단순 n + 1번 다익스트라를 써서 해결한 문제. 먼가 찝찝해서 문제 평가를 읽어보니 역방향 다익스트라를 쓰는 아이디어로 해결할 수 있다고 한다. 나중에 다시 한번 풀어봐야겠다.
문제 분석

이 문제는 x라는 도착점이 주어질 때 시작점에서 x를 찍고 다시 시작점으로 돌아오는 최소거리가 가장 길 때에 거리를 구하는 문제이다.
예를 들어 예제에 나오는 그래프에서는
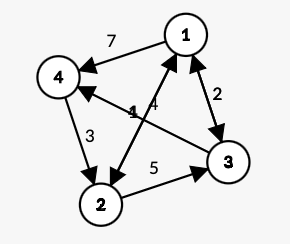
도착점이 2라고 할 때에, 시작점을 4으로 하면(4->2)(2->1->3->4) 최소거리가 10으로 가장 기므로 10이 정답이 된다.
발상 & 알고리즘 설계
이 문제는 다익스트라를 구현할 수 있다면 쉽게 해결할 수 있는 문제이다. 간선의 갯수가 적으므로 단순 n+1번 다익스트라를 돌려줘서 정답을 구해줘도 시간안에 해결할 수 있다.
한 가지 주의해야 할 점은 다시 돌아오는 것까지 최소 거리에 포함시켜야 하기에 도착점에서 시작점으로 한번 더 다익스트라를 진행해주어야 한다.
코드
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<climits>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n;
int m;
int x;
int answer = 0;
int temp = 0;
vector<pair<int, int>> v[1001] = {};
int check[1001] = {};
void dijkstra(int sv, int target){
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<>> pq;
fill(check, check + n + 1, INT_MAX);
pq.emplace(0, sv);
check[sv] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()){
int cur_i = pq.top().second;
int cur_cost = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
if(cur_i == target){
break;
}
for(int i = 0; i < v[cur_i].size(); i++){
int next_i = v[cur_i][i].first;
int next_cost = cur_cost + v[cur_i][i].second;
if(next_cost < check[next_i]){
check[next_i] = next_cost;
pq.emplace(next_cost, next_i);
}
}
}
temp += check[target];
if(sv != x){
dijkstra(x, sv);
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> x;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int from;
int to;
int cost;
cin >> from >> to >> cost;
v[from].emplace_back(to, cost);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(x == i)
continue;
temp = 0;
dijkstra(i, x);
answer = max(answer, temp);
}
cout << answer;
}