extract noun phrase
n-gram algorithm 을 사용하여 text 에서 noun phrase(명사구)를 추출 -
pseudo labeling
GLIP 과 같은 pre-trained open-vocabulary detector를 사용하여 각 이미지마다 주어진 명사구에 대해 pseudo boxes를 생성하고 region-text 쌍을 만듬 -
filtering
pre-trained CLIP 을 사용하여 image-text pairs and region-text pairs의 relevance (관련성)를 평가하고 low-relevance를 가진 pseudo annotation과 image를 filtering ,
추가적으로 NMS를 사용해서 중복 bounding box도 filtering 함
이 방법으로 CC3M 데이터로부터 246k의 이미지와 821k pseudo anntations를 만듬자세한 내용 appendix 참고
4. Experiments
pre-training it on large-scale dataset 에서의 effectiveness와 fine tuning의 성능 평가를 위해
LVIS benchmark and COCO benchmark에서 zero shot 성능 평가
4.1. Implementation Details
MMYOLO, MMDetection 상에서 구현
three variants of YOLO-World : small, medium, large
open-source CLIP 의 pretrained weight을 text encoder로 활용
속도 측정 : NVIDIA V100 GPU without extra acceleration mechanisms, e.g., FP16 or TensorRT
4.2. Pre-training
Experimental Setup.
pre-training stage
- optimizer : AdamW
- lr0 : 2e-3, weight decay : 0.05
- pretrained 100epoch with 32 v100 total bs 512
- data aug : follow yolov8 : color augmentation, random affine, random flip, and mosaic with 4 images for data augmentation.
- text encoder : frozen during pre-training
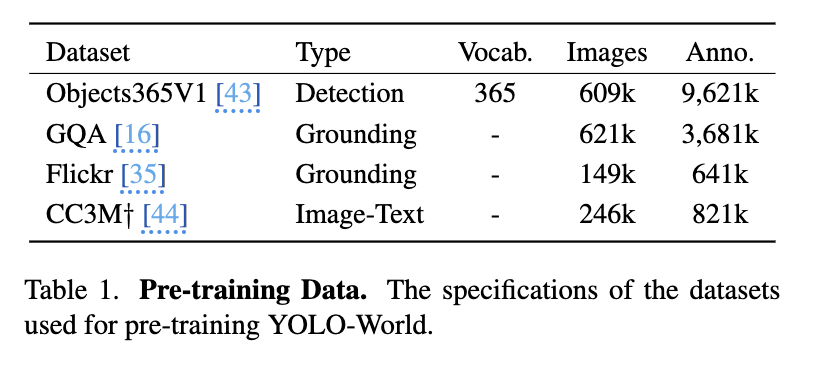
- data: 아래 표에 표시된 데이터+pseudo labeled CC3M
zero shot evaluation
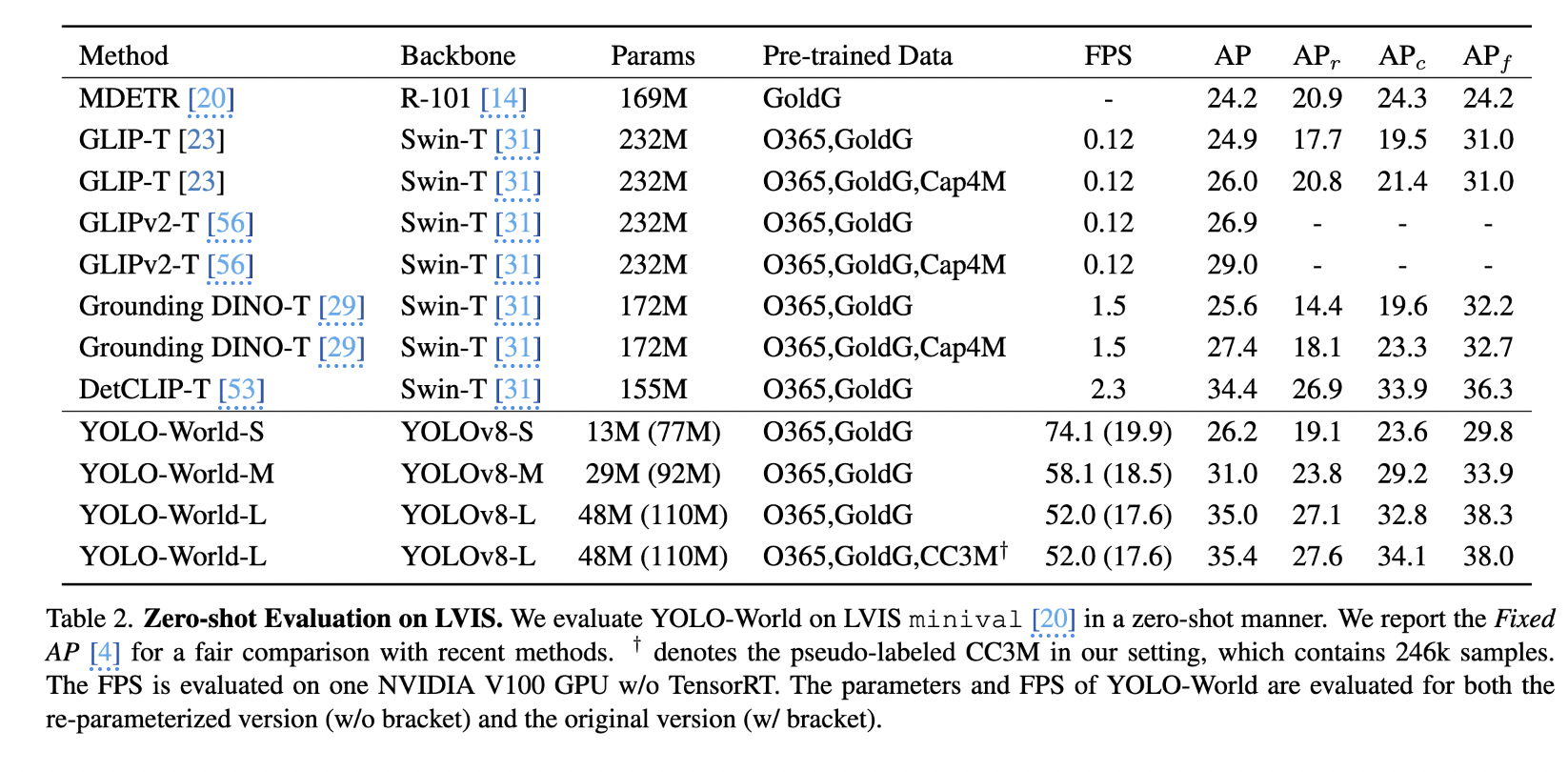
LVIS benchmark에서의 최근 SOTA 연구들 : Groudning DINO, DetCLIP, DetCLIPv2, GLIPv2 과 비교
The experimental results also demonstrate that small models, e.g., YOLO-World-S with 13M parameters, can be used for vision-language pre-training and obtain strong open-vocabulary capabilities.
4.4. Fine-tuning YOLO-World
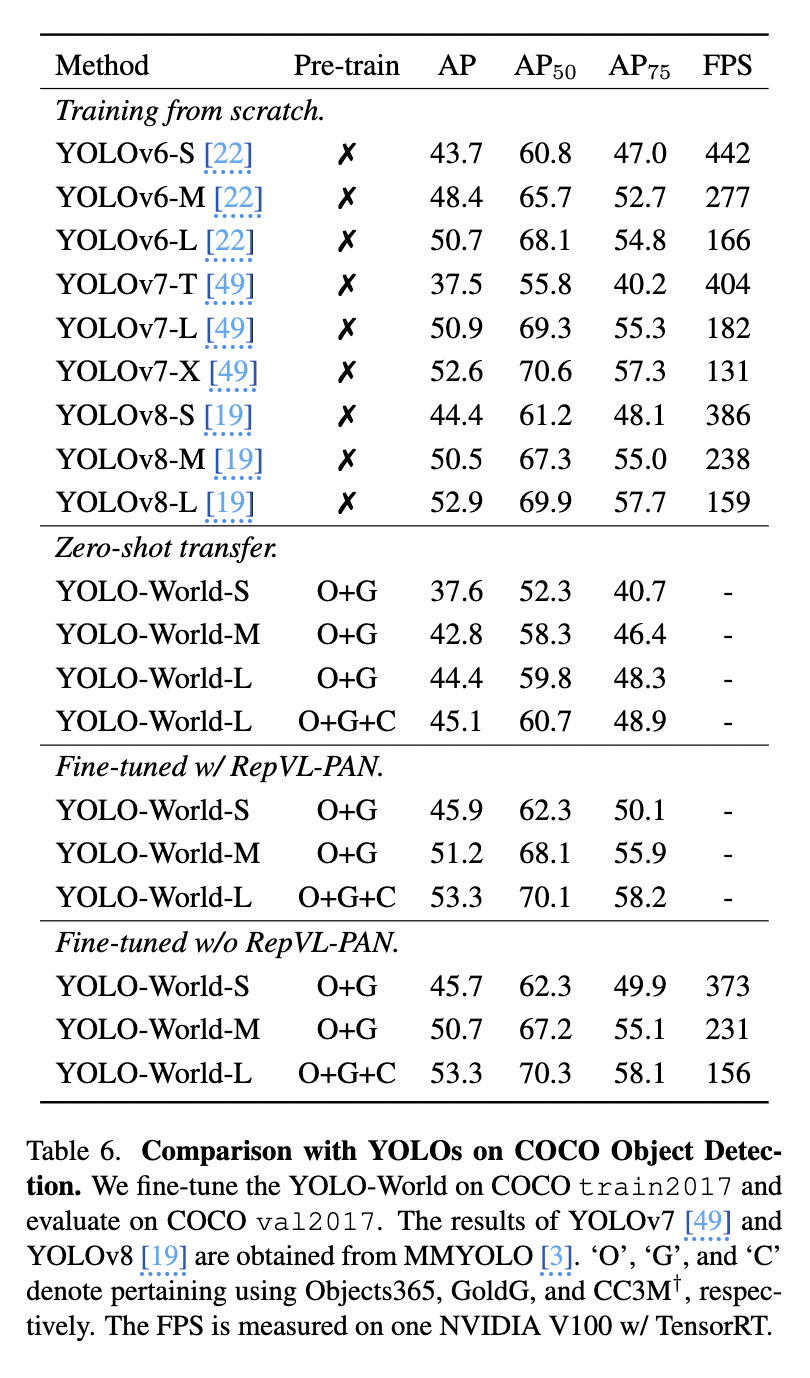
pre-training 효과를 보기 위해 COCO dataset and LVIS dataset을 fine tuning 시켜 성능 확인 , 자세한 training setup 논문 참고
coco dataset fine tuning 할 때는 RepVL-PAN 제거했음 : COCO 데이터 세트의 vocabulary 크기가 작다는 점을 고려하여 TensorRT를 사용한 추가 가속화를 하기 위해서
yolo-world large 모델이 이전 yolo 시리즈보다 더 나은 성능을 보임
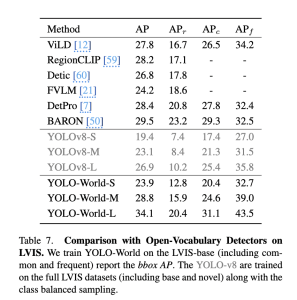
5. Conclusion
open-vocabulary capability를 real world application에서 활용하기 위해 real time 추론과 efficiency 향상을 목적으로 한 논문
- RepVL-PAN을 통해 기존의 yolo 를 vision-languge yolo로 확장했고
- 효과적인 pre-training scheme을 제안함.
- 실험을 통해 소형 모델에 대한 vision-language pre-training의 효과를 보였음
4.3 Ablation Experiments 논문 참고 - pretraining yolo-world의 성능, proposed RepVL-PAN 의 성능, 다른 text encoder를 사용했을 때의 성능비교
4.4 Open-Vocabulary Instance Segmentation 논문 참고
4.6. Visualizations 논문 참고
데모 사용해보기
DEMO : https://huggingface.co/spaces/stevengrove/YOLO-World
인풋으로 이미지와 검출하고자 하는 객체를 prompt로 넣으면 됨
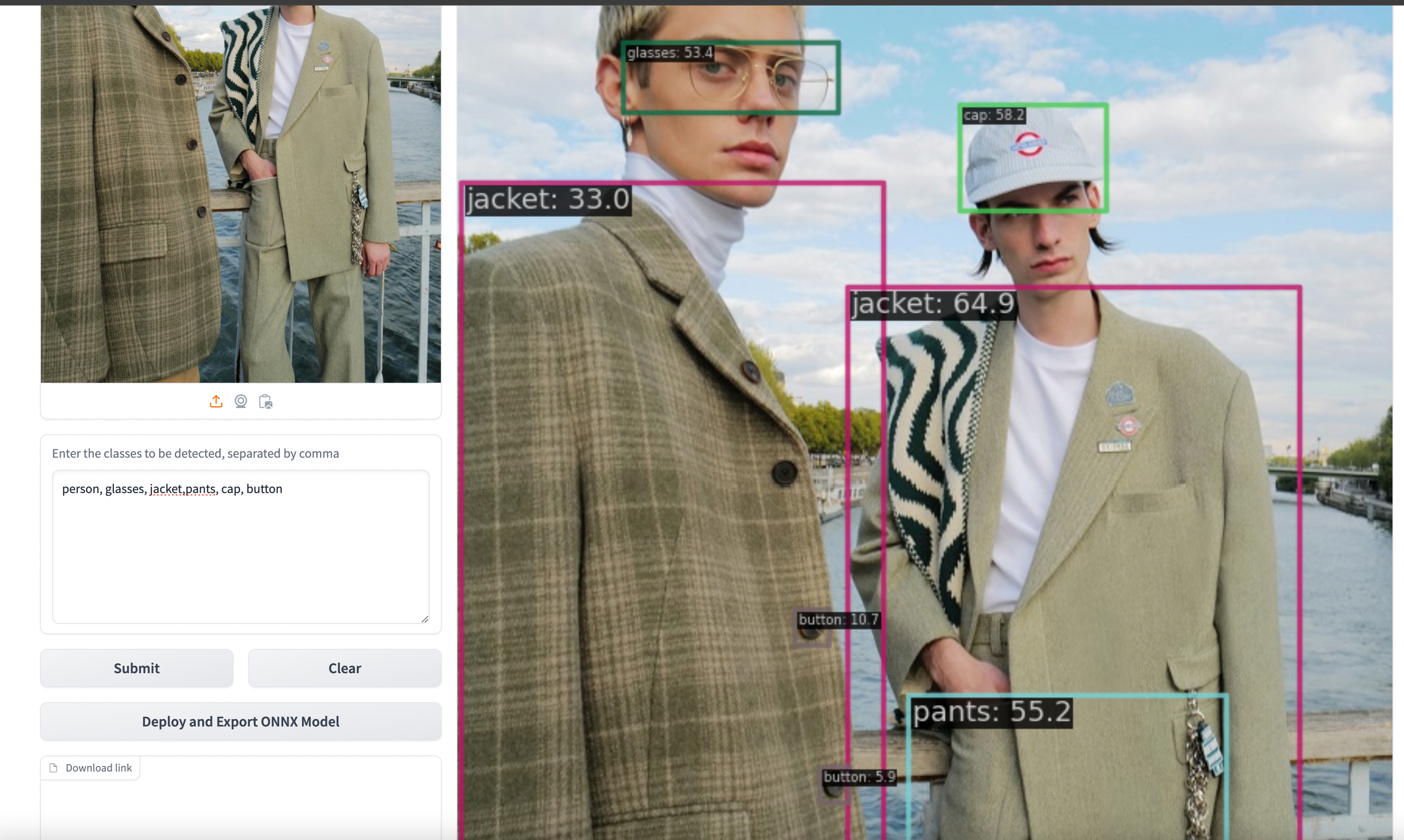
단추까지 잡는 모습,,,
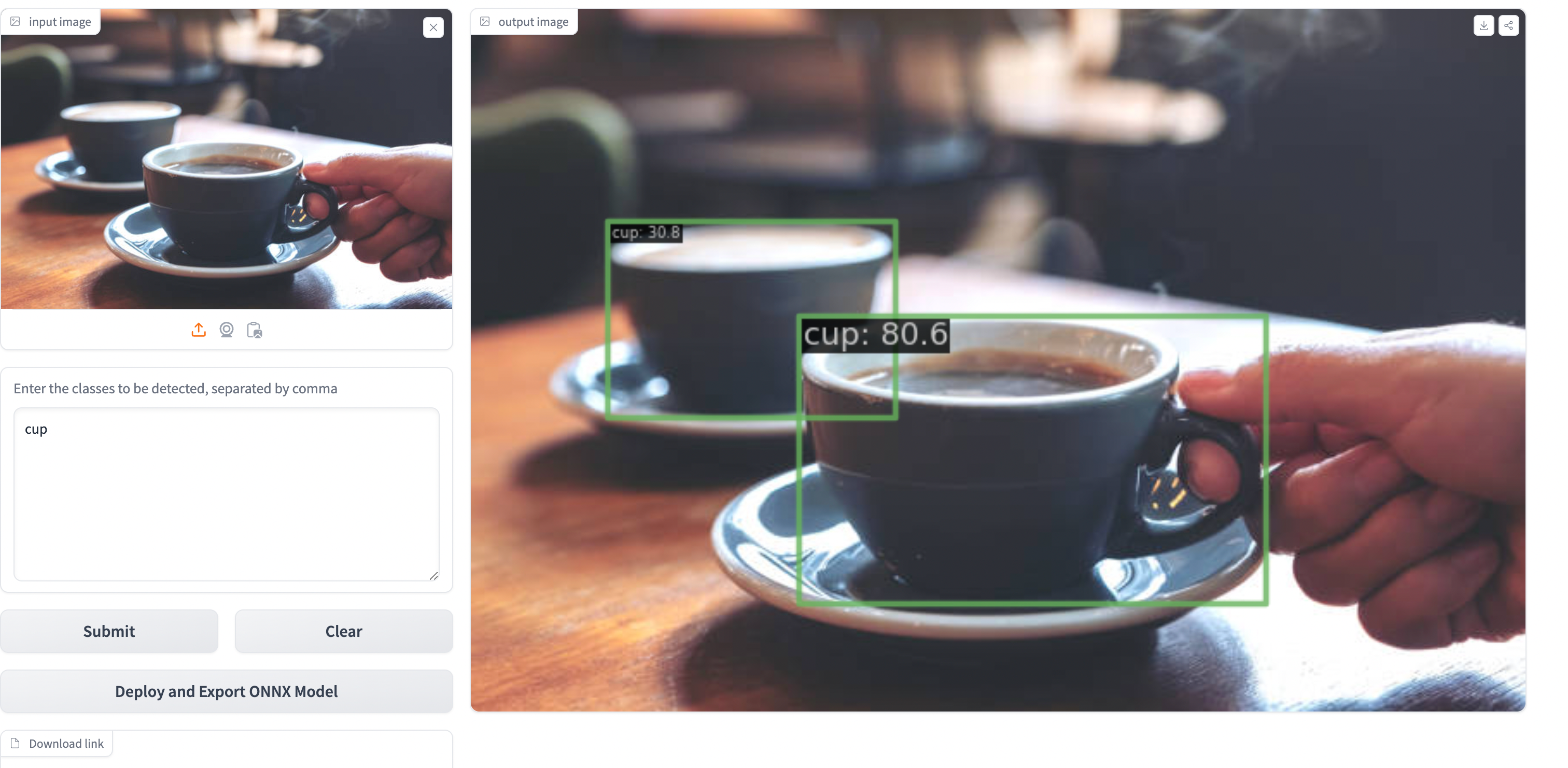

멀티모달로 학습이 되어서 같은 이미지를 넣어도 prompt를 바꿔서 넣으면 내가 검출하고자 하는 디테일한 객체를 조절가능
cup을 prompt로 넣었을 때는 이미지 안의 모든 컵을 검출하지만, 이미지 안에서 핵심이 되는 컵을 찾고자 하는 prompt로 넣었을 때는 이미지의 앞에 위치한 컵 하나만 검출하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
멀티모달 짱짱맨
