23.08.06 최초 작성
23.11.15 POSIX Message Queue, Semaphore 추가
- Inter Process Communication (IPC) : 프로세스 사이의 통신
주요 IPC 방법
- Message Queue
- Shared Memory
- Semaphore
1. IPC를 위한 절차
- IPC를 위한 Key 생성
- Identifier를 이용해 IPC 객체 생성
- 생성된 IPC 객체를 이용해 통신
- IPC 객체 삭제 후 종료
key : key_t형으로 32비트 정수형이다. 새로운 IPC 객체를 생성할 때 키를 지정하며 키가 다르면 다른 객체가 생성된다.
- 키의 구조
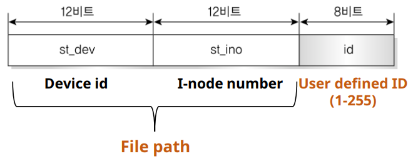
#include <sys/ipc.h>
key_t ftok(const char *path, int id);
///
path : 파일시스템에 존재하는 임의의 파일 경로
id : 키 값을 생성할 때 지정하는 임의의 번호
Return : key- IPC 구조체
1.1 IPC 정보 검색
ipcs
-a : 모두 출력
-m : shared memory 정보
-q : message queue 정보
-s : semaphore 정보1.2 IPC 정보 삭제
ipcrm 'object ID'2. Message Queue
- 메시지를 주고받는 Queue
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgget(key_t key, int msgflg);
key : IPC의 key
msgflg : 생성 방법 및 접근 권한 지정
Return : 생성/연결된 Message Queue 객체의 identifier#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys.ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgsnd(int msqid, const void *msgp, size_t msgsz, int msgflg);
///
msqid : Message Queue ID
msgp : 메시지를 담고 있는 공간
msgsz : 메시지의 크기
msgflg : Message Queue가 가득 찬 경우 동작 지정
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)2.1 메시지 수신
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
sszizt_t msgrcv(int msqid, void *msgp, size_t msgsz, long msgtyp, int msgflg);
///
msgflg : Message Queue가 비어있는 경우 동작 지정
msgtyp : 읽어올 메시지의 유형
Return : 실제 읽어 온 byte 수
(-1 : Error)2.2 Message Queue Control
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgctl(int msqid, iint cmd, struct msqid_ds *buf);
///
msqid : Message Queue ID
cmd : 수행할 제어 기능
buf : 제어기능에 사용되는 구조체
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)ex) 예제
svmsg_file_server: ipc 키를 생성해 메시지를 주고 받는 코드
#include "svmsg_file.h"
static void /* SIGCHLD handler */
grimReaper(int sig)
{
int savedErrno;
savedErrno = errno; /* waitpid() might change 'errno' */
while (waitpid(-1, NULL, WNOHANG) > 0)
continue;
errno = savedErrno;
}
static void /* Executed in child process: serve a single client */
serveRequest(const struct requestMsg *req)
{
int fd;
ssize_t numRead;
struct responseMsg resp;
fd = open(req->pathname, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) { /* Open failed: send error text */
resp.mtype = RESP_MT_FAILURE;
snprintf(resp.data, sizeof(resp.data), "%s", "Couldn't open");
msgsnd(req->clientId, &resp, strlen(resp.data) + 1, 0);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); /* and terminate */
}
/* Transmit file contents in messages with type RESP_MT_DATA. We don't
diagnose read() and msgsnd() errors since we can't notify client. */
resp.mtype = RESP_MT_DATA;
while ((numRead = read(fd, resp.data, RESP_MSG_SIZE)) > 0)
if (msgsnd(req->clientId, &resp, numRead, 0) == -1)
break;
/* Send a message of type RESP_MT_END to signify end-of-file */
resp.mtype = RESP_MT_END;
msgsnd(req->clientId, &resp, 0, 0); /* Zero-length mtext */
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct requestMsg req;
pid_t pid;
ssize_t msgLen;
int serverId;
struct sigaction sa;
/* Create server message queue */
serverId = msgget(SERVER_KEY, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL |
S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IWGRP);
if (serverId == -1)
errExit("msgget");
/* Establish SIGCHLD handler to reap terminated children */
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
sa.sa_flags = SA_RESTART;
sa.sa_handler = grimReaper;
if (sigaction(SIGCHLD, &sa, NULL) == -1)
errExit("sigaction");
/* Read requests, handle each in a separate child process */
for (;;) {
msgLen = msgrcv(serverId, &req, REQ_MSG_SIZE, 0, 0);
if (msgLen == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR) /* Interrupted by SIGCHLD handler? */
continue; /* ... then restart msgrcv() */
errMsg("msgrcv"); /* Some other error */
break; /* ... so terminate loop */
}
pid = fork(); /* Create child process */
if (pid == -1) {
errMsg("fork");
break;
}
if (pid == 0) { /* Child handles request */
serveRequest(&req);
_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
/* Parent loops to receive next client request */
}
/* If msgrcv() or fork() fails, remove server MQ and exit */
if (msgctl(serverId, IPC_RMID, NULL) == -1)
errExit("msgctl");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}2.3 POSIX Message Queue
mq_open: 메시지 큐 생성
#include <fcntl.h> /* For O_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h> /* For mode constants */
#include <mqueue.h>
mqd_t mq_open(const char *name, int oflag, mode_t mode, struct mq_attr *attr);
///
name : 메시지 큐 이름을 지정
oflag : 메시지 큐 옵션
mode : 메시지 큐를 만들때 권한을 설정 (O_CREAT과 같이 사용)
attr : 메시지 큐의 속성을 지정 (최대 메시지수, 최대 메시지 사이즈(바이트))
Return
Success : 사용할 수 있는 mqd_t
Fail : -1- oflag | O_RDONLY | O_WRONLY | O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 읽기 전용 | 쓰기 전용 | 읽기, 쓰기 전용 | exec시 메시지큐를 닫음 |
| O_CREAT | O_EXCL | O_NONBLOCK |
|---|---|---|
| 메시지 큐가 존재하지 않을시 메시지큐 생성 (mode와 attr에 인자 필요) | O_CREAT과 같이 사용 이미 파일이 존재하면 EEXIST 에러 | 비블록 형식으로 메시지큐 open (메시지 없으면 대기하지 않음) |
- attr 구조 struct mq_attr {
long mq_flags; /* 앞서 설정한 oflag */
long mq_maxmsg; /* 메시지 큐의 최대 크기 */
long mq_msgsize; /* 메시지의 최대 크기 (bytes) */
long mq_curmsgs; /* 메시지 큐에 메시지가 몇개 있는지 */
};mq_send,mq_timedsend: 메시지를 보내는 함수
#include <mqueue.h>
#include <time.h>
int mq_send(mqd_t mqdes, const char *msg_ptr,nsize_t msg_len, unsigned int msg_prio);
int mq_timedsend(mqd_t mqdes, const char *msg_ptr, size_t msg_len, unsigned int msg_prio,
const struct timespec *abs_timeout);
///
mqdes : 메시지 큐의 mqd_t
msg_ptr : 메시지 내용
msg_len : 메시지의 크기
msg_prio : 메시지의 우선순위
abs_timeout : 큐가 꽉 찼을 경우 지정된 시간동안 메시지 전송을 보류 (NON_BLOCK 플래그가 없어야함, time.h 필요)
Return
0 : Success, -1 : Failmq_receive,mq_timedreceive: 메시지를 받는 함수
#include <mqueue.h>
#include <time.h>
ssize_t mq_receive(mqd_t mqdes, char *msg_ptr, size_t msg_len, unsigned int *msg_prio);
ssize_t mq_timedreceive(mqd_t mqdes, char *msg_ptr, size_t msg_len, unsigned int *msg_prio,
const struct timespec *abs_timeout);
///
mqdes : 메시지 큐의 mqd_t
msg_ptr : 메시지 내용 저장할 공간
msg_len : 메시지의 크기 (attr에서 설정한 최대 크기보다 작으면 안됨)
msg_prio : 메시지의 우선순위
abs_timeout : 큐가 비었을 경우 지정된 시간동안 메시지 수신을 보류 (NON_BLOCK 플래그가 없어야함, time.h 필요)
Return
받은 메시지의 byte 수
-1 : Failmq_close: 메시지 큐 종료
#include <mqueue.h>
int mq_close(mqd_t mqdes);
///
mqdes : 닫을 메시지 큐 지정
Return
0 : Success, -1 : Failex) 예제 (POSIX)
pmsg_create:
// optind : argv에서 다음 요소의 인덱스
#include <mqueue.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
usageError(const char *progName)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-cx] [-m maxmsg] [-s msgsize] mq-name "
"[octal-perms]\n", progName);
fprintf(stderr, " -c Create queue (O_CREAT)\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -m maxmsg Set maximum # of messages\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -s msgsize Set maximum message size\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -x Create exclusively (O_EXCL)\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int flags, opt;
mode_t perms;
mqd_t mqd;
struct mq_attr attr, *attrp;
attrp = NULL;
attr.mq_maxmsg = 10;
attr.mq_msgsize = 2048;
flags = O_RDWR;
/* Parse command-line options */
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "cm:s:x")) != -1) {
switch (opt) {
case 'c':
flags |= O_CREAT;
break;
case 'm':
attr.mq_maxmsg = atoi(optarg);
attrp = &attr;
break;
case 's':
attr.mq_msgsize = atoi(optarg);
attrp = &attr;
break;
case 'x':
flags |= O_EXCL;
break;
default:
usageError(argv[0]);
}
}
if (optind >= argc)
usageError(argv[0]);
perms = (argc <= optind + 1) ? (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR) :
getInt(argv[optind + 1], GN_BASE_8, "octal-perms");
mqd = mq_open(argv[optind], flags, perms, attrp);
if (mqd == (mqd_t) -1)
errExit("mq_open");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}pmsg_send: 파이프로 메시지를 보냄
#include <mqueue.h>
#include <fcntl.h> /* For definition of O_NONBLOCK */
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
usageError(const char *progName)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-n] mq-name msg [prio]\n", progName);
fprintf(stderr, " -n Use O_NONBLOCK flag\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int flags, opt;
mqd_t mqd;
unsigned int prio;
flags = O_WRONLY;
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "n")) != -1) {
switch (opt) {
case 'n': flags |= O_NONBLOCK; break;
default: usageError(argv[0]);
}
}
if (optind + 1 >= argc)
usageError(argv[0]);
mqd = mq_open(argv[optind], flags);
if (mqd == (mqd_t) -1)
errExit("mq_open");
prio = (argc > optind + 2) ? atoi(argv[optind + 2]) : 0;
if (mq_send(mqd, argv[optind + 1], strlen(argv[optind + 1]), prio) == -1)
errExit("mq_send");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}pmsg_receive: 파이프에서 메시지를 수신해 내용 출력
#include <mqueue.h>
#include <fcntl.h> /* For definition of O_NONBLOCK */
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
usageError(const char *progName)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-n] mq-name\n", progName);
fprintf(stderr, " -n Use O_NONBLOCK flag\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int flags, opt;
mqd_t mqd;
unsigned int prio;
void *buffer;
struct mq_attr attr;
ssize_t numRead;
flags = O_RDONLY;
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "n")) != -1) {
switch (opt) {
case 'n': flags |= O_NONBLOCK; break;
default: usageError(argv[0]);
}
}
if (optind >= argc)
usageError(argv[0]);
mqd = mq_open(argv[optind], flags);
if (mqd == (mqd_t) -1)
errExit("mq_open");
if (mq_getattr(mqd, &attr) == -1)
errExit("mq_getattr");
buffer = malloc(attr.mq_msgsize);
if (buffer == NULL)
errExit("malloc");
numRead = mq_receive(mqd, buffer, attr.mq_msgsize, &prio);
if (numRead == -1)
errExit("mq_receive");
printf("Read %ld bytes; priority = %u\n", (long) numRead, prio);
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, buffer, numRead) == -1)
errExit("write");
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "\n", 1);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
3. Shared Memory
같은 메모리 공간을 프로세스들이 공유하는 것. 동시에 읽기, 쓰기가 가능하며 동기화 해줘야 한다.
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);
///
key : IPC key (IPC_PRIVATE : private shared memory 생성)
size : 공유할 메모리 크기 (byte 단위)
shmflg : 생성 방법 및 접근 권한
Return : 생성된 shared memory 객체의 identifier#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg); // 생성된 shared memory를 프로세스의 address space로 매핑
///
shmid : shared memory를 연결 할 주소
shmaddr : shared memory를 연결 할 주소 (NULL : 시스템이 적절한 주소 선택)
shmflg : shared memory에 대한 접근 권한
(0 : Read / Write, SHM_RDONLY : 읽기 권한)
Return : 매핑 된 주소
(-1 : Error)
---`
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr); //주소 공간 매핑 해제
///
shmaddr : 연결을 해제할 메모리 주소
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);
///
shmid : shared memory segment ID
cmd : 수행할 제어기능
buf : 제어기능에 사용되는 구조체
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)
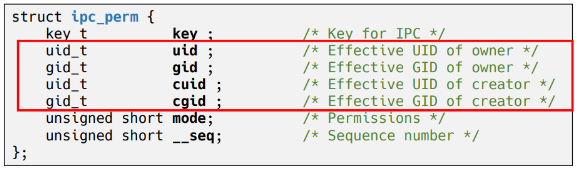
- Shared Memory에 대한 정보를 저장하는 구조체
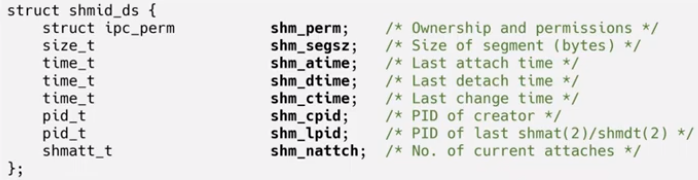
4. Semaphore
4.1 Semaphore
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
int semget(key_t key, int nsems, int semflg);
///
nsems : 생성할 Semaphore 갯수
semflg : Semaphore 접근 옵션
Return : 생성된 Semaphore의 identifier#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
int semop(int semid, struct sembuf *sops, size_t nsops);
///
semid : semget으로 생성한 Semaphore의 identifier
sops : 수행할 명령을 가지는 공간
nsops : sops가 가리키는 구조체의 수
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)- sembuf 구조체
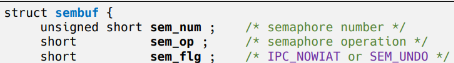
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
int semctl(int semid, int semnum, int cmd, ...);
///
semid : Semaphore의 identifier
semnum : 제어할 Semaphoer의 번호
cmd : 수행할 제어 기능
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)ex) 예제
svsem_demo: 세마포어를 제어하는 코드
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include "curr_time.h" /* Declaration of currTime() */
#include "semun.h" /* Definition of semun union */
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int semid;
if (argc < 2 || argc > 3 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s init-value\n"
" or: %s semid operation\n", argv[0], argv[0]);
if (argc == 2) { /* Create and initialize semaphore */
union semun arg;
semid = semget(IPC_PRIVATE, 1, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (semid == -1)
errExit("semid");
arg.val = getInt(argv[1], 0, "init-value");
if (semctl(semid, /* semnum= */ 0, SETVAL, arg) == -1)
errExit("semctl");
printf("Semaphore ID = %d\n", semid);
} else { /* Perform an operation on first semaphore */
struct sembuf sop; /* Structure defining operation */
semid = getInt(argv[1], 0, "semid");
sop.sem_num = 0; /* Specifies first semaphore in set */
sop.sem_op = getInt(argv[2], 0, "operation");
/* Add, subtract, or wait for 0 */
sop.sem_flg = 0; /* No special options for operation */
printf("%ld: about to semop at %s\n", (long) getpid(), currTime("%T"));
if (semop(semid, &sop, 1) == -1)
errExit("semop");
printf("%ld: semop completed at %s\n", (long) getpid(), currTime("%T"));
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}binary_sem:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include "semun.h" /* Definition of semun union */
#include "binary_sems.h"
Boolean bsUseSemUndo = FALSE;
Boolean bsRetryOnEintr = TRUE;
int /* Initialize semaphore to 1 (i.e., "available") */
initSemAvailable(int semId, int semNum)
{
union semun arg;
arg.val = 1;
return semctl(semId, semNum, SETVAL, arg);
}
int /* Initialize semaphore to 0 (i.e., "in use") */
initSemInUse(int semId, int semNum)
{
union semun arg;
arg.val = 0;
return semctl(semId, semNum, SETVAL, arg);
}
/* Reserve semaphore (blocking), return 0 on success, or -1 with 'errno'
set to EINTR if operation was interrupted by a signal handler */
int /* Reserve semaphore - decrement it by 1 */
reserveSem(int semId, int semNum)
{
struct sembuf sops;
sops.sem_num = semNum;
sops.sem_op = -1;
sops.sem_flg = bsUseSemUndo ? SEM_UNDO : 0;
while (semop(semId, &sops, 1) == -1)
if (errno != EINTR || !bsRetryOnEintr)
return -1;
return 0;
}
int /* Release semaphore - increment it by 1 */
releaseSem(int semId, int semNum)
{
struct sembuf sops;
sops.sem_num = semNum;
sops.sem_op = 1;
sops.sem_flg = bsUseSemUndo ? SEM_UNDO : 0;
return semop(semId, &sops, 1);
}4.2 POSIX Semaphore
POSIX API를 사용하는 방법은 두가지가 있다.
Unnamed Semaphore- 주로 shared memory 내의 메모리 영역을 이용한다.
Named Semaphore- ID를 갖는 별도의 객체를 생성한다.
- Shared memory 이외의 자원에 대한 동기화가 필요할 때 사용하기 좋다.
4.2.1 Unnamed Semaphore
sem_init: 세마포어 초기화 함수
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
///
sem: 초기화 할 semaphore 객체 위치
pshared
‐ 0: process 내에서 thread 간 공유
‐ 1: process 간 공유
value: semaphore 초기값
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)sem_destroy: 세마포어 리소스 반납하는 함수.
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
///
sem: 리소스를 반납할 semaphore 객체
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)4.2.2 Named Semaphore
sem_open: name Semaphore 열기 / 생성
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
sem_t *sem_open(const char *name, int oflag); //열기
sem_t *sem_open(const char *name, int oflag, mode_t, unsigned int value);
//생성
///
name: 세마포어 ID
oflag: mask of O_CREAT, O_EXCL
mode: 권한
value: semaphore 초기값
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)sem_close: name semaphore 닫기sem_unlink: named semaphore 삭제, 모든 프로세스가 해당 세마포어를 닫으면 삭제함
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_close(sem_t *sem);
int sem_unlink(const char *name);
///
sem: 세마포어 객체
name: 세마포어 ID
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)4.2.3 공통
sem_post: 갖고 있던 리소스 해제, 세마포어 값을 +1sem_wait: 리소스 획득 요청, 세마포어의 값을 -1, 세마포어의 값이 0보다 작아진다면 blocking 됨sem_trywait: 리소스 획득 시도sem_timedwait: 타임아웃을 설정하고 리소스 획득 요청
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem);
int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout);
///
sem: 세마포어 객체
abs_timeout: timeout 설정값
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)ex) 예제
psem_create: 세마포어 생성
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
usageError(const char *progName)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-cx] name [octal-perms [value]]\n", progName);
fprintf(stderr, " -c Create semaphore (O_CREAT)\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -x Create exclusively (O_EXCL)\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int flags, opt;
mode_t perms;
unsigned int value;
sem_t *sem;
flags = 0;
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "cx")) != -1) {
switch (opt) {
case 'c': flags |= O_CREAT; break;
case 'x': flags |= O_EXCL; break;
default: usageError(argv[0]);
}
}
if (optind >= argc)
usageError(argv[0]);
/* 기본 권한 rw-------; 기본 세마포어 값 0 */
perms = (argc <= optind + 1) ? (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR) :
getInt(argv[optind + 1], GN_BASE_8, "octal-perms");
value = (argc <= optind + 2) ? 0 : getInt(argv[optind + 2], 0, "value");
sem = sem_open(argv[optind], flags, perms, value);
if (sem == SEM_FAILED)
errExit("sem_open");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}psem_post: 세마포어 취득
#include <semaphore.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
sem_t *sem;
if (argc != 2)
usageErr("%s sem-name\n", argv[0]);
sem = sem_open(argv[1], 0);
if (sem == SEM_FAILED)
errExit("sem_open");
if (sem_post(sem) == -1)
errExit("sem_post");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
psem_wait: 리소스 획득 요청
#include <semaphore.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
sem_t *sem;
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s sem-name\n", argv[0]);
sem = sem_open(argv[1], 0);
if (sem == SEM_FAILED)
errExit("sem_open");
if (sem_wait(sem) == -1)
errExit("sem_wait");
printf("%ld sem_wait() succeeded\n", (long) getpid());
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
pshm_create: 공유메모리 생성
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
usageError(const char *progName)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-cx] shm-name size [octal-perms]\n", progName);
fprintf(stderr, " -c Create shared memory (O_CREAT)\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -x Create exclusively (O_EXCL)\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int flags, opt, fd;
mode_t perms;
size_t size;
void *addr;
flags = O_RDWR;
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "cx")) != -1) {
switch (opt) {
case 'c': flags |= O_CREAT; break;
case 'x': flags |= O_EXCL; break;
default: usageError(argv[0]);
}
}
if (optind + 1 >= argc)
usageError(argv[0]);
size = getLong(argv[optind + 1], GN_ANY_BASE, "size");
perms = (argc <= optind + 2) ? (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR) :
getLong(argv[optind + 2], GN_BASE_8, "octal-perms");
/* Create shared memory object and set its size */
fd = shm_open(argv[optind], flags, perms);
if (fd == -1)
errExit("shm_open");
if (ftruncate(fd, size) == -1)
errExit("ftruncate");
/* Map shared memory object */
if (size > 0) {
addr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED)
errExit("mmap");
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}