버튼 클릭했을 때 코드에서 프래그먼트 추가하기
프래그먼트는 액티비티의 XML 레이아웃에 넣어 화면에 추가하는 방법뿐만 아니라 코드에서 직접 추가하는 것도 가능하다
새로운 프래그먼트를 만들고, 버튼을 눌렀을 때 프래그먼트를 전환하도록 만들어보겠다.
코드는 프래그먼트(1) 에서 이어서 작성한다.
fragment_main.xml 파일을 복사해 fragment_menu.xml을 만든다.
그 후 구분을 위해 fragment_menu.xml의 글자들과 색을 변경한다.

MainFragment.java 파일도 복사해 MenuFragment.java를 만들고,
fragment_menu.xml 파일이 인플레이트 되도록 수정한다.
package org.techtown.samplefragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
public class MenuFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_menu, container, false);
}
}메인 프래그먼트 안의 버튼을 눌렀을 때 메뉴 프래그먼트로 전환되도록 만들어야 한다.
MainFragment.java의 내용을 아래와 같이 수정한다.
public class MainFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
ViewGroup rootView = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, container, false);
Button button = rootView.findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
MainActivity activity = (MainActivity) getActivity();
activity.onFragmentChanged(0);
}
});
return rootView;
}
}메인 프래그먼트 안에 표시되는 최상위 레이아웃은 인플레이션을 통해 참조한 rootView이다.
ViewGroup rootView = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, container, false);이 rootView의 findViewById 메소드를 사용해 레이아웃에 들어 있는 객체를 찾아낼 수 있다.
Button button = rootView.findViewById(R.id.button);다음은 버튼의 onClick 메소드 안이다.
프래그먼트에서 getActivity 메소드를 호출하면 프래그먼트가 올라가 있는 액티비티를 확인할 수 있다.
이를 사용해 메인 프래그먼트가 올라가 있는 MainActivity 객체를 참조한다.
MainActivity activity = (MainActivity) getActivity();그 후 참조한 MainActivity에서 구현한 onFragmentChanged 메소드를 사용해 프래그먼트를 전환한다.
activity.onFragmentChanged(0);프래그먼트를 관리하는 것은 액티비티가 하기 때문에 액티비티에서 프래그먼트를 전환하도록 MainActivity의 메소드를 사용한다.
이 메소드에 대해서는 후술한다.
다음으로 MainActivity.java의 내용을 수정한다.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
MainFragment mainFragment;
MenuFragment menuFragment;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mainFragment = (MainFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.mainFragment);
menuFragment = new MenuFragment();
}
public void onFragmentChanged(int index){
if(index == 0){
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.container, menuFragment).commit();
} else if(index == 1){
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.container, mainFragment).commit();
}
}
}메인 프래그먼트는 activity_main.xml 파일에 추가되어 있으므로 id를 사용해서 찾아야 한다.
하지만 프래그먼트는 뷰가 아니라서 Activity 클래스에 있는 findViewById 메소드를 찾을 수 없다.
대신 프래그먼트를 관리하는 FragmentManager 객체의 findFragmentById 메소드를 사용해서 찾을 수 있다.
메인 액티비티에서 프래그먼트를 다루기 위한 매니저 객체는 getSupportFragmentManager 메소드를 호출하여 참조한다.
메인 프래그먼트는 findFragmentById 메소드를 사용해 찾은 후 변수에 할당한다.
mainFragment = (MainFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.mainFragment);메뉴 프래그먼트는 new 연산자를 사용해 새로운 객체로 만들어 변수에 할당한다.
menuFragment = new MenuFragment();프래그먼트를 전환하는 onFragmentChanged 메소드를 정의한다.
이 메소드로 전달된 값이 0이면 메뉴 프래그먼트로, 1이면 메인 프래그먼트를 표시하도록 하였다.
public void onFragmentChanged(int index){
if(index == 0){
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.container, menuFragment).commit();
} else if(index == 1){
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.container, mainFragment).commit();
}
}FragmentManager 객체의 replace 메소드를 사용해 프래그먼트를 바꿀 수 있다.
replace 메소드로 전달되는 첫 번째 파라미터는 프래그먼트를 담고 있는 레이아웃의 id이다.
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.container, menuFragment).commit();이 프래그먼트 매니저 객체를 사용할 때는 트랜젝션이 사용된다.
프래그먼트 매니저에서 프래그먼트의 추가, 삭제, 교체 등의 작업을 할 때 오류가 생기면 원래대로 돌릴 수 있어야 한다. 이를 위해 트랜잭션 객체를 만들어 실행한다.
트랜젝션 객체는 beginTransaction 메소드를 호출하면 시작되고, commit 메소드를 호출하면 실행된다.
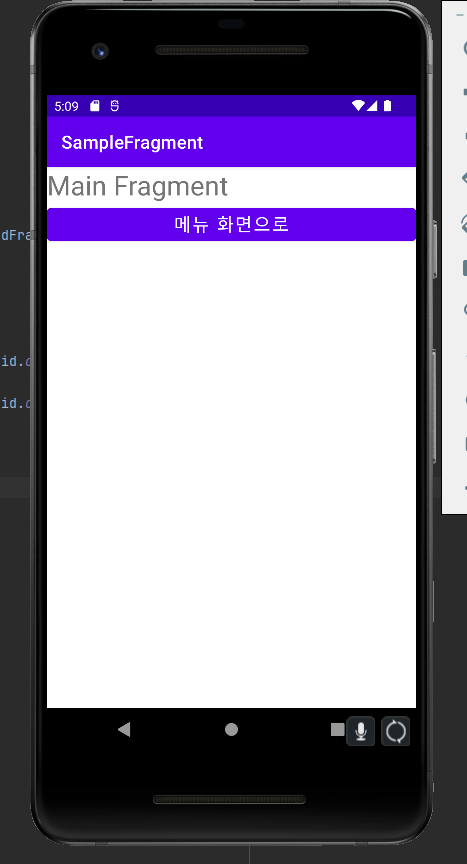
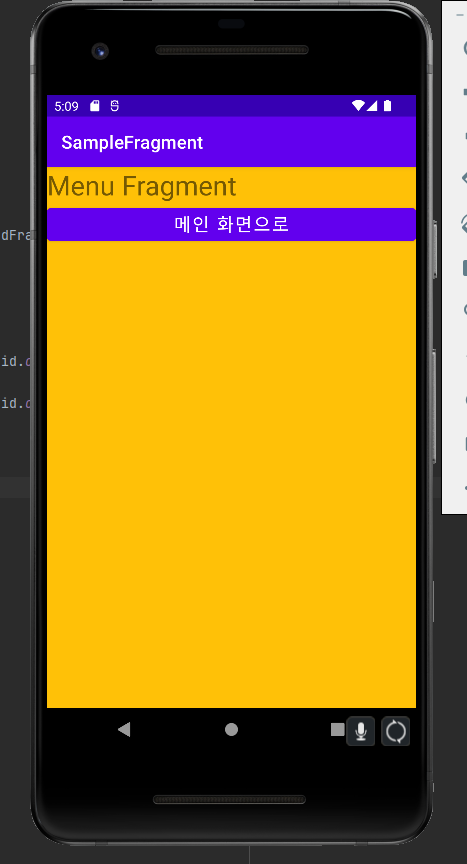
앱을 실행하면 맨 처음에 메인 프래그먼트가 보이고, 버튼을 누르면 메뉴 액티비티로 변경되는것을 확인 할 수 있다.