🥚문제링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/15685
- 구현
- 시뮬레이션
🍳코드
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
arr = [[0]*(101) for _ in range(101)]
dirs = {0: (0, 1), 1: (-1, 0), 2: (0, -1), 3: (1, 0)}
def dragon(g):
dragon_dir = []
while g >= 0:
# dragon_dir가 비어있는 경우 (시작)
if len(dragon_dir) == 0:
dragon_dir.append(d)
# dragon_dir 수정해주기
else:
dragon_dir = next_dragon_dir(dragon_dir)
g -= 1
return dragon_dir
def next_dragon_dir(dragon_dir):
new_dragon_dir = list(reversed(dragon_dir))
for i in range(len(new_dragon_dir)):
if new_dragon_dir[i] == 3:
new_dragon_dir[i] = 0
else:
new_dragon_dir[i] += 1
return dragon_dir + new_dragon_dir
def is_square(r, c):
# r, c에서 →, ↓, ← 방향을 검사했을 때
# 네 방향이 모두 1이면 1 * 1 정사각형의 네 꼭지점이 모두 커브의 일부
count = 1 # 일단 (r, c)가 1이므로 count 1로 시작한다
moves = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1)]
for move in moves:
n_r = r + move[0]
n_c = c + move[1]
if 0 <= n_r < 101 and 0 <= n_c < 101:
if arr[n_r][n_c] == 1:
count += 1
r = n_r
c = n_c
else:
return False
else:
return False
if count == 4:
return True
else:
return False
# x좌표가 arr에서의 col, y좌표가 arr에서의 row임에 유의한다
for _ in range(int(input().strip())):
col, row, d, g = map(int, input().split())
dragon_dir = dragon(g)
# (row, col)에서 시작해서 dragon_dir의 방향들로 이동하며
# arr을 1로 바꾸어간다
# 시작점
arr[row][col] = 1
for direction in dragon_dir:
d_row, d_col = dirs[direction]
n_row = row + d_row
n_col = col + d_col
arr[n_row][n_col] = 1
# update
row = n_row
col = n_col
ans = 0
for r in range(101):
for c in range(101):
if arr[r][c] == 1:
if is_square(r, c):
ans += 1
print(ans)🧂아이디어
구현
⬛ 2차원 리스트에 드래곤커브를 어떻게 표현할 것인가?
- 문제 설명의 '드래곤커브의 끝점에 다음 세대 드래곤 커브 이어 붙히기', '1 x 1 정사각형의 네 꼭짓점이 드래곤 커브의 일부인 것의 개수 출력' ... 등에서 점이 중요함을 알 수 있다!
- 선분은 신경쓰지 말고, 점을 기준으로 표시하면 된다.

- 위와 같은 2차원리스트
arr에 드래곤 커브를 구성하는 점들을 표시한다.
(예시)
⬛ 드래곤 커브의 규칙
- 예제입력 1의
4 1 2 3입력을 예로 들면 - x좌표: 4, y좌표: 2, 시작방향: 1(→), 세대: 3
- (방향)
0: →, 1: ↑, 2: ←, 3: ↓=0: (0, 1), 1: (-1, 0), 2: (0, -1), 3: (1, 0)
- (방향)
- 3세대까지의 이동 방향을 살펴보면 아래와 같다.
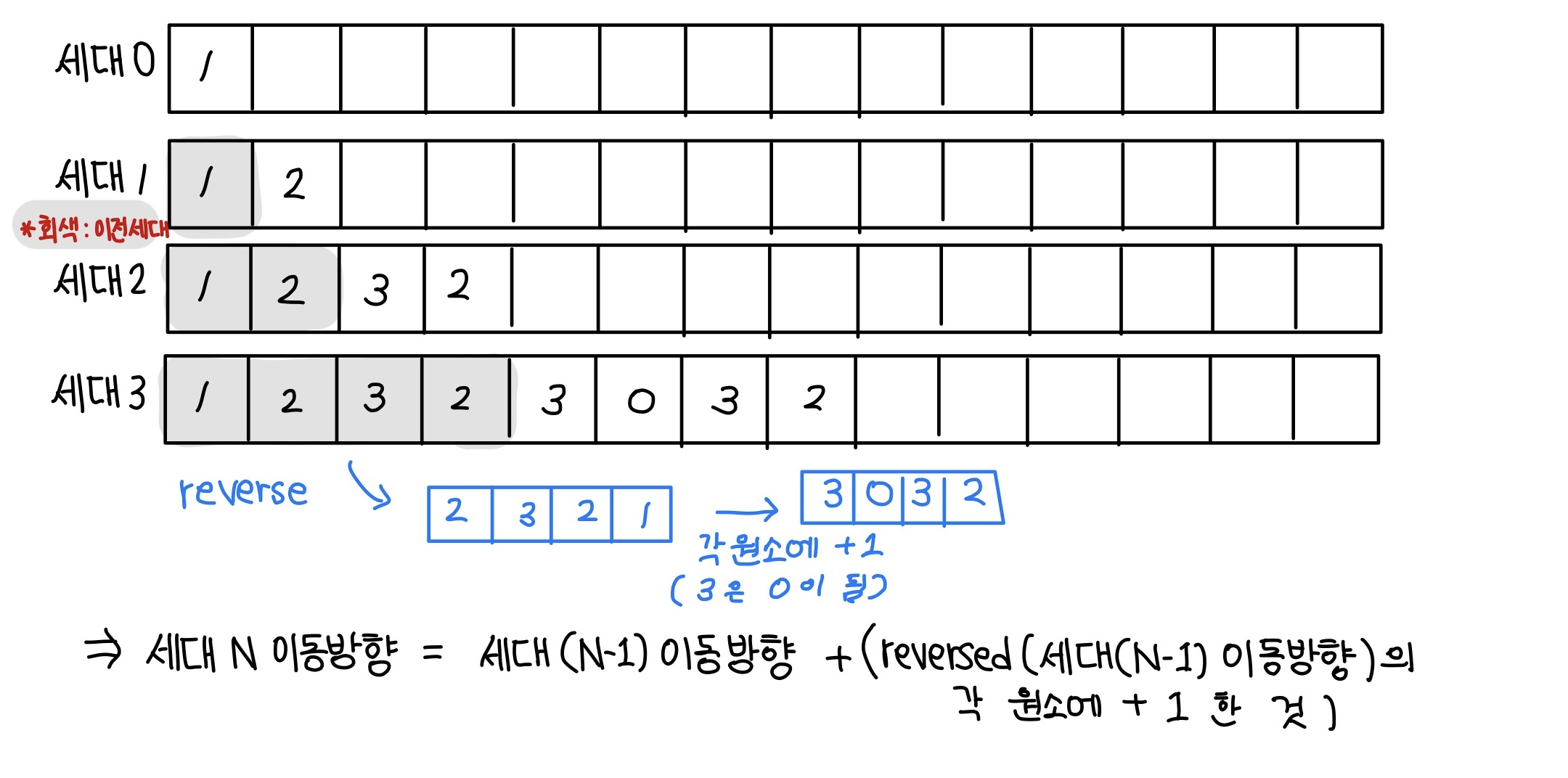
- 세대N이동방향 = 세대(N-1)이동방향 + (reversed(세대(N-1) 이동방향)의 각 원소에 +1 한 것) 이라는 규칙을 찾아낼 수 있다.
- 시작 좌표인 (4, 2)에서 세대3 이동방향 리스트에 저장된 방향대로 좌표를 움직여주며
arr상에 1을 표시해주면 드래곤 커브를 구성하는 점들을 표시할 수 있다.
⬛ 네 꼭짓점이 모두 드래곤 커브의 일부인 것의 개수 구하기
- arr[r][c] == 1인 (r, c)에서 →, ↓, ← 방향을 검사했을 때
- (r, c)를 포함하여 4 방향
(r, c+1), (r+1, c+1), (r+1, c)이 모두 1이면 1 x 1 정사각형의 네 꼭지점이 모두 커브의 일부이다. - arr[r][c] == 1인 모든 (r, c)에 대해 위를 검사한 뒤 네 꼭지점이 모두 커브의 일부인 것의 개수를 출력한다.
🧐
처음 문제를 보고는 복잡하고 어려울거라고 생각했는데, 문제에서 주는 상황을 곧이곧대로 구현하는 것이 아니라 (e.g., 90도 회전시킨 다음 0세대 드래곤 커브의 끝 점에 붙이기, 선분그리기 등...) 단순화해서 필요한 부분만 구현하려고 하니 풀이 방향이 보였다.

필기 깔끔하네요! 덕분에 잘 배워갑니다~!