24.01.10 최초 작성
1. per-CPU variable
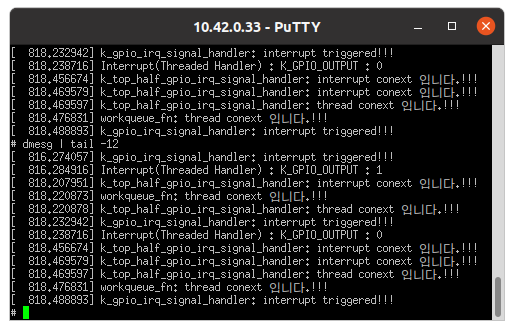
-
SMP 시스템에서 각 cpu마다 담당하는 변수를 두어 공유 데이터를 최소화하는 방법
-
queue_work_on(): cpu를 지정해worker thread를 실행
static irq_handler_t k_top_half_gpio_irq_signal_handler(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id)
{
...
atomic_inc(&k_atomic_cpu_num);
queue_work_on(atomic_read(&k_atomic_cpu_num) % num_online_cpus(), k_workqueue, &work);
// 인터럽트 핸들러 실행마다 다른 cpu에 worker thread를 실행시킴
// num_online_cpus() : 활성화된 cpu 갯수
...
}smp_processor_id(): 현재 스레드가 실행 중인 cpu id를 반환
DEFINE_PER_CPU(int, call_count);
static void workqueue_fn(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct k_list *new_node = NULL;
int this_cpu = smp_processor_id();
int *this_count = &per_cpu(call_count, this_cpu);
pr_info("cpu: %d, count: %d\n", this_cpu, *this_count);
*this_count += 1;
new_node = kmalloc(sizeof(struct k_list), GFP_KERNEL);
new_node->data = k_value++;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&new_node->list);
write_lock(&k_rwlock);
list_add_tail(&new_node->list, &k_list_head);
write_unlock(&k_rwlock);
}2. atomic
- 공유 데이터에 접근할 때(
write) 하드웨어적으로 다른 작업이 이뤄지는 것을 방지 - 공유 데이터 연산을
lock없이 연산 가능
atomic_inc():atomic_t데이터를 1 증가atomic_read():atomic_t데이터를 읽음
// `atomic_t` 자료형을 0으로 초기화
atomic_t k_atomic_cpu_num = ATOMIC_INIT(0);
static irq_handler_t k_top_half_gpio_irq_signal_handler(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id)
{
...
atomic_inc(&k_atomic_cpu_num);
queue_work_on(atomic_read(&k_atomic_cpu_num) % num_online_cpus(), k_workqueue, &work);
// 인터럽트 핸들러 실행마다 다른 cpu에 worker thread를 실행시킴
// num_online_cpus() : 활성화된 cpu 갯수
...
}3. lock-less list

lock이 필요 없는non-blocking알고리즘 활용하는linked list
- 인터럽트가 발생할 때 마다 워크큐에 데이터 저장, 데이터를 읽을 시 워크큐에 저장한 데이터 읽고 삭제
struct llist_node,struct llist_head:llist자료형 선언init_llist_head():llisth_head초기화
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/llist.h>
// llist 정의
struct k_list {
struct llist_node llnode;
int data;
};
// llist head 정의
struct llist_head k_list_head;
static int __init k_module_init(void)
{
...
k_workqueue = create_workqueue("k_wq");
init_llist_head(&k_list_head); //llist head 초기화
...
}llist_add(),llist_del_all(): 리스트에 노드 추가, 리스트의 모든 노드 저장
static void workqueue_fn(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct k_list *temp_node = NULL;
if (in_interrupt()) {
pr_info("workqueue_fn: interrupt conext 입니다.!!!\n");
} else {
pr_info("workqueue_fn: thread conext 입니다.!!!\n");
}
temp_node = kmalloc(sizeof(struct k_list), GFP_KERNEL);
temp_node->data = k_value++;
llist_add(&temp_node->llnode, &k_list_head);
}
static ssize_t k_driver_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *offset)
{
struct k_list *node, *tmp;
struct llist_node *head;
int list_count = 0;
head = llist_del_all(&k_list_head);
if (!head)
return 0;
llist_for_each_entry_safe(node, tmp, head, llnode) {
pr_info("list_count : %d, data : %d\n", list_count++, node->data);
kfree(node);
}
pr_info("Node count: %d\n", list_count);
return BUF_SIZE;
}