
Chapter 6. Proxies
(해석 또는 이해가 잘못된 부분이 있다면 댓글로 편하게 알려주세요.)
❤️ 원문 번역 ❤️
Proxy Hierarchies
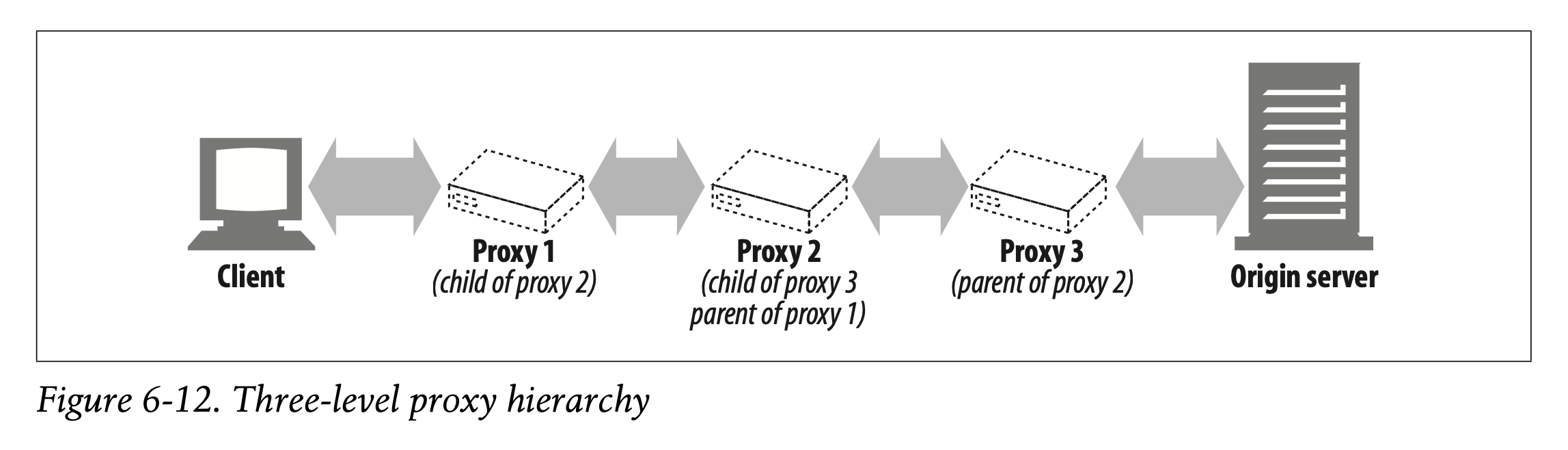
Proxies can be cascaded in chains called proxy hierarchies. In a proxy hierarchy, messages are passed from proxy to proxy until they eventually reach the origin server (and then are passed back through the proxies to the client), as shown in Figure 6-12.
-
프록시는 프록시 계층이라고 불리는 체인에 폭포처럼 연결될 수 있습니다.
-
프록시 계층에서 메시지는 Figure 6-12처럼 origin 서버에 최종적으로 도착할 때까지 프록시에서 프록시로 전달됩니다.
Proxy servers in a proxy hierarchy are assigned parent and child relationships. The next inbound proxy (closer to the server) is called the parent, and the next outbound proxy (closer to the client) is called the child. In Figure 6-12, proxy 1 is the child proxy of proxy 2. Likewise, proxy 2 is the child proxy of proxy 3, and proxy 3 is the parent proxy of proxy 2.
-
프록시 계층의 프록시 서버에는 부모와 자식 관계를 할당합니다.
-
다음 인바운드 프록시(서버 쪽에 가까운 프록시)를 부모, 다음 아웃바운드 프록시(클라이언트 쪽에 가까운 프록시)를 자식으로 정의합니다.
-
Figure 6-12에서 프록시 1은 프록시 2의 자식 프록시입니다.
-
마찬가지로 프록시 2는 프록시 3의 자식 프록시이고, 프록시 3은 프록시 2의 부모 프록시입니다.
Proxy Hierarchy Content Routing
The proxy hierarchy in Figure 6-12 is static—proxy 1 always forwards messages to proxy 2, and proxy 2 always forwards messages to proxy 3. However, hierarchies do not have to be static. A proxy server can forward messages to a varied and changing set of proxy servers and origin servers, based on many factors.
-
Figure 6-12의 프록시 계층은 정적입니다. 프록시 1은 항상 프록시 2에 메시지를 전송하고, 프록시 2는 항상 프록시 3에 메시지를 전송합니다.
-
하지만 계층이 항상 정적인 것은 아닙니다.
-
프록시 서버는 다양한 요소를 바탕으로 다양하고 변화하는 origin 서버와 프록시 서버 집합으로 메시지를 전송할 수 있습니다
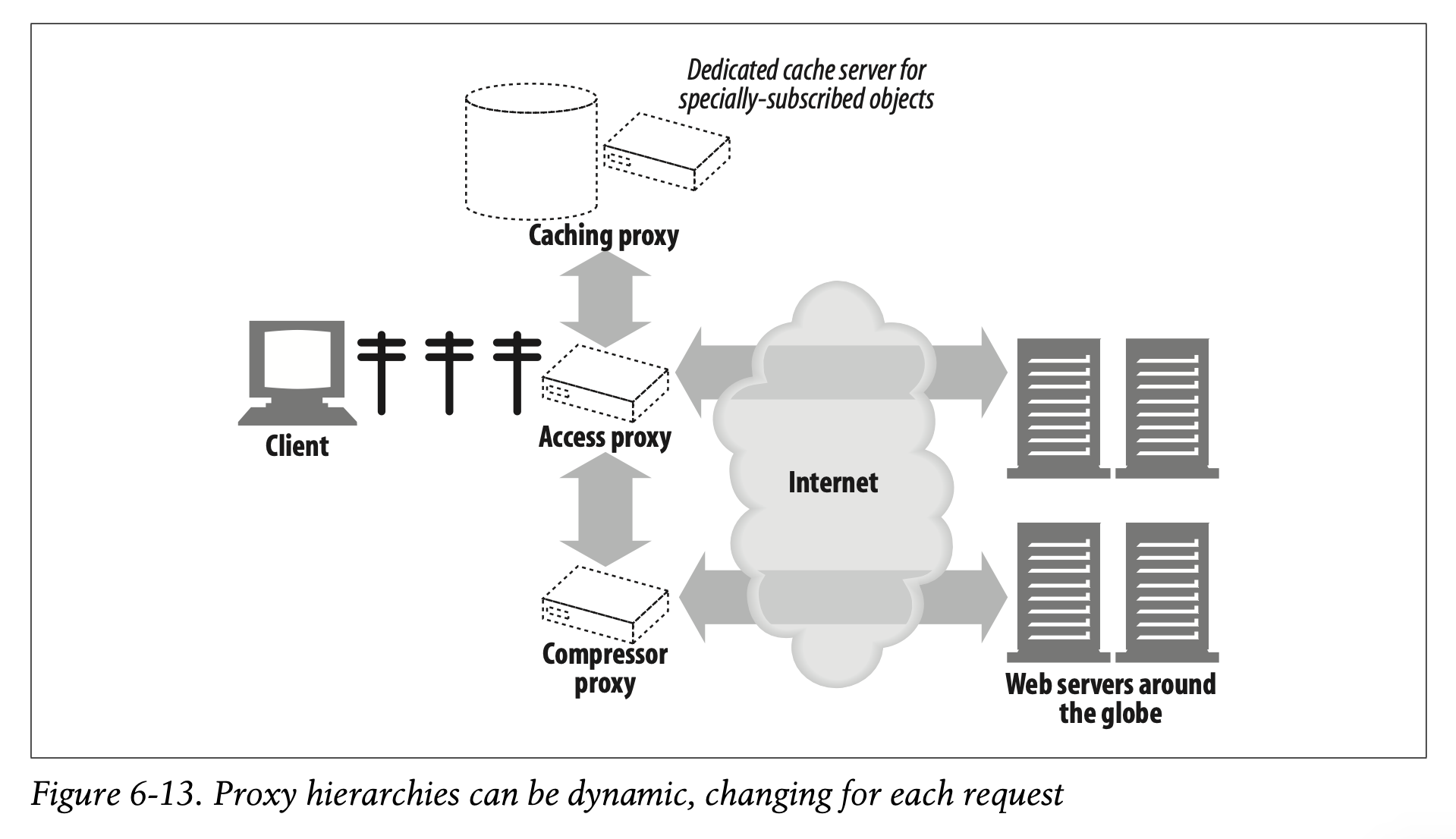
For example, in Figure 6-13, the access proxy routes to parent proxies or origin servers in different circumstances:
- If the requested object belongs to a web server that has paid for content distribution, the proxy could route the request to a nearby cache server that would either return the cached object or fetch it if it wasn’t available.
- If the request was for a particular type of image,the access proxy might route the request to a dedicated compression proxy that would fetch the image and then compress it, so it would download faster across a slow modem to the client.
-
예를 들어 Figure 6-13에서 액세스 프록시는 상황에 따라 부모 프록시나 origin 서버로 라우팅합니다.
-
만약 요청받은 객체가 콘텐츠 배포 비용을 지불한 웹 서버에 속해 있다면, 프록시는 요청을 인근의 cache 서버로 라우팅하여 캐싱된 객체를 반환하거나 이 객체가 이용 불가능하다면 새로 불러옵니다.
-
만약 요청이 특정한 타입의 이미지에 대한 것이라면, 액세스 프록시는 전용 압축 프록시에 요청을 라우팅할 수도 있습니다. 압축 프록시는 이미지를 불러온 후 압축하여 느린 모뎀을 통해 클라이언트로 빠르게 다운로드할 수 있게 합니다.
Here are a few other examples of dynamic parent selection:
- Dynamic Parent Selection의 예시에는 다음과 같은 것이 있습니다.
Load balancing
A child proxy might pick a parent proxy based on the current level of workload on the parents, to spread the load around.
- Load Balancing : 자식 프록시가 부하를 분산하기 위해 현재 부모의 부하 정도를 바탕으로 부모 프록시를 선택할 수 있습니다.
Geographic proximity routing
A child proxy might select a parent responsible for the origin server’s geographic region.
- Geographic Proximity Routing : 자식 프록시가 origin 서버의 지리적 영역을 담당하는 부모를 선택할 수 있습니다.
(지리적 근접성을 기반으로 효율적인 경로를 선택하는 방식)
Protocol/type routing
A child proxy might route to different parents and origin servers based on the URI. Certain types of URIs might cause the requests to be transported through special proxy servers, for special protocol handling.
-
Protocol/type Routing : 자식 프록시가 URI를 바탕으로 서로 다른 부모와 origin 서버에 라우팅할 수 있습니다.
-
어떤 URI는 특수한 프로토콜 핸들링을 위해 특수한 프록시 서버를 통해 요청이 전달될 수 있게 합니다.
Subscription-based routing
If publishers have paid extra money for high-performance service, their URIs might be routed to large caches or compression engines to improve performance.
- Subscription-based Routing : 만약 배포자가 고성능 서비스를 위해 추가 비용을 지불했다면, 그들의 URI는 큰 캐시나 성능 향상을 위한 압축 엔진으로 라우팅될 수 있습니다.
Dynamic parenting routing logic is implemented differently in different products, including configuration files, scripting languages, and dynamic executable plug-ins.
- 구성 파일, 스크립트 언어, 동적으로 실행 가능한 플러그인을 포함하여 Dynamic Parenting 라우팅 로직은 장치마다 다르게 구현됩니다.
🧡 요약 정리 🧡
Proxy Hierarchies
- 인바운드 프록시(부모 프록시) : 프록시 계층에서 서버 쪽에 가까운 프록시
- 아웃바운드 프록시(자식 프록시) : 프록시 계층에서 클라이언트 쪽에 가까운 프록시
Dynamic Parent Selection
- Load Balancing : 아웃바운드 프록시가 인바운드 프록시의 부하 정도를 바탕으로 인바운드 프록시를 선택하여 라우팅
- Geographic Proximity Routing : 아웃바운드 프록시가 지리적 근접성을 기반으로 인바운드 프록시를 선택하여 라우팅
- Protocol/type Routing : 아웃바운드 프록시가 URI를 바탕으로 인바운드 프록시를 선택하여 라우팅
- Subscription-based Routing : 리소스 공급자가 추가 비용을 지불했을 때 큰 캐시나 성능 향상을 위한 엔진으로 라우팅
💛 감상 💛
- 글은 4월 7일에 올려놓고 요약 정리를 4월 10일에 하는 게... 저도 참 게으르다는 생각이 드네요. 앞으로는 미루지 않고 열심히 정리하겠습니다.
