오늘은 SQL관련해 배운 내용을 예제를 풀며 복습했다.
근데 시작하자마자 난관을 맞이했다. 왠지 모르겠는데 mysql이 실행이 안되어서 지웠다가 다시 깔고 난리를 쳤다.
맥 homebrew로 설치 삭제하는 방법
이 블로그를 참고해서 삭제하고 다시 세팅했다.
예제로 풀어본 대표적인 케이스
1. 요구사항을 확인해서 알맞은 테이블 구성하기
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) not NULL,
`email` varchar(255) not NULL
);
CREATE TABLE `content` (
`id` int PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` varchar(255) not null ,
`body` varchar(255) not null ,
`created_at` timestamp not NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`userId` int,
FOREIGN KEY (`userId`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`)
);
CREATE TABLE `category` (
`id` int PRIMARY KEY not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) not null
);
CREATE TABLE `content_category` (
`id` int not null PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`contentId` int not null,
`categoryId` int not null
);
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` int not null primary key AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) not null
);
ALTER TABLE `user` ADD roleId int;
ALTER TABLE `user` ADD FOREIGN KEY (`roleId`) REFERENCES `role` (`id`);
ALTER TABLE `content` ADD FOREIGN KEY (`userId`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`);
ALTER TABLE `content_category` ADD FOREIGN KEY (`contentId`) REFERENCES `content` (`id`);
ALTER TABLE `content_category` ADD FOREIGN KEY (`categoryId`) REFERENCES `category` (`id`);이미 생성된 테이블에 데이터를 추가하고, FOREIGN KEY로 pk, fk연결을하니까 오류가 났다.
자바처럼 1번부터 차례대로 착착 읽어가면서 테이블을 확인하는게 아니고, 추가할 때 확인하는 거로 이해했다.
그래서 이미 있던 테이블에 데이터를 추가해서 연결할 떄는 ALTER TABLE을 이용해야한다.
근데 그냥 항상 ALTER TABLE을 사용하는게 낫다고 했던걸로 기억한다..
2. 현재있는 데이터베이스에 존재하는 모든 테이블 정보를 보기 위한 SQL문
SHOW TABLES;3. user 테이블의 구조를 보기위한 SQL문
DESC user;4. user 테이블에 존재하는 모든 컬럼을 포함한 모든 데이터를 확인하기 위한 SQL문
SELECT * FROM user;
// user 테이블에서 특정 컬럼의 데이터만 찾을 때
SELECT name FROM user;5. user 테이블에 데이터를 추가하기 위한 SQL문
INSERT INTO user (name,email) VALUE ('DONGA' , 'donga@email.com');6. content 테이블의 테이터를 수정하기 위한 SQL문
UPDATE content SET body = '변경할 내용(변경 후)' WHERE title = '변경할 위치 (변경 전)';7. user 테이블에서 특정 조건을 가진 데이터를 찾기위한 SQL문
SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = 'luckyKim';
//특정 조건이 아닌 데이터를 찾을 때
SELECT * FROM user WHERE name <> 'luckyKim';8. content의 title 과 그 콘텐츠를 작성한 user의 name을 찾기위한 SQL문
//저자가 없더라도 컨텐츠의 title을 찾아야할 때
SELECT content.title, user.name FROM content LEFT JOIN user ON content.userId = user.id;
//저자가 있는 콘텐츠의 title만 찾을 때
SELECT content.title, user.name FROM content JOIN user ON content.userId = user.id;
-
INNER JOIN : 기준 테이블과 조인 테이블 모두 데이터가 존재해야 조회된다.
-
OUTTER JOIN : 기준 테이블에만 데이터가 존재하면 조회된다.
9. 어느 role에도 속하지 않는 user의 모든 컬럼 데이터를 찾기위한 SQL문
SELECT * FROM user LEFT JOIN role ON user.roleId = role.id WHERE role.id IS NULL;
10. '00'이 작성한 content의 title을 찾기 위한 SQL문
SELECT content.title FROM content LEFT JOIN user ON content.userId = user.id WHERE user.name = 'DONGA';
//donga가 작성한 content의 category name을 찾기 위한 SQL문
SELECT category.name FROM category LEFT JOIN content_category ON category.id = content_category.categoryId " +
"LEFT JOIN content ON content_category.contentId = content.id " +
"LEFT JOIN user ON content.userId = user.id " +
"WHERE user.name = 'donga';11. '00'이 작성한 글의 개수 (컬럼명: ContentCount)를 출력하기 위한 SQL문
SELECT COUNT(title) AS ContentCount FROM content " +
"LEFT JOIN user ON content.userId = user.id " +
"WHERE user.name = 'donga';
//각 user(컬럼명: name)가 작성한 글의 개수 (컬럼명: ContentCount)를 출력하기 위한 SQL
SELECT user.name AS name, COUNT(content.id) AS ContentCount FROM user " +
"LEFT JOIN content ON user.id = content.userId " +
"GROUP BY name;SQL에서 가장 힘들었던게 JOIN 이었는데 위 예제를 풀면서 구조를 보고 특정 조건을 구하는 연습을 하니까 '아 이렇게하니까 되는구나' 정도를 알았다.
또, 테스트 통과하는지 확인하기 전에 터미널에서 이 조건문을 넣으면 어떤 결과가 나오는지 확인해가며 문제를 풀었다.
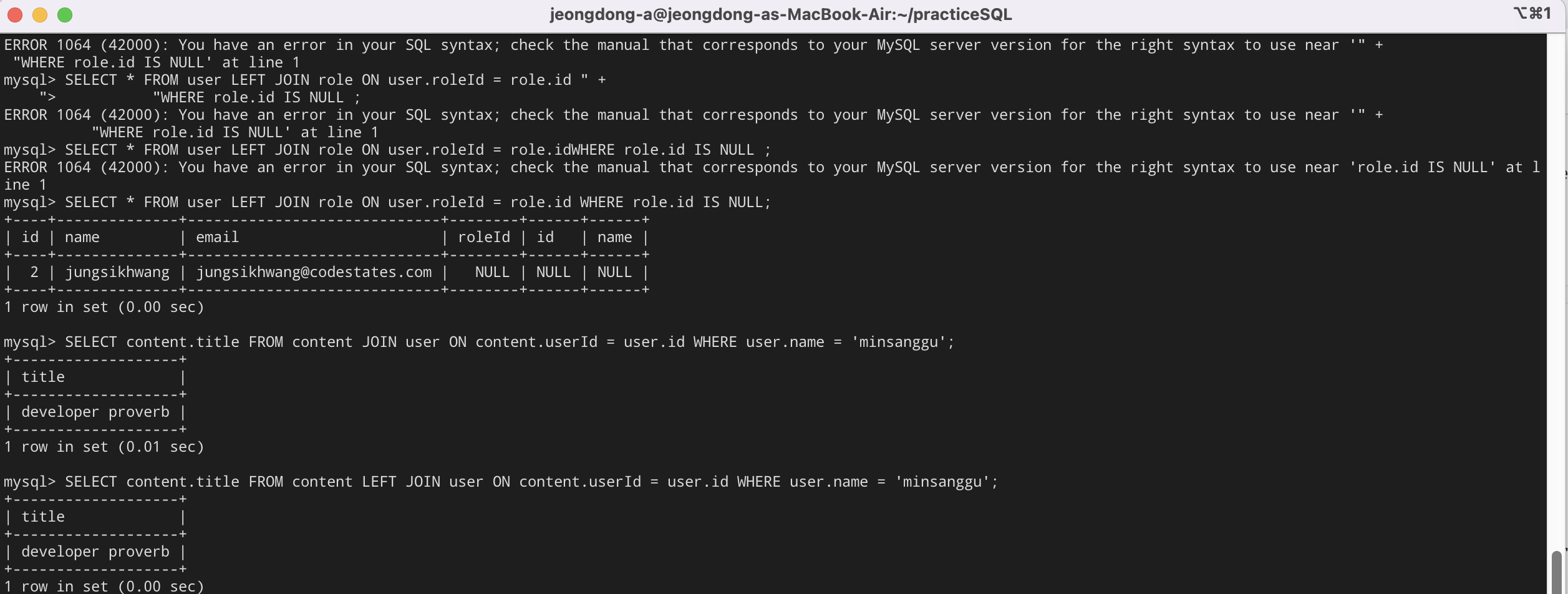
요렇게 에러도 만나, 어떤 데이터가 나오는지 확인했다.
이렇게 하니까 작동하는 구조에대해서 좀 손에 익은 것 같다.
