문제
보드의 크기와 보드판의 블록 상태가 주어졌을 때, 최대 5번 이동해서 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 블록의 값을 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
문제접근
2048 게임의 구현이 대략 어떤식으로 이뤄지는지 알 수 있었던 재밌는 문제였다. 학교 심화프로그래밍 시간에 어영부영 2048 프로젝트를 했던 기억이 있는데, 이제야 원리를 이해할 수 있었다.
- 우리가 취할 수 있는 action은 4가지다.
왼쪽 이동,위쪽 이동,오른쪽 이동그리고아래쪽 이동이다. - Bruteforce의 원칙을 생각한다.
고정- >행동->해제원칙은 이 문제에도 적용할 수 있다. - 보드의 크기는 최대 20 X 20이므로 bruteforce를 적용할 수 있다.
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N, ans;
vector<vector<int>> board;
void action(int actionSelector) {
queue<int> q;
switch(actionSelector) {
case 0: // 왼쪽으로 움직이는 경우
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
if (board[y][x]) q.push(board[y][x]);
board[y][x] = 0;
}
int curRowIdx = 0; // 현재 i번째 행의 인덱스
while (!q.empty()) {
int tempVar = q.front(); q.pop();
if (board[y][curRowIdx] == 0) board[y][curRowIdx] = tempVar;
else if (board[y][curRowIdx] == tempVar) board[y][curRowIdx++] *= 2;
else board[y][++curRowIdx] = tempVar;
}
}
break;
case 1: // 오른쪽으로 움직이는 경우
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = N - 1; x >= 0; --x) {
if (board[y][x]) q.push(board[y][x]);
board[y][x] = 0;
}
int curRowIdx = N - 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int tempVar = q.front(); q.pop();
if (board[y][curRowIdx] == 0) board[y][curRowIdx] = tempVar;
else if (board[y][curRowIdx] == tempVar) board[y][curRowIdx--] *= 2;
else board[y][--curRowIdx] = tempVar;
}
}
break;
case 2: // 위쪽으로 움직이는 경우
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
if (board[y][x]) q.push(board[y][x]);
board[y][x] = 0;
}
int curColIdx = 0; // 현재 i번째 열의 인덱스
while (!q.empty()) {
int tempVar = q.front(); q.pop();
if (board[curColIdx][x] == 0) board[curColIdx][x] = tempVar;
else if (board[curColIdx][x] == tempVar) board[curColIdx++][x] *= 2;
else board[++curColIdx][x] = tempVar;
}
}
break;
case 3: // 아래쪽으로 움직이는 경우
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
for (int y = N - 1; y >= 0; --y) {
if (board[y][x]) q.push(board[y][x]);
board[y][x] = 0;
}
int curColIdx = N - 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int tempVar = q.front(); q.pop();
if (board[curColIdx][x] == 0) board[curColIdx][x] = tempVar;
else if (board[curColIdx][x] == tempVar) board[curColIdx--][x] *= 2;
else board[--curColIdx][x] = tempVar;
}
}
break;
}
}
void solve(int depth) {
if (depth == 5) { // 5회 행동 종료시
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y)
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x)
ans = max(ans, board[y][x]);
return;
}
vector<vector<int>> currBoard(N, vector<int>(N));
copy(begin(board), end(board), begin(currBoard));
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
action(i); // 고정
solve(depth + 1); // 행동
copy(begin(currBoard), end(currBoard), begin(board)); // 해제
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> N; // 보드의 크기 (N X N)
board = vector<vector<int>> (N, vector<int>(N, 0));
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y)
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x)
cin >> board[y][x];
solve(0);
cout << ans << '\n';
}- 각 행동은 queue를 사용해서 해당 행 또는 열의 모든 원소를 저장한 뒤 다시 순차적으로 pop() 하는 방식으로 구현한다.
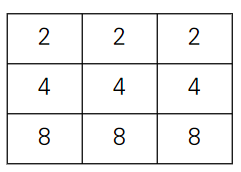
- 다음과 같이 주어진 게임판이 있다고 가정하자.
- 왼쪽으로 움직인다면 다음과 같은 과정을 거친다.
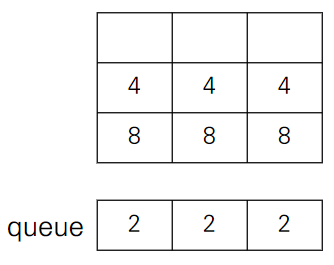
- 먼저 0번째 행의 0번째 열부터 차례대로 queue에 push한다.
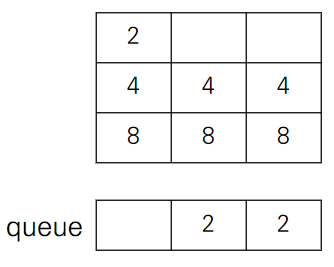
- 현재 [0][0]이 0이므로 그냥 queue의 front 값을 넣어주고 pop한다.
- 현재 [0][0]이 2이고 queue의 front 값도 2이므로 queue의 front 값을 pop하고 [0][0]값을 2배로 늘려준다.
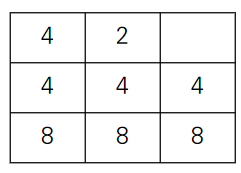
- 현재 [0][1]이 0이므로 그냥 queue의 front 값을 넣어주고 pop한다.
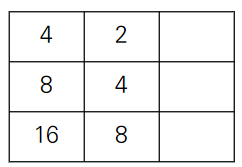
- 이를 모든 행에 대해 수행하면 왼쪽 이동 연산이 완료된다.
결과