Memory management
- ideally programmers want memory that is
- fast
- large
- nonvolatile
- Memory hierarchy
- small amount of fast, expensive memory - cache
- some medium speed, medium price main memory
- gigabytes of slow, cheap disk storage
- Memory manager
- part of the operating sys that manages the memory hierachy
Basic Memory Management
Monoprogramming without swapping or paging
- an operating sys with one user process
- Only one process at a time is running
- Three simple ways of organizing memory
- 하나의 user process와 운영체제
- (a) mainframes, minicomputers
- (b) palmtop computers, embeded systems
- (c) personal computers
Multiprogramming with fixed partitions

- Fixed Memory partitions
- separate input queues for each partition
- partition마다 input queue 단점 :수용할 수 있는 가장작은 partition에 가는데 partition 3에는 갈 수 없고 다른 곳에 배당되기 때문에 partition 3는 이용되지 않을 수 있다.
- single input queue -> 사이즈만 맞으면 먼저 도착한 작은 job들에게 유리하다.
- separate input queues for each partition
Relocation and protection
Multiprogramming의 두가지 문제점이다. 메모리안에 여러 프로세스가 존재하기 때문.
- Cannot be sure where program will be loaded in memory.
- Relocation
- address locations of variables. code routines cannot be absolute
- Protection
- must keep a program out of other processes partitions
- Relocation
- Relocation and protection
- Modify the instruction as the program is loaded into memory
- Linker should tell which program words are addresses to be relocated
- Protection code
- Linker should tell which program words are addresses to be relocated
- User base and limit register
- address locs added to base value to map to physical addr
- address locations larger than limit value is an error
- address locs added to base value to map to physical addr
- Modify the instruction as the program is loaded into memory
Excutable file이 look에 loading되면 주소가 partition에 배당되면 ㅣㅐㅐㅏ + 주소가 되어야 함?? 무슨말일까...
Relocation 해결법
1. program memory 로딩될 때, call look + 주소번지 이런식으로 instruction을 변경한다.
2. base reg & limit register 사용, 로딩시 inst 바꾸지 않고 그냥 로딩 call 주소 번지 base register에 (loading된 파티션 값)저장된 값 (주소)을 더해준다.
Protection 해결법
1. limit register 사용, program partition 1에 배당, 주소 100k partition 사이즈가 limit register로 저장하고, call 100k와 limit register 사이즈를 비교하여 다른 메모리를 침범하지 않게 한다.
단점 :loading은 빠르나 비교하기 때문에 수행이 느리다.
Swapping & Virtual memory
| Swapping | Virtual memory |
|---|---|
| Bring in each process in its entirety, running it for a while, then put it back on dist | Allows programs to run even when they are only partially in main memory |
Swapping
Multiprogramming with Variable partitions
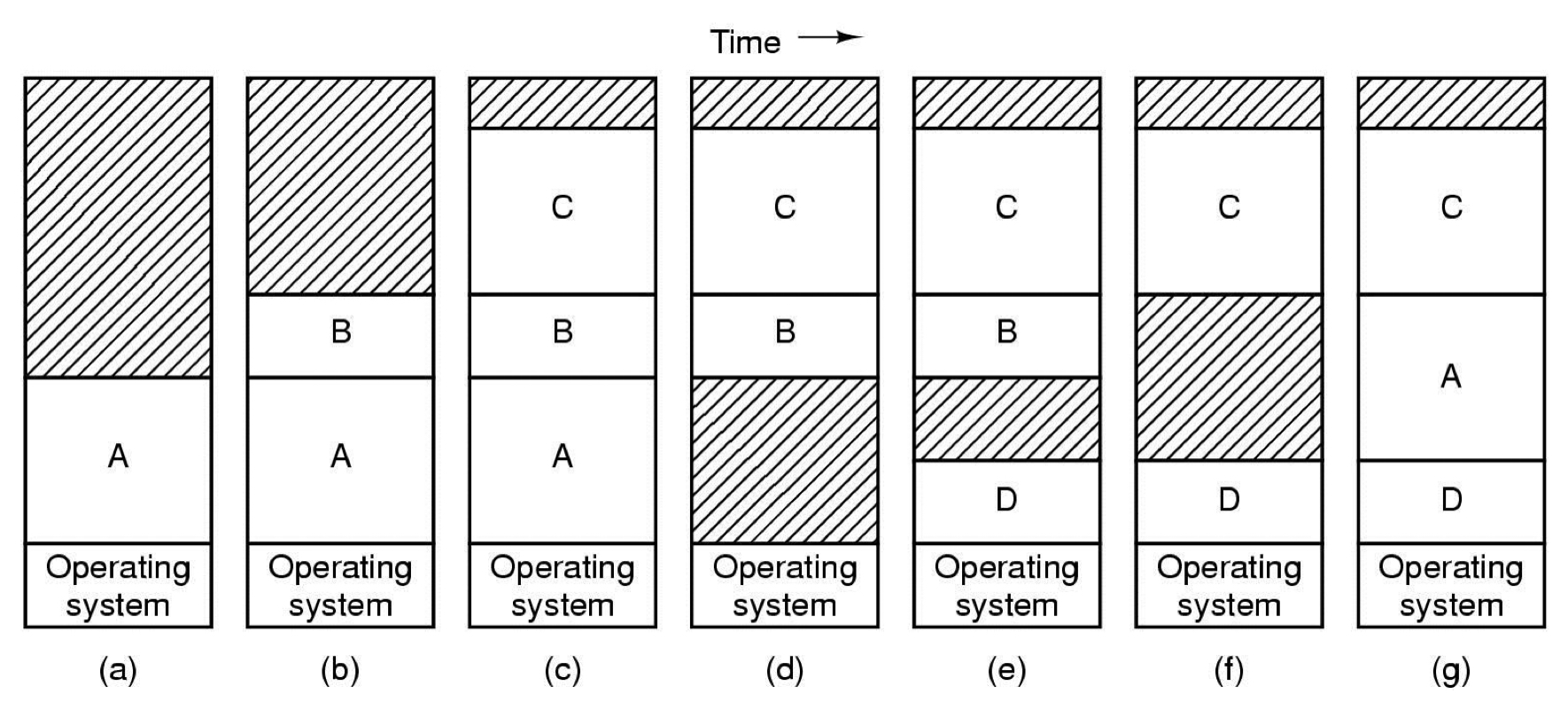
- Memory allocation changes as
- processes come into memory
- leave memory
- Shaded regions are unused memory
- Memory compaction
- Combine multiple holes into one big one by moving all the processes downward.
- Swapping has room for allocating space for growing data segment
- also for stack & data segment
Keeping track of memory usage
메모리 동적으로 할당. 메모리 사용을 keep track하는 방법 2가지.
- Bitmap
- Free list
Bit Maps
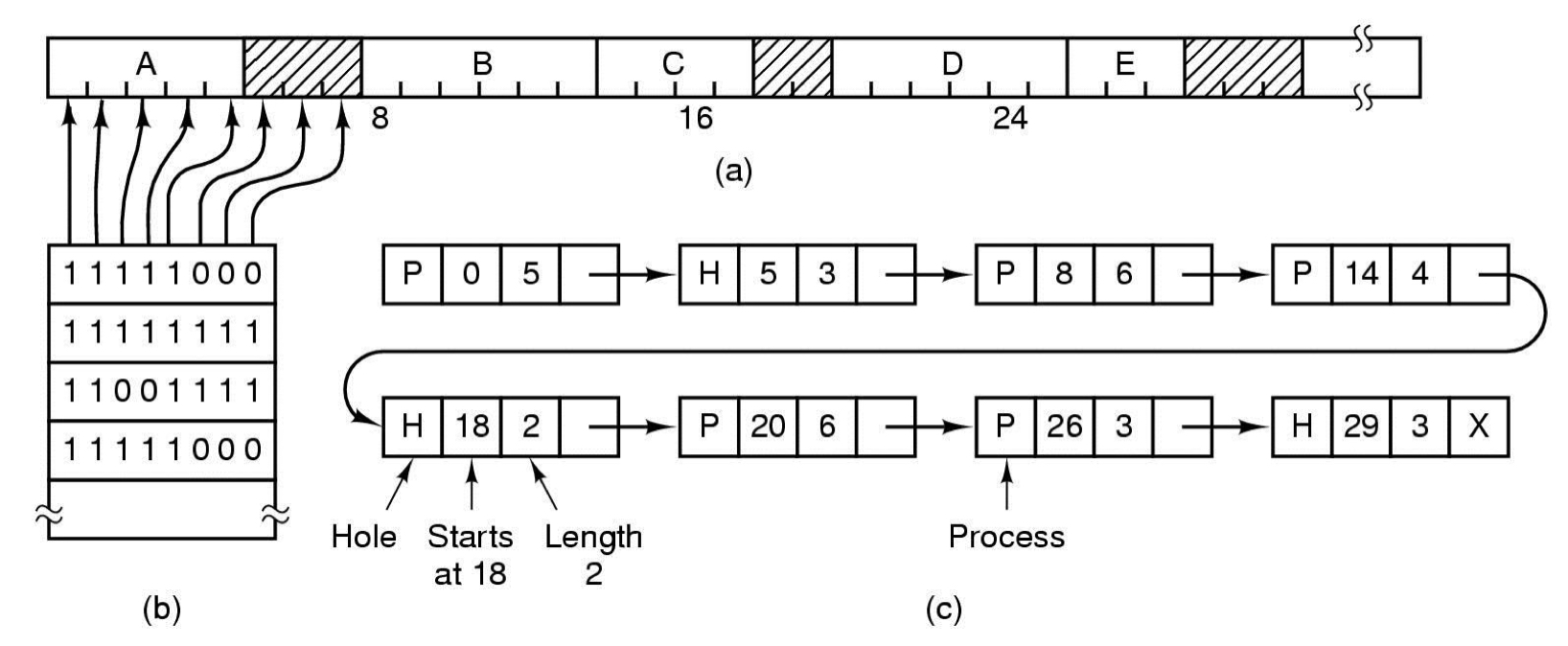
- Part of memory with 5 processes, 3 holes
- tick marks show allocation units
- shaded regions are free
- Size of the allocation unit
- The smaller the allocation unit, the larger the bitmap
- The larger the allocation unit, the more memory is wasted
- Searching a bitmap for a run of a given length is a slow op.
process 새로 생성되면 메모리 새로 할당. alloc unit 7이되는 것을 찾아야한다. 0이 7개 연속되는 것 찾는것은 처음 부터 찾으면 O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다.
(b) 할당되어 있으면 bitmap - 1 할당 x - 0
Linked Lists
- Allocating memory for a newly created process
- First fit
- Scans along the list until it finds a hole that is big enough
- Best fit
- Searches the entire list and takes the smallest hole available
- Worst fit
- Takes the largest hole available
- First fit
Virtual Memory
- Programs that are too big to fit in the available memory
- Solution
-
Overlay (program 조각낸다.)
- A programmer splits the program into pieces, called overlays.
- when the first overlay is done, it calls another overlay, which is swapped into the memory from the disk.
- A programmer splits the program into pieces, called overlays.
-
Virtual memory (Os가 알아서 함)
- Computer handles the job
- paging **
-
paging
- Virtual address
- Program generated address
- MOV REG, 1000
- Forms the virtual address space
- Virtual address space is divided up into units called pages and the corresponding units in the physical memory are called page frames (매우 중요)
- Program generated address
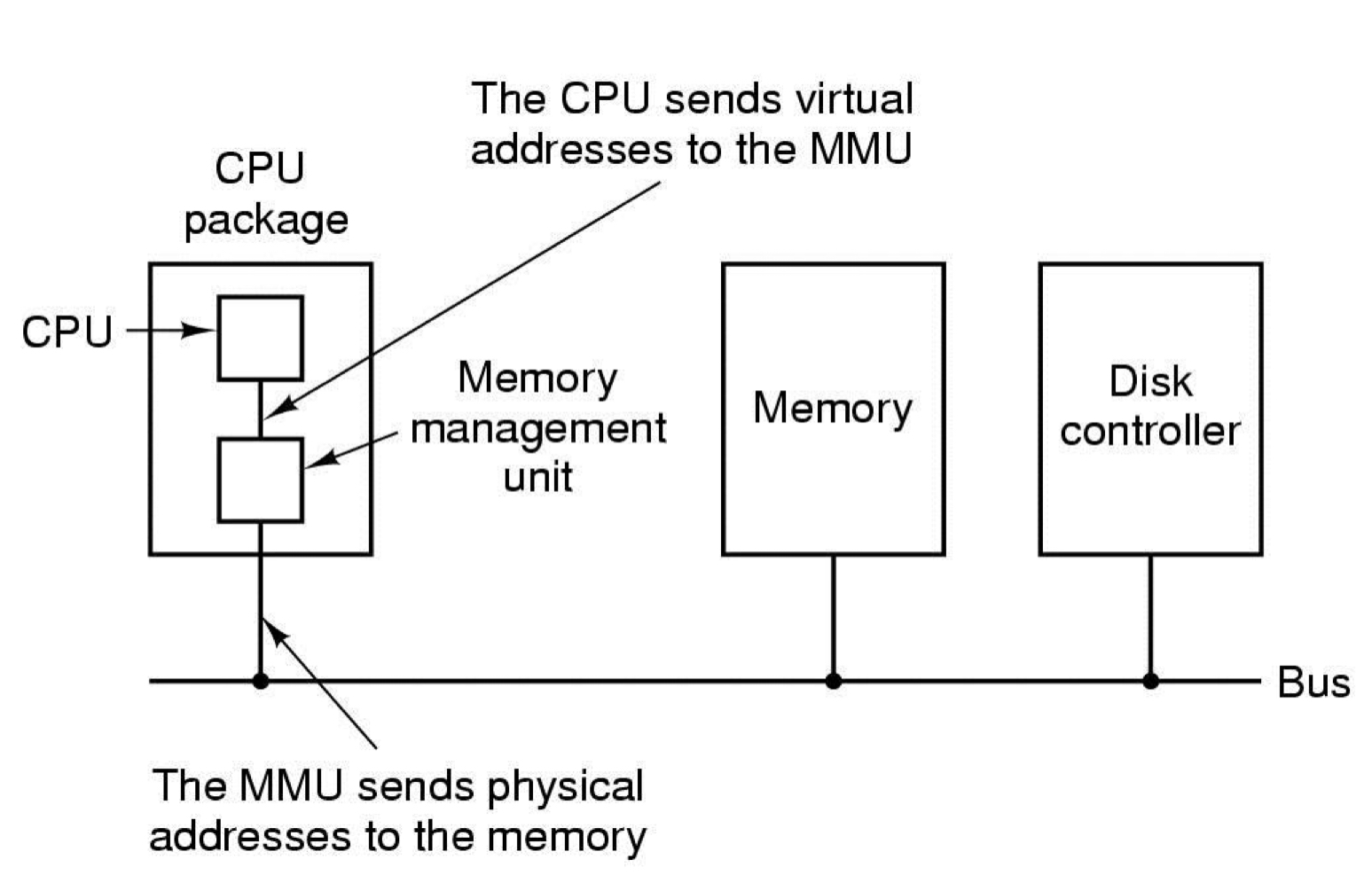
- The relation between virtual addressees and physical memory addresses given by page table.
- Page falut
- When the MMU notices that the page is unmapped, it causes the CPU to trap to the operating system.
- The OS picks a little-used page frame and writes its cotents back to the disk
- It then fetches the page just referenced into the page frame just freed, changes the map, and restarts the trapped instruction.
virtual memory가 physical memory의 어디를 참조하고 있는지 저장하고 있다.
