Try to solve problems in JavaScript, Python, and Java.
This is TIL(memo of key learnings) for solving problems in these languages,
but mostly python.
Solved Problems 📝
241217
Key Learnings 🤔
what is an Anagram?
an anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the characters of another word or phrase.
"listen" is an anagram of "silent."
- use all character exactly Once: every original character must appear exactly once in the rearranged word.
- strings(trimmed) have the same length: after removing spaces and punctuation, the lengths of the two strings must match.
approaches to solve anagram problems with Python.
with Counter in python: https://docs.python.org/3/library/collections.html#collections.Counter
Approach A. Check Character Frequencies
Approach B. Compare Frequency Counters
approach A: Check Character Frequencies
- length check: If the lengths of the strings are not the same, return False immediately.
- create a frequency object: use collections.Counter module for create a frequency counter for the original string.

- compare with target string: iterate over the target string and check if each character’s frequency matches the original.
why String is iterable in python?
Strings are iterable in Python because they are sequences of characters.
any object is considered iterable if it:
- implements the
__iter__method - implements the
__getitem__method for accessing elements by index.
approach B: Compare Frequency Counters
use Counter to count the character frequencies for both the original and target strings.
- compare the two Counter objects directly using the == operator.
why does counter(originString) == Counter(targetString) work?
The == operator checks for equality of content, not memory location.
Two Counter objects are considered equal if they contain the exact same counts for all elements, regardless of order.
types of iterables in python
- sequence types: Strings, Lists, Tuples, Ranges (support indexing)
- set types: Sets, Frozen Sets (unordered collections)
- dictionaries: iterate over keys by default, .keys(), .values(), .items().
- generator objects: created by generator functions (using yield), generator expressions.
- file objects
- custom Iterables: objects that implement
__iter__or__getitem__method. - iterators
how to accessing characters in a string in java
unlike python & js, java does not support indexing with square brackets [index] for strings.

👉 java doesn’t allow operator overloading. instead, use the charAt() method
String example = "listen";
char firstChar = example.charAt(0); // ljava's HashMap vs js's Map
| Functionality | Java HashMap | JavaScript Map |
|---|---|---|
| Get | .get(key) .getOrDefault(key, defaultValue) | .get(key) |
| Insert/Update | .put(key, value) | .set(key, value) |
| Check for Keys | .containsKey(key) | .has(key) |
| Clear | .clear() | .clear() |
| Size | .size() (method) | .size (access property) |
| Iterate | for (Map.Entry<Key, Value> entry : map.entrySet()) | for (let [key, value] of map) |
-
javaScript
Mapallows method chaining, simplifies multiple operations:map.set('key1', 'value1').set('key2', 'value2'); -
javaScript
Mapcan be initialized directly during declaration. but javaHashMaprequires using.put()after object creation.// js const map = new Map([['key1', 'value1'], ['key2', 'value2']]);// java HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("key1", "value1"); map.put("key2", "value2"); -
javaScript
Mappreserves the insertion order of keys, whereas JavaHashMapdoes not. (useLinkedHashMapin java for ordered HashMap)
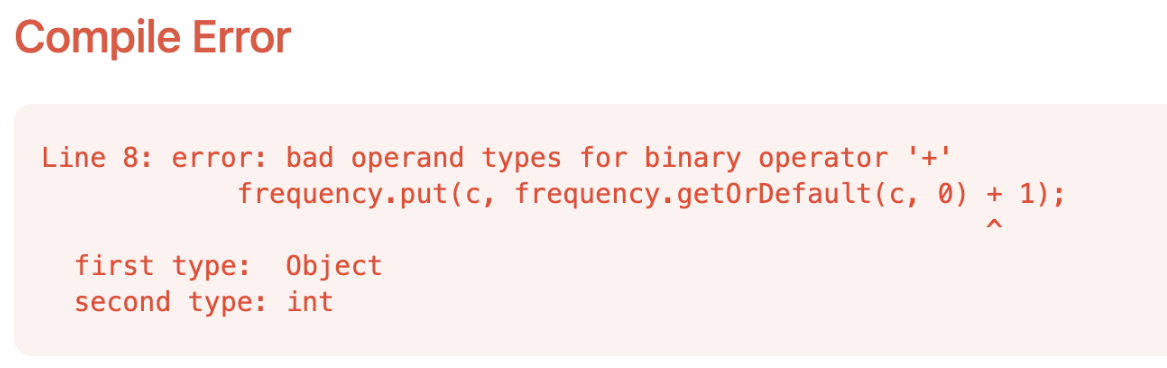
using HashMap with Generics in java
specify the key and value types when declaring a HashMap to avoid type errors:
HashMap<Character, Integer> frequency = new HashMap<>();