링크
문제
N×M크기의 배열로 표현되는 미로가 있다.
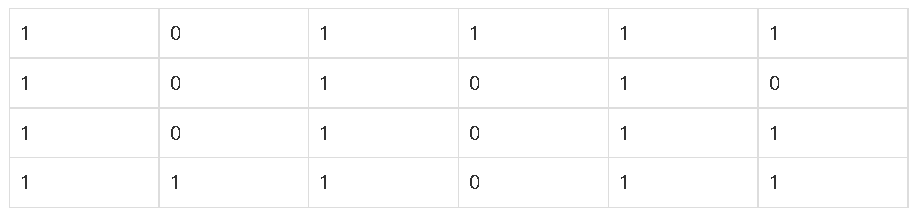
미로에서 1은 이동할 수 있는 칸을 나타내고, 0은 이동할 수 없는 칸을 나타낸다. 이러한 미로가 주어졌을 때, (1, 1)에서 출발하여 (N, M)의 위치로 이동할 때 지나야 하는 최소의 칸 수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오. 한 칸에서 다른 칸으로 이동할 때, 서로 인접한 칸으로만 이동할 수 있다.
위의 예에서는 15칸을 지나야 (N, M)의 위치로 이동할 수 있다. 칸을 셀 때에는 시작 위치와 도착 위치도 포함한다.
입력
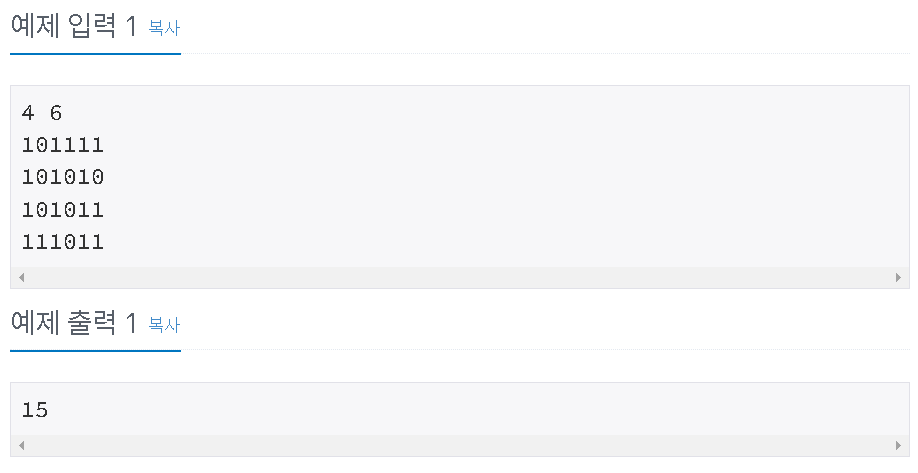
첫째 줄에 두 정수 N, M(2 ≤ N, M ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 M개의 정수로 미로가 주어진다. 각각의 수들은 붙어서 입력으로 주어진다.
출력
첫째 줄에 지나야 하는 최소의 칸 수를 출력한다. 항상 도착위치로 이동할 수 있는 경우만 입력으로 주어진다.
# Code
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
//1이 이동할 수 있는 경로
public class Main {
public static int arr[][];
public static boolean visited[][];
public static int[] dx= {0,0,-1,1};
public static int[] dy= {-1,1,0,0};
public static int row;
public static int column;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
row=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
column=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr=new int[row][column];
visited=new boolean[row][column];
for(int i=0; i<row; i++)
{
String str=br.readLine();
for(int j=0; j<column; j++)
{
arr[i][j]=str.charAt(j)-'0';
}
}
BFS(0,0);
System.out.println(arr[row-1][column-1]);
}
public static void BFS(int x, int y)
{
Queue<int[]> q=new LinkedList<int[]>();
q.add(new int[] {x,y});
visited[x][y]=true;
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int now[]=q.poll();
int nowX=now[0];
int nowY=now[1];
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
int nx=nowX+dx[i];
int ny=nowY+dy[i];
if(nx<=-1 || nx>=row || ny<=-1 || ny>=column)
continue;
if(visited[nx][ny] || arr[nx][ny]==0)
continue;
q.add(new int[] {nx, ny});
arr[nx][ny]=arr[nowX][nowY]+1;
visited[nx][ny]=true;
}
}
}
}

