
Chapter 14. Secure HTTP
(해석 또는 이해가 잘못된 부분이 있다면 댓글로 편하게 알려주세요.)
✏️ 원문 번역
Preface
The previous three chapters reviewed features of HTTP that help identify and authenticate users. These techniques work well in a friendly community, but they aren’t strong enough to protect important transactions from a community of motivated and hostile adversaries.
-
이전의 세 챕터에서 사용자를 식별하고 인증하기 위한 HTTP 특성에 대해 살펴 보았습니다.
-
이러한 기술은 우호적인 커뮤니티 내에서 잘 동작하는 한편 적대적인 커뮤니티로부터 중요한 트랜잭션을 보호할 만큼 강력하지는 않습니다.
This chapter presents a more complicated and aggressive technology to secure HTTP transactions from eavesdropping and tampering, using digital cryptography.
- 이번 챕터에서는 디지털 암호화를 통해 감청이나 변조로부터 HTTP 트랜잭션을 보호하기 위한 더 복잡하고 공격적인 기술을 이야기하기하고자 합니다.
Making HTTP Safe
People use web transactions for serious things. Without strong security, people wouldn’t feel comfortable doing online shopping and banking. Without being able to restrict access, companies couldn’t place important documents on web servers. The Web requires a secure form of HTTP.
-
사람들은 중요한 정보를 담은 웹 트랜잭션을 주고받기도 합니다.
-
강력한 보안이 없다면 온라인 쇼핑이나 뱅킹 과정에서 불편함을 느낄 것입니다.
-
접근을 제한하지 않으면 기업은 웹 서버에 중요한 문서를 보관할 수 없습니다.
-
웹은 안전한 형태의 HTTP가 필요합니다.
The previous chapters talked about some lightweight ways of providing authentication (basic and digest authentication) and message integrity (digest qop=“auth-int”). These schemes are good for many purposes, but they may not be strong enough for large purchases, bank transactions, or access to confidential data. For these more serious transactions, we combine HTTP with digital encryption technology.
-
이전 챕터에서는 주어진 인증(Basic Authentication & Digest Authentication)과 메시지 무결성(digest qop="auth-int")을 제공하는 몇 가지 단순한 기법에 대해 논의하였습니다.
-
위의 기법은 특정 상황에서 효율적으로 사용되지만 대량 구매, 은행 거래, 기밀 데이터 접근과 같은 상황에서는 충분히 강력하지 않을 수 있습니다.
-
중요한 트랜잭션에 대해서는 HTTP와 디지털 암호화 기술을 결합해야 합니다.
A secure version of HTTP needs to be efficient, portable, easy to administer, and adaptable to the changing world. It also has to meet societal and governmental requirements. We need a technology for HTTP security that provides:
• Server authentication (clients know they’re talking to the real server, not a phony)
• Client authentication (servers know they’re talking to the real user, not a phony)
• Integrity (clients and servers are safe from their data being changed)
• Encryption (clients and servers talk privately without fear of eavesdropping)
• Efficiency (an algorithm fast enough for inexpensive clients and servers to use)
• Ubiquity (protocols are supported by virtually all clients and servers)
• Administrative scalability (instant secure communication for anyone, anywhere)
• Adaptability (supports the best known security methods of the day)
• Social viability (meets the cultural and political needs of the society)
-
보안 HTTP는 효율적이면서도 쉽게 전송되고 관리할 수 있어야 하며, 변화하는 세상에 적응할 수 있어야 합니다.
-
사회적인 요구사항과 정책적인 요구사항을 충족하는 것은 물론입니다.
-
우리는 다음과 같은 기능을 제공하는 HTTP 보안 기술이 필요합니다.
- Server Authentication : 클라이언트가 가짜 서버가 아닌 실제 서버와 통신하고 있다는 사실을 아는 것
- Client Authentication : 서버가 가짜 클라이언트가 아닌 실제 클라이언트가 통신하고 있다는 사실을 아는 것
- Integrity : 클라이언트와 서버가 변화하고 있는 데이터로부터 안전한 것
- Encryption : 클라이언트와 서버가 감청의 우려 없이 사적으로 통신할 수 있는 것
- Efficiency : 저렴한 클라이언트와 서버가 사용할 수 있을 만큼 충분히 빠른 알고리즘을 사용하는 것
- Ubiquity : 모든 클라이언트와 서버에서 프로토콜이 지원되게 하는 것
- Administrative Scalability : 누구와 어디서든 즉시 보안 통신을 할 수 있게 하는 것
- Adaptability : 가장 잘 알려진 보안 메서드를 지원하는 것
- Social Viability : 사회의 문화적, 정책적 요구를 충족하는 것
HTTPS
HTTPS is the most popular secure form of HTTP. It was pioneered by Netscape Communications Corporation and is supported by all major browsers and servers.
-
HTTPS는 가장 보편적으로 사용되는 HTTP 보안 형태입니다.
-
Netscape Communications Corporation에 의해 연구되어 모든 주요 브라우저와 서버에서 지원되고 있습니다.
You can tell if a web page was accessed through HTTPS instead of HTTP, because the URL will start with the scheme https:// instead of http:// (some browsers also display iconic security cues, as shown in Figure 14-1).
-
HTTPS의 URL은 http:// 대신 https://로 시작하기 때문에 HTTP가 아닌 HTTPS를 사용하여 웹 페이지에 접근하고 있는지 알 수 있습니다.
-
일부 브라우저는 Figure 14-1처럼 상징적인 보안 단서를 표시하기도 합니다.

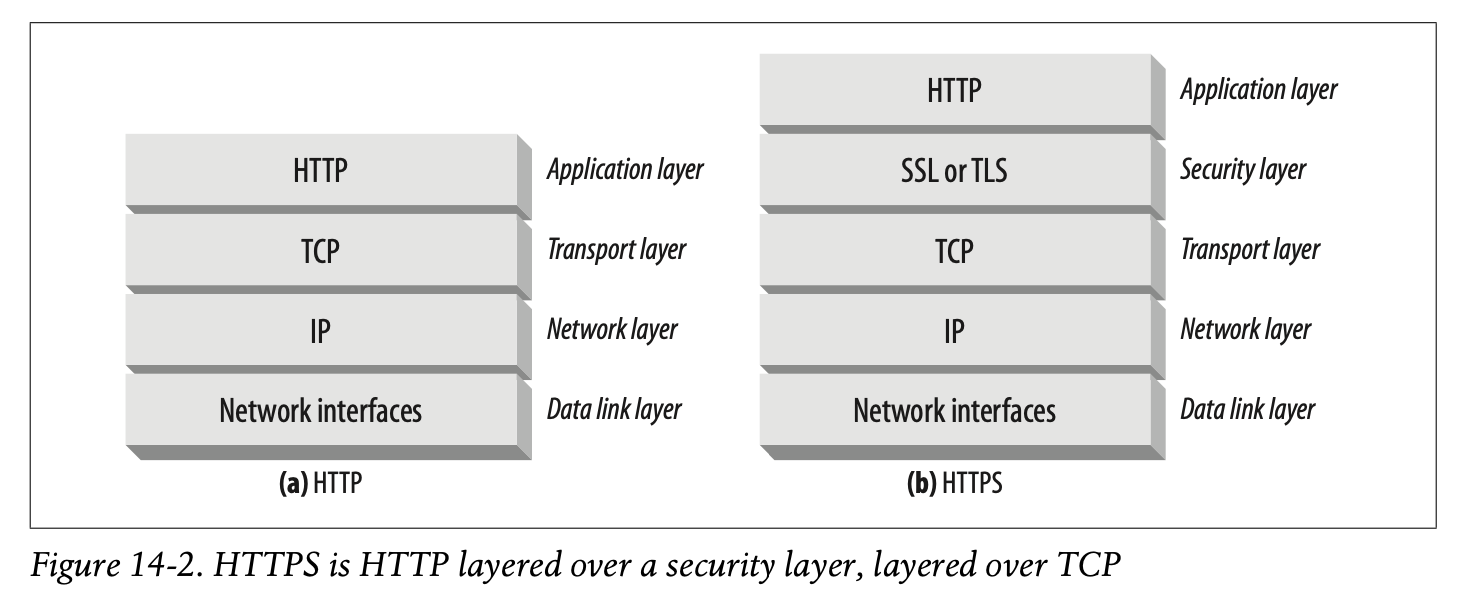
When using HTTPS, all the HTTP request and response data is encrypted before being sent across the network. HTTPS works by providing a transport-level cryptographic security layer—using either the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS)—underneath HTTP (Figure 14-2). Because SSL and TLS are so similar, in this book we use the term “SSL” loosely to represent both SSL and TLS.
-
HTTPS를 사용하면 네트워크로 전송하기 전 모든 HTTP 요청과 응답 데이터가 암호화됩니다.
-
HTTPS는 HTTP 하단에서 Secure Sockets Layer(SSL)나 Transport Layer Security(TLS)를 사용함으로써 Trasnport 레벨의 보안 암호화를 제공합니다. (Figure 14-2)
-
SSL과 TLS는 매우 유사하므로 본 교재에서는 SSL과 TLS를 통틀어 "SSL"이라는 용어로 느슨하게 표현합니다.
Because most of the hard encoding and decoding work happens in the SSL libraries, web clients and servers don’t need to change much of their protocol processing logic to use secure HTTP. For the most part, they simply need to replace TCP input/output calls with SSL calls and add a few other calls to configure and manage the security information.
-
웹 클라이언트와 서버는 보안 HTTP를 사용하기 위해 사용중인 프로토콜의 처리 로직을 구태여 바꾸지 않아도 됩니다.
-
SSL 라이브러리에서 대부분의 하드 인코딩과 디코딩을 수행하기 때문입니다.
-
대부분의 경우 TCP 입출력 호출을 SSL 호출로 변경하고, 보안 정보를 구성하고 관리하기 위한 일부 함수만 추가로 호출함으로써 간단하게 이루어질 수 있습니다.
✏️ 요약
HTTPS
: HTTP와 디지털 암호화 기술을 결합하여 트랜잭션의 감청과 변조를 방지하는 기술
- 중요한 정보를 담은 트랜잭션의 경우 Authentication, Integrity Check만으로 불충분 -> 데이터 자체에 대한 암호화 필요
- Transport 레벨에서 모든 HTTP 요청 및 응답 데이터 암호화
- Secure Sockets Layer(SSL) 혹은 Transport Layer Security (TLS) 사용
- SSL 라이브러리를 통해 데이터 하드 인코딩 및 디코딩 수행
✏️ 감상
SSL vs TLS
SSL과 TLS 모두 Transport Layer 위에서 시스템간 전송중인 데이터를 암호화하기 위한 통신 프로토콜로 알려져 있다. SSL은 네트워크상에서 안전한 통신 채널을 만들기 위한 전통적인 프로토콜이다. 오래된 프로토콜인 만큼 비효율적인 측면도 꽤 많고 암호화 기술의 수준도 높지 않다.
보안 프로토콜의 경우 클라이언트와 서버가 서로를 인증하기 위하여 Handshake를 맺고 암호화 키를 주고받는 절차를 거친다. 이때 TLS는 SSL의 Handshake 절차를 개선하여 연결 설정 과정에서 발생하는 오버헤드를 줄인다. SSL에서 사용하는 MD5와 같은 암호화 알고리즘은 오늘날 슈퍼컴퓨터로 쉽게 collision을 발견할 수 있을 정도로 취약하다. 때문에 TLS는 MD5 대신 더 복잡한 해시 알고리즘을 사용하여 HMAC(메시지 무결성 확인을 위한 코드)을 생성하도록 변경되었다.
+ SSL과 TLS의 동작 과정은 거의 동일하다.
- Handshake : 클라이언트와 서버간 연결 설정 및 세션 생성 (암호화 방식 및 인증 방식 결정)
- 인증서 전송 : 서버가 클라이언트로 자신의 공개 키가 포함된 인증서 전송
- 세션 키 생성 : 실질적인 암호화에 사용할 키 생성
- 데이터 암호화 : 세션 키로 데이터를 암호화하여 전송
- 데이터 무결성 확인 : HMAC을 통해 변조 여부 확인
- 세션 종료 : 클라이언트와 서버 사이의 세션 종료
