23.08.05 최초 작성
23.11.16 예제, mprotect, mlock 추가
23.12.11 내용 추가(madvise())
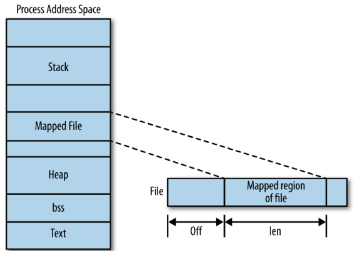
메모리의 영역을 파일에 매핑하는 것. 파일에 대한 접근을 메모리에 접근하는 것 처럼 처리할 수 있으며 다른 프로세스와 통신 할 수 있다.
VMA (vm_area_struct)
- 리눅스에서 메모리 공간을 관리하는 단위
/proc/PID/maps에서 확인 가능
예외 처리
Segmetation Fault: 할당하지 않은 영역 접근Normal Page Fault:Demand PagingProtection Exception: 접근 권한 벗어남 (리눅스에선Segmetation Fault)
1. 메모리 매핑
#include <sys/mman.h>
void* mmap (void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset); // Page 단위로 이루어진다
///
addr : 매핑할 메모리 주소의 hint (일반적으로 NULL)
length : 매핑 할 길이
prot : Memory Protection Mode
(PROT_NONE : 접근할 수 없음, PROT_READ, WRITE, EXEC : 읽기, 쓰기, 실행 권한)
(file descriptor의 open mode와 다르면 안됨)
flags : 매핑 형태와 동작 방식 지정
(MAP_FIXED : 매핑 할 주소 지정
MAP_PRIVATE : 프로세스 간 변경 내용이 공유 및 반영되지 않음
MAP_SHARED : 프로세스 간 매핑 된 내용이 공유됨
fd : 매핑할 파일의 file descriptor
offset : 매핑 시작 지점을 지정 (Page Size의 배수)
Return : 할당된 메모리 주소
(MAP_FAILED : Fail)1.2 매모리 매핑 제거
#include <sys/mman.h>
int munmap(void *addr, size_t length);
///
addr : 매핑 시작 주소
length : 매핑 길이
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : fail)ex) 예제
memcat: 비공개 파일의 내용을 읽어서 출력하는 코드
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *addr;
int fd;
struct stat sb;
if (argc != 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s file\n", argv[0]);
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1)
errExit("open");
/* Obtain the size of the file and use it to specify the size of
the mapping and the size of the buffer to be written */
if (fstat(fd, &sb) == -1)
errExit("fstat");
/* Handle zero-length file specially, since specifying a size of
zero to mmap() will fail with the error EINVAL */
if (sb.st_size == 0)
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
addr = mmap(NULL, sb.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, fd, 0);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED)
errExit("mmap");
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, addr, sb.st_size) != sb.st_size)
fatal("partial/failed write");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}1.3 파일 동기화
#include <sys/mman.h>
int msync (void *addr, size_t length, int flags); //강제로 write-back 수행
///
flags
(MS_SYNC : write-back 끝날 때 까지 대기
MS_ASYNC : write-back 비동기적으로 수행
MS_INVALIDATE : 메모리에 변경 된 내용 무효화1.4 파일 크기 변경
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length);
///
path / fd : 파일 경로 or file descriptor
lenght : 늘릴 공간의 크기 (0으로 채워짐)1.5 메모리 보호모드 변경
mprotect: 메모리에 대한 접근을 제어하는 함수
#include <sys/mman.h>
int mprotect(void *addr, size_t length, int prot);
///
addr : 접근을 제어할 주소
length :주소 기준으로 관여할 길이
prot : 설정 값
PROT_NONE : 접근할 수 없다.
PROT_READ : 읽기
PROT_WRITE : 쓰기
PROT_EXEC : 실행
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : fail)ex) 예제
t_mprotect: 특정 영역의 메모리의 보호 설정을 확인하는 코드
#define _BSD_SOURCE /* Get MAP_ANONYMOUS definition from <sys/mman.h> */
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
#define LEN (1024 * 1024)
#define SHELL_FMT "cat /proc/%ld/maps | grep zero"
#define CMD_SIZE (sizeof(SHELL_FMT) + 20)
/* Allow extra space for integer string */
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char cmd[CMD_SIZE];
char *addr;
/* Create an anonymous mapping with all access denied */
addr = mmap(NULL, LEN, PROT_NONE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED)
errExit("mmap");
/* Display line from /proc/self/maps corresponding to mapping */
printf("Before mprotect()\n");
snprintf(cmd, CMD_SIZE, SHELL_FMT, (long) getpid());
system(cmd);
/* Change protection on memory to allow read and write access */
if (mprotect(addr, LEN, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE) == -1)
errExit("mprotect");
printf("After mprotect()\n");
system(cmd); /* Review protection via /proc/self/maps */
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}1.6 메모리 잠금
mlock,munlock: 물리 메모리에 상주 보장 & 해제
#include <sys/mman.h>
int mlock(const void *addr, size_t len);
int munlock(const void *addr, size_t len);1.7 메모리 영역에 대한 힌트 제공
madvise(): 해당 메모리 공간에 수행 할 명령에 대한 힌트 반환
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
int madivse(void *addr, size_t length, int advice);
///
addr : 힌트를 얻을 주소
length : 힌트를 얻을 주소의 길이
advice : 앞으로 해당 메모리 공간에 수행할 명령
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : fail)advice값 정리
| MADV_NORMAL | MADV_RANDOM | MADV_SEQUENTIAL | MADV_WILLNEED | MADV_DONTNEED | MADV_SPACEAVAIL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 특별한 작업 없음 | 무작위 페이지 참조 | 순차 페이지 참조 | 해당 페이지 필요 예상 | 해당 페이지 필요 X 예상 | 해당 메모리 예약되었는지 확인 |
ex) 예제
#define _BSD_SOURCE /* Get mincore() declaration and MAP_ANONYMOUS
definition from <sys/mman.h> */
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
/* Display residency of pages in range [addr .. (addr + length - 1)] */
static void
displayMincore(char *addr, size_t length)
{
unsigned char *vec;
long pageSize, numPages, j;
#ifndef _SC_PAGESIZE
pageSize = getpagesize(); /* Some systems don't have _SC_PAGESIZE */
#else
pageSize = sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE);
#endif
numPages = (length + pageSize - 1) / pageSize;
vec = malloc(numPages);
if (vec == NULL)
errExit("malloc");
if (mincore(addr, length, vec) == -1)
errExit("mincore");
for (j = 0; j < numPages; j++) {
if (j % 64 == 0)
printf("%s%10p: ", (j == 0) ? "" : "\n", addr + (j * pageSize));
printf("%c", (vec[j] & 1) ? '*' : '.');
}
printf("\n");
free(vec);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *addr;
size_t len, lockLen;
long pageSize, stepSize, j;
if (argc != 4 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s num-pages lock-page-step lock-page-len\n", argv[0]);
#ifndef _SC_PAGESIZE
pageSize = getpagesize();
if (pageSize == -1)
errExit("getpagesize");
#else
pageSize = sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE);
if (pageSize == -1)
errExit("sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE)");
#endif
len = getInt(argv[1], GN_GT_0, "num-pages") * pageSize;
stepSize = getInt(argv[2], GN_GT_0, "lock-page-step") * pageSize;
lockLen = getInt(argv[3], GN_GT_0, "lock-page-len") * pageSize;
addr = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED)
errExit("mmap");
printf("Allocated %ld (%#lx) bytes starting at %p\n",
(long) len, (unsigned long) len, addr);
printf("Before mlock:\n");
displayMincore(addr, len);
/* Lock pages specified by command-line arguments into memory */
for (j = 0; j + lockLen <= len; j += stepSize)
if (mlock(addr + j, lockLen) == -1)
errExit("mlock");
printf("After mlock:\n");
displayMincore(addr, len);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}2. 매모리 매핑을 이용한 IPC
같은 메모리 매핑 영역을 공유해 프로세스들 사이의 통신이 가능하다.
Inter Process Communication 방법들
- Pipe
- Message Queue
- Shared Memory
- Semaphore
ex) 예제
t_mmap: 공유 메모리를 통해 IPC를 수행하는 코드
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
#define MEM_SIZE 10
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *addr;
int fd;
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s file [new-value]\n", argv[0]);
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
errExit("open");
addr = mmap(NULL, MEM_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED)
errExit("mmap");
if (close(fd) == -1) /* No longer need 'fd' */
errExit("close");
printf("Current string=%.*s\n", MEM_SIZE, addr);
/* Secure practice: output at most MEM_SIZE bytes */
if (argc > 2) { /* Update contents of region */
if (strlen(argv[2]) >= MEM_SIZE)
cmdLineErr("'new-value' too large\n");
memset(addr, 0, MEM_SIZE); /* Zero out region */
strncpy(addr, argv[2], MEM_SIZE - 1);
if (msync(addr, MEM_SIZE, MS_SYNC) == -1)
errExit("msync");
printf("Copied \"%s\" to shared memory\n", argv[2]);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}