Question
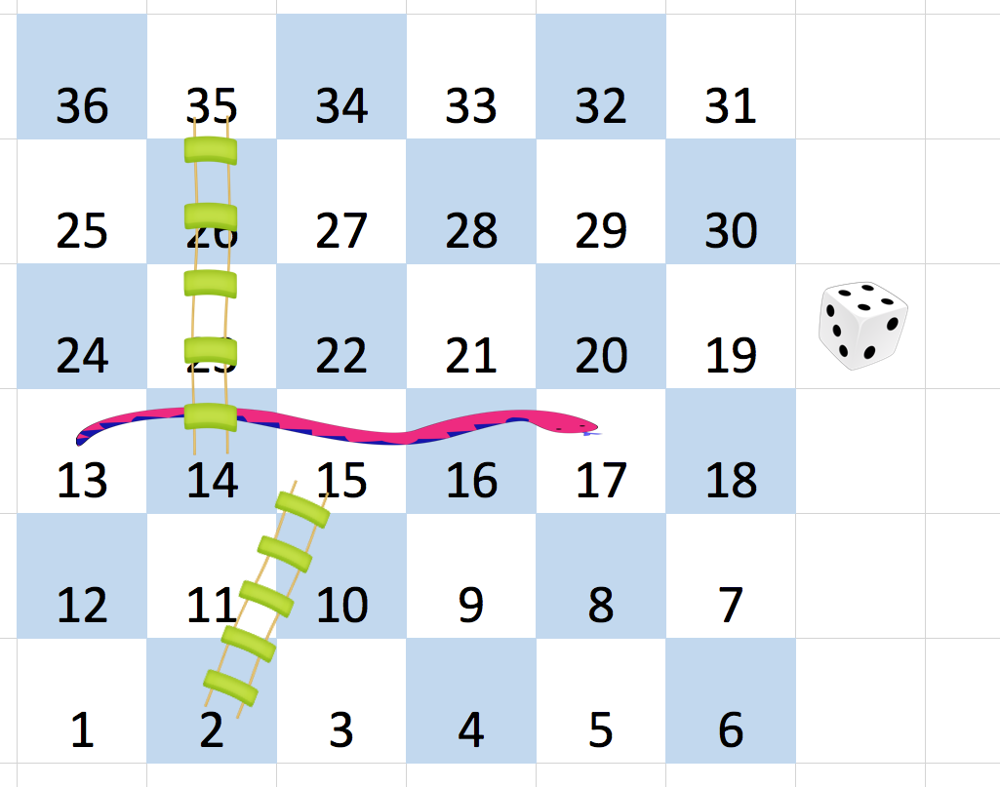
You are given an n x n integer matrix board where the cells are labeled from 1 to n2 in a Boustrophedon style starting from the bottom left of the board (i.e. board[n - 1][0]) and alternating direction each row.
You start on square 1 of the board. In each move, starting from square curr, do the following:
- Choose a destination square
nextwith a label in the range[curr + 1, min(curr + 6, n2)].- This choice simulates the result of a standard 6-sided die roll: i.e., there are always at most 6 destinations, regardless of the size of the board.
- If
nexthas a snake or ladder, you must move to the destination of that snake or ladder. Otherwise, you move tonext. - The game ends when you reach the square n2.
Aboardsquare on rowrand columnchas a snake or ladder ifboard[r][c] != -1. The destination of that snake or ladder isboard[r][c]. Squares1and n2 do not have a snake or ladder.
Note that you only take a snake or ladder at most once per move. If the destination to a snake or ladder is the start of another snake or ladder, you do not follow the subsequent snake or ladder.
- For example, suppose the board is
[[-1,4],[-1,3]], and on the first move, your destination square is2. You follow the ladder to square3, but do not follow the subsequent ladder to4.
Return the least number of moves required to reach the square n2. If it is not possible to reach the square, return-1.
Constraints:
n == board.length == board[i].length2 <= n <= 20board[i][j]is either-1or in the range[1, n2].- The squares labeled
1and n2 do not have any ladders or snakes.
class Solution:
def snakesAndLadders(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> int:문제가 길어보이지만 내용은 간단합니다. 그림과 같은 정사각형 보드가 있다고 할 때, 가장 빠르게 마지막 숫자까지 도달하는 횟수를 반환해야 합니다.
이 때 board는 지름길(또는 함정으로도 볼 수 있는)이 없는 곳은 -1, 있는 곳은 이동해야하는 숫자를 값으로 가집니다.
지름길은 1회용이고 만약 마지막 숫자에 도달할 수 없는 경우엔 -1을 반환합니다.
제가 생각한 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
class Solution:
def rc(self,num: int, L: int):
r = L-1 - (num-1)//L
c = (num-1)%L
if (L-1-r)%2==0:
return (r,c)
return (r,L-1-c)
def snakesAndLadders(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> int:
L = len(board)
q = deque([(0,1)])
visited = set()
while q:
cnt,num = q.popleft()
if num == L*L:
return cnt
if num not in visited:
visited.add(num)
for dice_num in range(1,7):
next_num = num + dice_num
if next_num > L*L:
break
next_r,next_c = self.rc(next_num,L)
if board[next_r][next_c] != -1:
next_num = board[next_r][next_c]
q.append((cnt+1,next_num))
return -1rc(num,L): 숫자num와 보드의 변 길이L을 받아서 해당 숫자의 보드판에서 행,열 값을 반환하는 함수입니다.- 마지막행부터 시작하므로 행 값
r는L-1에서 값을 빼주는 방식으로 구합니다. - 열 값
c는 마지막 행을 시작으로 정방향, 역방향으로 값이 바뀝니다. 따라서 정방향으로 정의 후, 마지막 행을 0으로 시작해서 홀수행인지 짝수행인지 판단합니다. - 짝수행이라면 정방향으로 반환, 홀수행이라면 c값을 역방향으로 반환합니다.
- 마지막행부터 시작하므로 행 값
- 보드길이
L, 너비 탐색을 위해(주사위 던진 횟수, 현재 숫자)를 원소로 가지는 큐 자료형인q, 같은 보드 숫자 체크를 막기 위한visited를 정의합니다.- 너비탐색의 이유는 반환 결과가 가장 빨리 목적지에 도달하는 값을 반환하기 위해서입니다. 처음으로 목적지가 나오는 값이 가장 빠른 횟수로 도달했다는 의미가 됩니다.
- 큐를 통해 너비 탐색을 시작합니다.
- 만약 현재 확인하려는 숫자가 목적지의 숫자면 횟수를 반환합니다.
- 현재 숫자가 아직 탐색하지 않은(
num not in visited) 숫자라면 탐색을 시작합니다.- 현재 숫자에서 주사위를 굴려 더할 수 있는 숫자인 +1 ~ +6을
for문을 통해 모두 탐색합니다. 더한 숫자를next_num으로 둡니다. next_num가 보드판 숫자를 넘어가면for문을 탈출합니다.next_num의 보드판에 지름길이 있다면next_num을 보드판의 숫자로 재정의합니다.(next_num,던진횟수+1)을q에 추가합니다.
- 현재 숫자에서 주사위를 굴려 더할 수 있는 숫자인 +1 ~ +6을
while문을 탈출했다는 것은 모든 경우를 확인해도 마지막까지 도달하지 못했다는 의미이므로-1을 반환합니다.
너비 탐색으로 방향을 잡고 중복 탐색을 막기 위한 visited를 사용하자는 방향으로 정한 후부터는 어렵지 않았던 문제입니다.
다만 속도가 느리게 나오길래 좀 더 빠른 사람의 코드를 참고해보니 제 코드의 rc 함수에서 시간이 걸린 듯 합니다. 좀 더 빨랐던 사람들의 코드는 매번 r,c를 구하는 것이 아닌 r,c의 값을 초기화한 후 r,c의 위치에 따라 다음 r,c를 정하는 방식이였습니다.
조건 처리가 많아서 가독성이 떨어져서인지 수학식으로 처리하는게 좀 더 괜찮아 보입니다. (물론 최적화가 중요한 상황이면 당연히 조건문 처리로 해야합니다!)