우선순위 큐는 일반 큐와 다르게 요소의 삽입 순서(FIFO)가 아니라 우선순위에 따라 요소를 정렬하고 처리한다.
데이터에서 가장 작은 값이나 가장 큰 값을 자주 조회하고 삭제해야 하는 경우, 우선순위 큐는 O(log n) 시간 복잡도로 이를 처리할 수 있어 효율적이다.
우선 순위 큐는 실시간 서비스를 제공하는 애플리케이션에서 활용할 수 있다.
소켓(WebSocket)으로 전달되는 데이터의 타입별 우선순위와 타임스탬프를 조합하여 우선순위 큐로 관리하면, 중요도가 높은 데이터는 즉시 처리하고 덜 중요한 데이터는 대기열에 추가하여 순차적으로 처리할 수 있다.
이 외에도 애니메이션 관리, 리소스 로딩 최적화 등 다양한 상황에서 활용될 수 있다.
O(log n)
로그 시간 복잡도 O(log n)는 알고리즘이 데이터의 크기 n에 따라 굉장히 빠르게 실행되는 것을 의미한다.
한 번의 연산마다 탐색 범위를 절반씩 줄이기 때문에, 처리 시간이 매우 효율적이다.
- 데이터가 1,000개면 최대 10번의 연산
- 데이터가 1,000,000개라도 최대 20번의 연산만 필요!
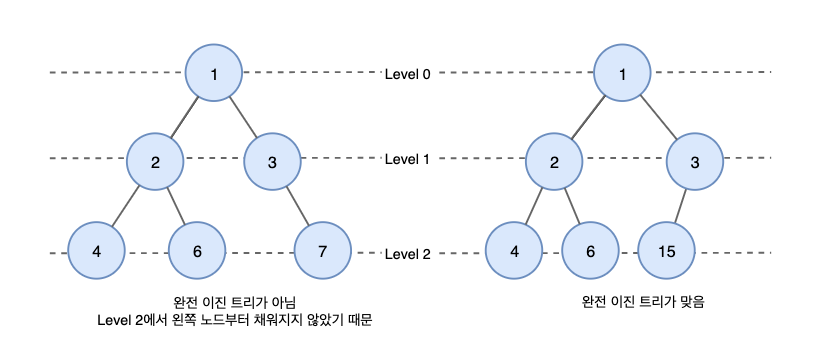
우선순위 큐는 완전 이진트리를 기반으로 구현된다.
시간 복잡도
우선 순위 큐
- 삽입(enqueue) : O(log n)
요소를 추가할 때 힙 구조를 유지하기 위해 비교 및 교환 작업이 필요 - 제거(dequeue) : O(log n)
최우선 요소를 제거하고 힙을 재정렬
일반 큐
- 삽입(enqueue) : O(1)
큐의 뒤쪽에 새로운 요소를 추가하는 작업은 상수 시간. - 제거(dequeue) : O(n)
연결 리스트가 아닌 경우 요소를 제거한 뒤 나머지 요소를 재정렬해야 하므로 O(n) 소요
구현
class Heap {
constructor(array = []) {
this.heap = array.slice(); // 배열 복사
this.#buildHeap(); // 초기 힙 빌드
}
/*************** 프라이빗 메소드 ***************/
#getParentIndex(index) {
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
#getLeftChildIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 1;
}
#getRightChildIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 2;
}
#swap(index1, index2) {
[this.heap[index1], this.heap[index2]] = [this.heap[index2], this.heap[index1]];
}
#buildHeap() {
const startIndex = Math.floor(this.heap.length / 2) - 1;
for (let i = startIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
this.#heapifyDown(i);
}
}
#heapifyUp() {
let index = this.heap.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = this.#getParentIndex(index);
if (this.compare(this.heap[parentIndex], this.heap[index])) {
this.#swap(parentIndex, index);
index = parentIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
#heapifyDown(index = 0) {
const length = this.heap.length;
let extreme = index;
while (true) {
const leftChildIndex = this.#getLeftChildIndex(index);
const rightChildIndex = this.#getRightChildIndex(index);
if (leftChildIndex < length && this.compare(this.heap[extreme], this.heap[leftChildIndex])) {
extreme = leftChildIndex;
}
if (rightChildIndex < length && this.compare(this.heap[extreme], this.heap[rightChildIndex])) {
extreme = rightChildIndex;
}
if (extreme !== index) {
this.#swap(index, extreme);
index = extreme;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
/*************** 퍼블릭 메소드 ***************/
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
this.#heapifyUp();
}
remove() {
if (this.heap.length === 0) throw new Error("Heap is empty");
if (this.heap.length === 1) return this.heap.pop();
const root = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
this.#heapifyDown();
return root;
}
peek() {
if (this.heap.length === 0) throw new Error("Heap is empty");
return this.heap[0];
}
}
class MinHeap extends Heap {
compare(parent, child) {
return parent > child; // 최소 힙
}
}
class MaxHeap extends Heap {
compare(parent, child) {
return parent < child; // 최대 힙
}
}초기 힙 빌드
초기 힙 빌드시, 원소를 하나하나 삽입하면 O(n \log n)의 시간이 소요되지만, 아래와 같은 방법으로 빌드하면 O(n)에 최적화할 수 있다.
1. 리프 노드는 작업할 필요가 없다:
-
리프 노드는 자식 노드가 없기 때문에 힙 조건(부모 ≤ 자식)을 검사하거나 교환할 필요가 없다.
-
즉, 리프 노드는 부모 노드보다 크기만 하면 된다. (최소 힙 인 경우.. 최대 힙은 그 반대)
-
리프 노드는 항상 배열의 후반부에 위치하며, 그 위치는 floor(this.heap.length / 2 ) 이다.
-
예를 들어, 배열 길이가 8이라면 리프 노드는 인덱스 4, 5, 6, 7 이다.
-
heapifyDown()은 부모 노드와 자식 노드만 비교하며, 필요하면 값을 교환한다.
2. 그래서 왜 O(n)?
-
heapifyDown()의 작업량은 부모 노드의 깊이에 따라 달라진다.
-
트리의 구조상, 상위 노드들은 적고, 하위 노드들은 많다는 점이 중요
-
상위 노드: 작업량은 많지만 노드 수가 적다.
-
하위 노드: 작업량은 적지만 노드 수가 많다.
-
이 균형 덕분에 전체 작업량은 O(n)에 가깝게 수렴한다.