Higher Order Function - Map, Filter, Reduce
First Class Function
A first class function is a function that was built with the intention of being passed around to other functions. It does one specific thing, does not have side effects, and is not intended to be called directly, but rather, to be used by ‘other functions.’
Those ‘other functions’ which accept one of those ‘first class functions’ as an argument are called higher order functions. Higher order functions also might be functions that return a function.
In a higher order function, when one of the parameters passed in is a function, that function is a callback function because it will be called back and used within the higher order function.
A higher order function is named as such because when using a callback to perform an operation within itself, the function has a ‘higher’ purpose than a regular function. When it returns a function, it also has a ‘higher’ purpose.
First-class functions
First-class-citizens get special treatments in the Javascript world. A programming language is said to have first-class functions when functions in that language (in which case javascript), a function can be passed as an argument to other functions, can be returned by another function and can be assigned as a value to a variable. Function in javascript can:
Assign a function to a variable
Pass a function as an argument
Return a function
In JavaScript, everything you can do with other types like object, string or number, you can do with functions. You can pass them as parameters to other functions (callbacks), assign them to variables and pass them around etc. this is why functions in javascript are known as First-Class Functions.
Higher order functions
Higher order functions are functions that operate on other functions, either by taking them as arguments or by returning them. In simple words, A higher-Order function is a function that receives a function as an argument, returns the functions as output or receives a function as an argument and returns the functions as output.Taking another function as an argument is often referred as a callback function. This is a concept that javascript uses a lot.
Built-in higher order functions
Eg. forEach(), find(), filter(), map(), reduce(), sort(), some(), every(), etc.
Array.prototype.map and array.prototype.filter and array.prototype.reduce are some of higher-order functions built into the language.
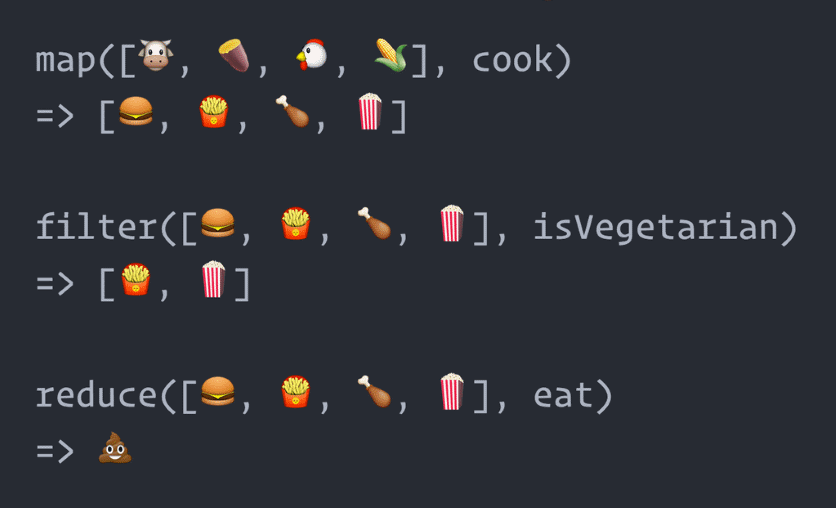
filter
will run a callback function on every elements in an array and will return either true of false for each item, if true, it will push the item to the new array
The filter() method creates a new array with all elements that pass the test provided by the callback function. The filter() function will run a callback function on every item in an array and will return either true or false for each of them. If true, it will push the item to the new array. The callback function passed to the filter() method accepts 3 arguments: element, index, and array.
map
will run a callback function ( provided as arguments) on every elements in the array and will push each result into a new array
The map() method creates a new array by calling the callback function provided as an argument on every element in the input array. The map() method will take every returned value from the callback function and creates a new array using those values
Parameter vs Argument
Parameter is at the time of declaration, Argument is an actual value of supply for the parameter
Function greet(name)
console.log( ‘Hello’+ name)
greet(‘john’)5개의 댓글
These concepts are foundational in JavaScript and are essential for building more modular and maintainable code, especially in functional programming paradigms. mapquest
It is a function that can be treated as a value, meaning it can be passed as an argument to other functions, returned from other functions, and assigned to variables. https://headsoccer.pro/
"Great topic! Higher-order functions like map, filter, and reduce are such powerful tools in programming. They not only make code more concise and readable but also encourage a functional programming mindset, which can lead to cleaner and more efficient solutions.
I especially love how map simplifies transforming data, filter makes it so easy to extract what you need, and reduce is like a Swiss Army knife for aggregating values. Do you have a favorite use case or any tips for someone just getting started with these functions?
https://theheadsoccerunblocked.com



Hot damn! Another great post! Much appreciated detective Scone.