
Chapter 12. Basic Authentication
(해석 또는 이해가 잘못된 부분이 있다면 댓글로 편하게 알려주세요.)
✏️ 원문 번역
Basic Authentication
Basic authentication is the most prevalent HTTP authentication protocol. Almost every major client and server implements basic authentication. Basic authentication was originally described in the HTTP/1.0 specification, but it has since been relocated into RFC 2617, which details HTTP authentication.
-
Basic Authentication은 가장 널리 사용되는 HTTP 인증 프로토콜입니다.
-
대부분의 주요한 클라이언트와 서버가 Basic Authentication을 구현하고 있습니다.
-
Basic Authentication이 처음 소개된 것은 HTTP/1.0 명세입니다.
-
하지만 HTTP 인증에 관한 상세 내용은 RFC 2617로 이전되었습니다.
In basic authentication, a web server can refuse a transaction, challenging the client for a valid username and password. The server initiates the authentication challenge by returning a 401 status code instead of 200 and specifies the security realm being accessed with the WWW-Authenticate response header. When the browser receives the challenge, it opens a dialog box requesting the username and password for this realm. The username and password are sent back to the server in a slightly scrambled format inside an Authorization request header.
-
Basic Authentication에서 웹 서버는 클라이언트에게 유효한 username과 password를 요청함으로써 트랜잭션을 거절할 수 있습니다.
-
서버는 접근해야 하는 보안 영역을 WWW-Authenticate 응답 헤더에 작성한 후 200 대신 401 상태 코드를 반환하여 인증 Challenge를 초기화합니다.
-
브라우저가 Challenge를 받으면 해당 영역에 대한 username과 password를 요청하는 다이얼로그 박스를 실행합니다.
-
username과 password는 요청 헤더 내에서 뒤섞인 채로 Authorization 요청 헤더에 실려 서버로 반환됩니다.
Basic Authentication Example
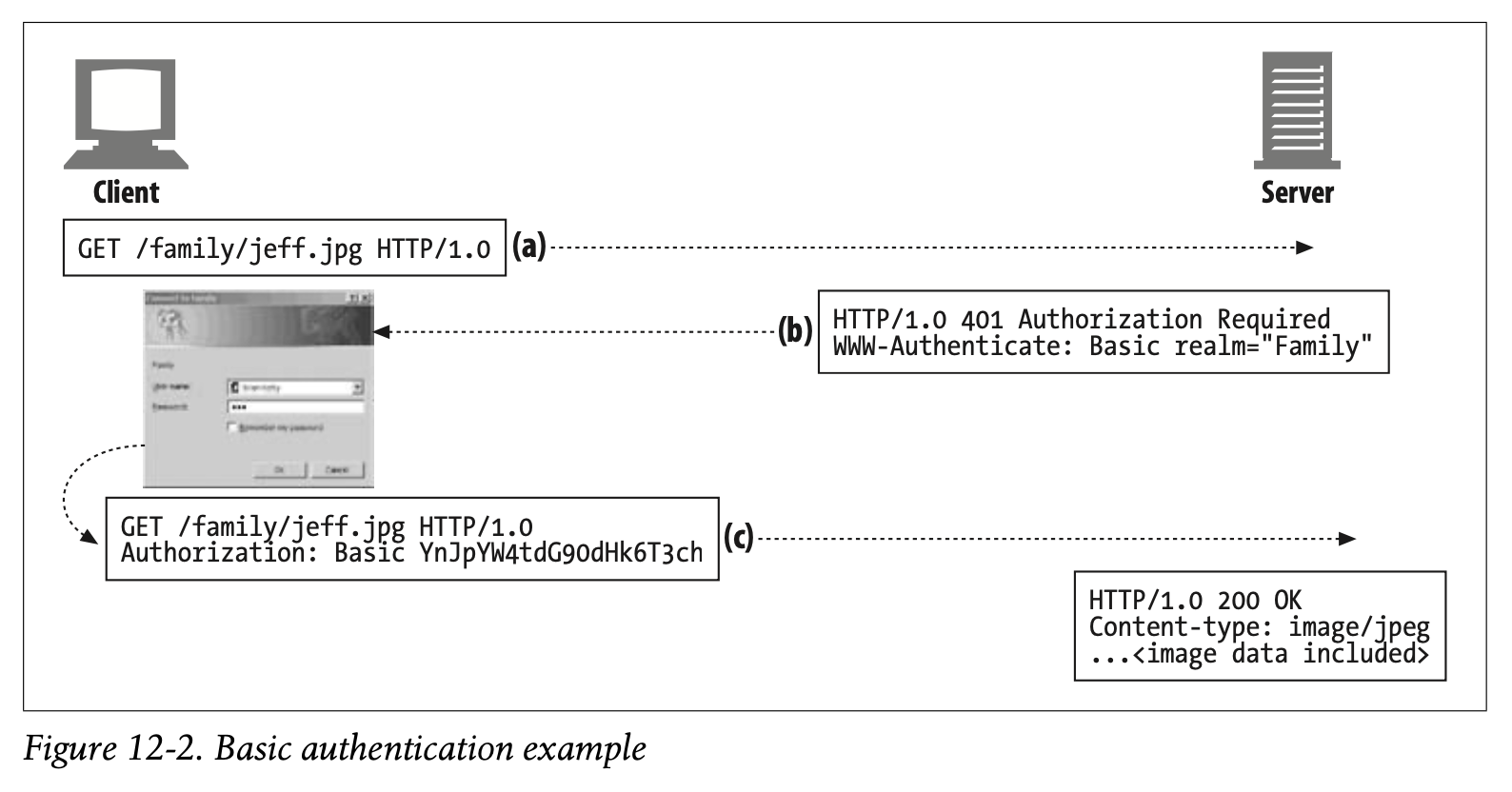
Figure12-2, earlier in this chapter, showed a detailed example of basic authentication:
• In Figure12-2a, a user requests the personal family photo /family/jeff.jpg.
• In Figure12-2b, the server sends back a 401 Authorization Required password challenge for the personal family photo, along with the WWW-Authenticate header. The header requests basic authentication for the realm namedFamily.
• In Figure12-2c, the browser receives the 401 challenge and pops open a dialog box asking for the username and password for the Family realm. When the user enters the username and password, the browser joins them with a colon, sencodes them into a “scrambled” base-64 representation (discussed in the next section), and sends them back in the Authorization header.
• In Figure 12-2d, the server decodes the username and password, verifies that they are correct, and returns the requested document in an HTTP 200 OK message.
-
앞서 등장한 Figure 12-2에서 Basic Authentication의 과정을 설명하였습니다.
-
Figure 12-2a에서 사용자는 개인적인 가족 사진인 /family/jeff.jpg에 대한 요청을 전송합니다.
-
Figure 12-2b에서 서버는 개인적인 가족 사진에 대한 비밀번호 요청을 수행하기 위해 WWW-Authenticate 헤더를 포함하여 401 Authorization Required를 반환합니다. 헤더는 Family로 명명된 영역에 대한 Basic Authentication을 요청합니다.
-
Figure 12-2c에서 브라우저는 401 Challenge를 받아 Family 영역에 대한 username과 password를 요청하는 다이얼로그 박스를 실행합니다. 사용자가 username과 password를 입력하면 브라우저는 콜론과 함께 스크램블된 Base-64 표현으로 인코딩하여 Authorization 헤더로 반환합니다.
-
Figure 12-2d에서 서버는 username과 password를 디코딩하여 신원 정보가 일치하는지 검증합니다. 그리고 요청받은 문서를 HTTP 200 OK 메시지에 실어 전달합니다.
The HTTP basic authentication WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers are summarized in Table 12-2.
- HTTP Basic Authentication의 WWW-Authenticate 헤더와 Authorization 헤더에 대한 설명은 Table 12-2에서 확인할 수 있습니다.

Note that the basic authentication protocol does not make use of the Authentication-Info header we showed in Table 12-1.
- Basic Authentication 프로토콜은 Tablel 12-1에 나타난 Authentication-Info 헤더를 사용하지 않는다는 점에 유의합니다.
Base-64 Username/Password Encoding
HTTP basic authentication packs the username and password together (separated by a colon), and encodes them using the base-64 encoding method. If you don’t know what base-64 encoding is, don’t worry. You don’t need to know much about it, and if you are curious, you can read all about it in Appendix E. In a nutshell, base-64 encoding takes a sequence of 8-bit bytes and breaks the sequence of bits into 6-bit chunks. Each 6-bit piece is used to pick a character in a special 64-character alphabet, consisting mostly of letters and numbers.
-
HTTP Basic Authentication은 username과 password를 Base-64 인코딩 기법을 사용한 후 콜론으로 구분하여 함께 전송합니다.
-
Base-64 인코딩이 무엇인지 알지 못하더라도 걱정할 필요는 없습니다.
-
Base-64에 대해 자세히 알 필요는 없습니다.
-
그래도 궁금하시다면 Appendix E의 내용을 참조해주시기 바랍니다.
-
간단히 말해 Base-64 인코딩은 8비트 바이트 시퀀스를 6비트 청크로 분할하는 과정입니다.
-
각각의 6비트 조각은 문자와 숫자로 구성된 특수한 64자의 알파벳 문자를 선택하는 데 사용됩니다.
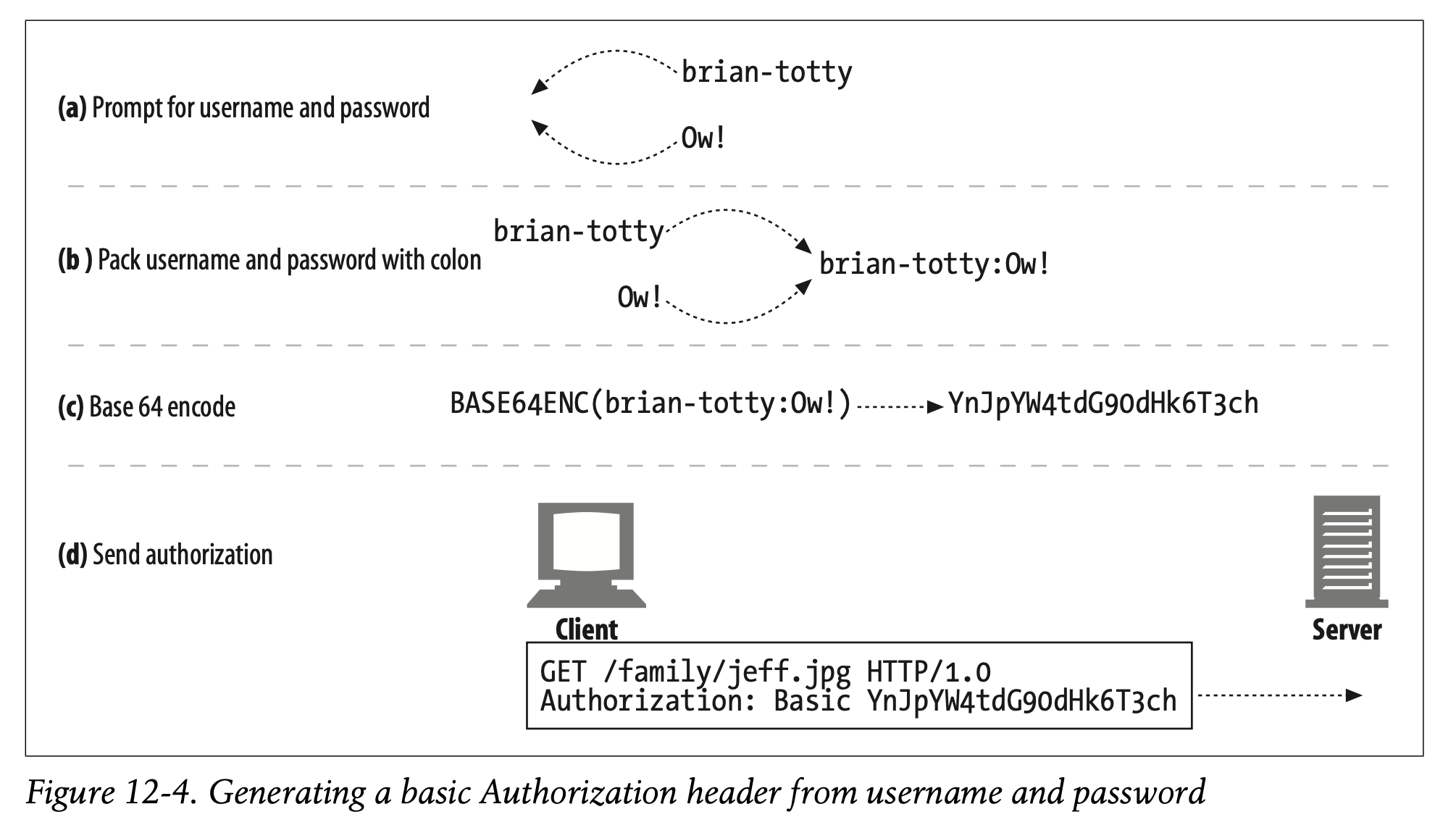
Figure 12-4 shows an example of using base-64 encoding for basic authentication. Here, the username is “brian-totty” and the password is “Ow!”. The browser joins the username and password with a colon, yielding the packed string “brian-totty:Ow!”. This string is then base 64–encoded into this mouthful: “YnJpYW4tdG90dHk6T3ch”.
-
Figure 12-4는 Base-64 인코딩을 사용하여 Basic Authentication을 수행한 예시를 나타냅니다.
-
username은 "brian-totty"이며 password는 "Ow!"입니다.
-
브라우저는 username과 password를 콜론으로 구분하여 "brian-totty:Ow!"와 같은 압축된 문자열을 생성합니다.
-
이 문자열은 Base-64로 인코딩되어 "YnJpYW4tdG90dHk6T3ch"로 표현됩니다.
Base-64 encoding was invented to take strings of binary, text, and international character data (which caused problems on some systems) and convert them temporarily into a portable alphabet for transmission. The original strings could then be decoded on the remote end without fear of transmission corruption.
-
Base-64 인코딩은 이진 문자열, 텍스트 문자열, 국제 문자 데이터 문자열(일부 시스템에서 문제를 야기) 등을 전송 가능한 알파벳 형태로 임시 변환하기 위해 고안되었습니다.
-
원본 문자열은 전송 과정에서 손상을 걱정할 필요없이 원격 서버의 끝에서 복호화할 수 있습니다.
Base-64 encoding can be useful for usernames and passwords that contain international characters or other characters that are illegal in HTTP headers (such as quotation marks, colons, and carriage returns). Also, because base-64 encoding trivially scrambles the username and password, it can help prevent administrators from accidentally viewing usernames and passwords while administering servers and networks.
-
Base-64 인코딩은 국제 문자나 HTTP 헤더에 허용되지 않는 문자(따옴표, 콜론, CR 등)를 포함하고 있는 username과 password에 유용하게 쓰일 수 있습니다.
-
또한 Base-64 인코딩은 username과 password를 살짝 섞어놓기 때문에 서버와 네트워크를 관리하는 과정에서 관리자에게 username과 password가 노출되는 것을 방지할 수 있습니다.
✏️ 요약
Basic Authentication
: HTTP/1.0에서 소개되어 RFC 2617에서 상세히 설명된 HTTP의 인증 프로토콜
- Challenge : WWW-Authenticate 헤더를 통해 특정 보안 영역에 대한 Basic Authentication 요청 (401 Authorization Required 반환)
- Base-64 Encoding : "username:password" 문자열을 나타내는 8비트 바이트 시퀀스를 6비트 청크로 분할
- HTTP 헤더에 허용되지 않는 문자가 포함된 문자열도 손실/손상 없이 전송 가능
- 관리자에게 username과 password 노출 방지
- Authorization : Authorization 헤더에 인코딩된 인증 정보를 실어 서버에 전달
- 200 OK : 신원 정보 일치 여부를 확인한 서버가 200 OK와 함께 리소스 반환
✏️ 감상
Base-64 인코딩에 대해 자세히 알아보자
Base-64는 8비트의 이진 데이터를 ASCII 영역의 문자열로 변환하는 인코딩 기법이다.
예를 들어 "Man"이라는 글자는 "M", "a", "n"으로 이루어져 있으며 각각의 아스키코드는 "77 = 01001101", "97 = 01100001", "110 = 01101110"이다. 즉 "Man"을 아스키코드로 변환하면 "010011010110000101101110"이다. Base-64는 6비트로 청크를 나누므로 "010011/010110/000101/101110"로 구분된다. 이때 각각의 청크가 나타내는 인덱스 번호는 "19", "22", "5", "46"이다. Base-64 인코딩 표에서 인덱스에 해당하는 문자를 찾아 변환하면 "Man"의 인코딩 결과가 "TWFu"라는 사실을 알 수 있다.
일반적으로 Base-64 인코딩을 사용하는 경우 크기가 약 33% 커지는 경향이 있다. 데이터 크기가 증가함에도 Base-64 인코딩을 사용하는 까닭은 안정성을 위함이다.
위의 사례만 봐도 알 수 있다시피 Base-64는 보안 용도로 사용 가능한 기술이 아니다. 인코딩 결과를 역으로 추적하는 것이 가능하기 때문이다. Basic Authentication의 궁극적인 문제점도 여기에 있다. 아무리 인코딩을 수행하더라도 사용자의 정보가 그대로 헤더에 들어가게 되기 때문이다. 인코딩한 정보가 중요한 정보라면 반드시 TLS를 함께 사용하는 것이 권장되며, 가장 확실한 것은 전달할 내용 자체를 암호화하는 것이다.
