문제
문제 링크: https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/60063
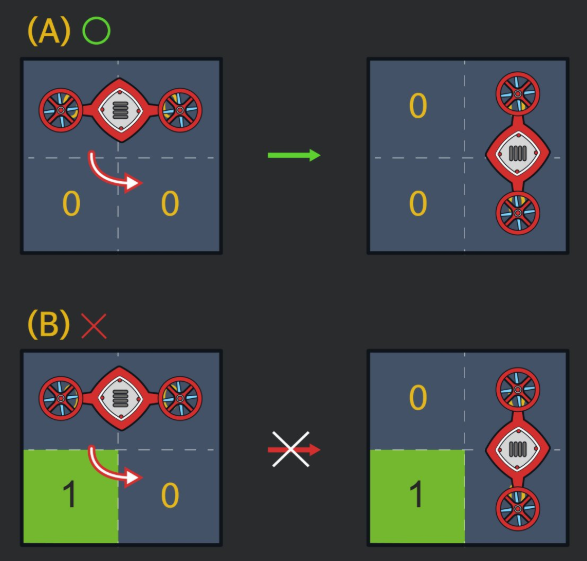
(1, 1)과 (1, 2) 두 칸을 차지하는 드론을 움직이거나 회전시켜서 (N, N)에 도착할 수 있는 최소 행동 횟수를 구하라.
문제접근
문제 풀이 전
- 최소 행동 횟수를 구하기 위해서는 당연히 bruteforce 방식으로 BFS로 풀어야 함을 떠올린다.
- 이동은 상, 하, 좌, 우 4방향이 가능하다.
- Q. 좌상단에서 우하단으로 이동하니 윗방향과 왼쪽방향으로 이동할 필요는 없지 않나?
- 아니다. 반례가 존재하므로 생각해보자. 반례는 코드 항목 아래에 기술한다.
- Q. 좌상단에서 우하단으로 이동하니 윗방향과 왼쪽방향으로 이동할 필요는 없지 않나?
- 회전은 왼쪽 회전, 오른쪽 회전이 가능하다.
- 좋은 코드를 작성하기 위해서는 우선 명확한 말로 설명이 가능해야 한다.
- 단순히 방향에 대한 고려없이 왼쪽 회전, 오른쪽 회전이라고 표현하는 것은 당사자조차 햇갈리게 만든다.
- 드론이 가로방향일 때는? 드론이 세로방향일 때는?
- 드론의 방향을 정하면 왼쪽 회전과 오른쪽 회전을 명확히 표현할 수 있게 된다.
- 좌익 또는 우익 중 어느 한 쪽이라도
(N, N)좌표에 도달한다면 BFS를 중지한다.
문제 풀기 과정
- 이 문제의 정답률은 1.4% 이다. 이 문제가 어려운 이유는 두 가지다.
- 일반적인 BFS 문제와는 달리 점이 한 칸이 아니라 두 칸이라는 점이다.
- 드론의 방향에 따라 회전을 고려해줘야 한다.
- 상, 하, 좌, 우 4방향에 대한 이동은 드론의 방향과 관계없다.
(y, x)기준 상:(y-1, x), 하:(y+1, x), 좌:(y, x-1), 우:(y, x+1)const int d[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};으로 표현.
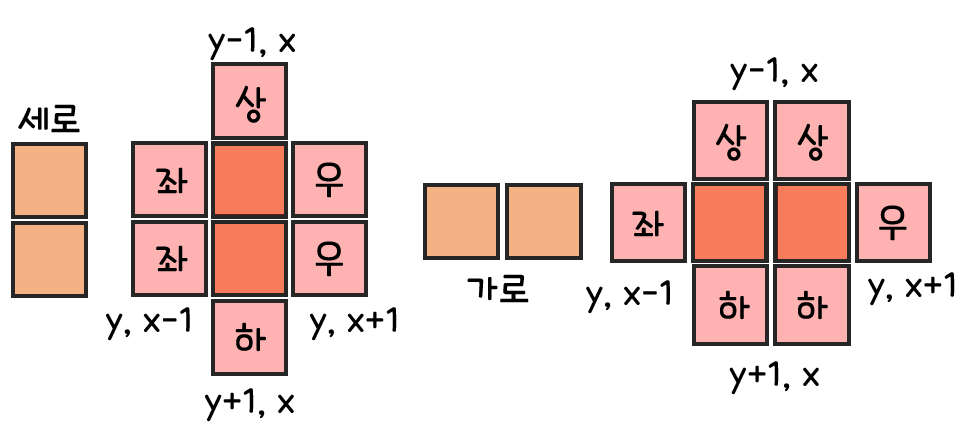
- 회전 이동은 드론의 방향과 관계가 있다.
- 드론이 가로 방향일 때 왼쪽으로 회전하면,
(y, x)는(y-1, x)로 변경된다. - 드론이 가로 방향일 때 오른쪽으로 회전하면,
(y, x)는(y+1, x)로 변경된다. - 드론이 세로 방향일 때 왼쪽으로 회전하면,
(y, x)는(y, x-1)로 변경된다. - 드론이 세로 방향일 때 오른쪽으로 회전하면,
(y, x)는(y, x+1)로 변경된다.
- 드론이 가로 방향일 때 왼쪽으로 회전하면,
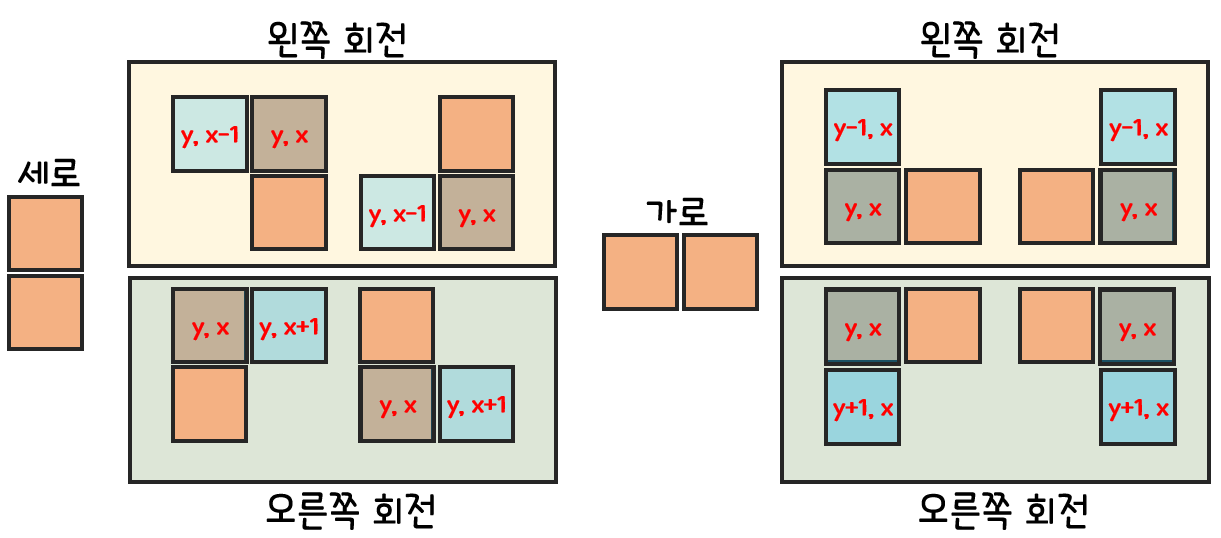
- 현재 드론의 위치에서 8가지 이동을 통해 드론이 갈 수 있는 모든 위치를 파악한다.
- 해당 점이
board의 범위를 벗어나지 않는다면 갈 수 있다. - 해당 점을 이동화는 과정에서 벽과 만나지 않는다면 갈 수 있다.
- 해당 점이
- 갈 수 있는 점 후보들 중에서 아직 BFS를 통해 방문하지 않은 점이 있다면
queue에 넣는다.- 가능한 다른 이동 경로 상에서 이미 탐색한 점은 다시 방문할 필요가 없다.
- 왜냐하면 이 문제는
최소 cost를 구하는 문제이기 때문이다. 만일 이 조건을 무시한다면 무한 loop가 발생할 여지가 있다. - 결과적으로,
visited배열을 만들어서 현재까지 탐색한 점의 정보를 저장할 필요가 있다.
코드
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
static int N;
typedef struct Node {
int ly, lx, ry, rx;
Node(int a, int b, int c, int d) {
this->ly = a; this->lx = b;
this->ry = c; this->rx = d;
}
}Node;
inline bool isSafe(Node cur) { // 현재 좌표가 board 범위내에 있는지 확인한다.
return ((0 <= cur.ly && cur.ly < N) && (0 <= cur.lx && cur.lx < N) &&
((0 <= cur.ry && cur.ry < N) && (0 <= cur.rx && cur.rx < N)));
}
vector<Node> getNextPos(Node cur, vector<vector<int>> board) {
const int d[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
vector<Node> ret;
// [행동 1]: 상, 하, 좌, 우 4방향에 대해 이동한다.
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
Node nextPos(cur.ly + d[i][0], cur.lx + d[i][1], cur.ry + d[i][0], cur.rx + d[i][1]);
if (isSafe(nextPos) && board[nextPos.ly][nextPos.lx] == 0 && board[nextPos.ry][nextPos.rx] == 0)
ret.push_back(nextPos);
}
int offset[2] = {-1, 1};
// [행동 2]: 드론이 세로 방향일 때 시계방향, 시계반대방향으로 회전한다.
if (cur.ly == cur.ry) {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
int newLy = cur.ly + offset[i], newRy = cur.ry + offset[i];
if (isSafe(Node(newLy, cur.lx, newRy, cur.rx)) && !board[newLy][cur.lx] && !board[newRy][cur.rx]) {
ret.push_back(Node(newLy, cur.lx, cur.ly, cur.lx));
ret.push_back(Node(newRy, cur.rx, cur.ry, cur.rx));
}
}
}
// [행동 3]: 드론이 가로 방향일 때 회전한다.
else {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
int newLx = cur.lx + offset[i], newRx = cur.rx + offset[i];
if (isSafe(Node(cur.ly, newLx, cur.ry, newRx)) && !board[cur.ly][newLx] && !board[cur.ry][newRx]) {
ret.push_back(Node(cur.ly, newLx, cur.ly, cur.lx));
ret.push_back(Node(cur.ry, newRx, cur.ry, cur.rx));
}
}
}
return ret;
}
int solution(vector<vector<int>> board) {
N = board.size();
queue<pair<Node, int>> q;
q.push({Node(0, 0, 0, 1), 0}); // 현재 드론의 좌표정보와 이동횟수(cost)
vector<Node> visited; // 지금까지 성공적으로 방문한 좌표 정보를 저장하는 컨테이너.
visited.push_back(Node(0, 0, 0, 1));
// Start BFS
while(!q.empty()) {
Node pos = q.front().first;
int cost = q.front().second;
q.pop();
// 좌측 좌표, 우측 좌표 중 한 칸이라고 (N-1, N-1)에 도달하면 탐색을 중단한다.
if ((pos.ly == N - 1 && pos.lx == N - 1) || (pos.ry == N - 1 && pos.rx == N - 1))
return cost;
// 현재 좌표로부터 갈 수 있는 모든 칸을 vector에 저장한다.
vector<Node> nextPos = getNextPos(pos, board);
for (int i = 0; i < nextPos.size(); ++i) {
bool safeFlag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < visited.size(); ++j)
// 이미 탐색한 칸은 더 이상 갈 필요가 없다. (무한 loop 방지)
if (nextPos[i].ly == visited[j].ly && nextPos[i].lx == visited[j].lx
&& nextPos[i].ry == visited[j].ry && nextPos[i].rx == visited[j].rx) {
safeFlag = false;
break;
}
// 현재 좌표가 처음 방문하는 새로운 좌표라면 queue와 vector에 push 해준다.
if (safeFlag) {
q.push({nextPos[i], cost + 1});
visited.push_back(nextPos[i]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}반례
input :
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
result : 21
input :
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
result : 11
input:
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]]
result : 33결과