📖저자님의 책 소개 영상: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q13Uj_5bH9M
🗓️TIL (this week I learned)
수 읽기, 정리, 몸풀기 문제1
목 배열, 해시 복습
금 🤔🤔🤔🤔
토 🤔🤔🤔🤔
- 여기는 풀면서 IQ 상승을 노려볼 만한다🤣
12-1 백트래킹과 백트래킹 알고리즘 개념⭐⭐⭐
🔷 백트래킹: 가능성이 없는 곳에서는 되돌아가고 가능성이 있는 곳을 탐색하는 알고리즘
- 핵심: 해가 될 가능성을 판단하는 것
- 유망 함수(promising function):
- 유망 = 해가 될 가능성이 있다.. - Constraint Satisfaction Problems (제약 충족 문제): 수많은 제약 조건을 충족하는 상태(states)를 찾아내는 수학 문제.
- ex) 스도쿠, 십자말 풀이, 8퀸 문제, 4색 문제(지도 색칠), 배낭문제, 문자열 파싱, 조합 최적화 등
🔷 N-퀸 문제: 체스판에 개를 배치했을 때, 퀸을 놓을 수 있는 경우의 수가 몇 개인지를 찾는 게 논점이다.
참고:
https://cs.lmu.edu/~ray/notes/backtracking/
n-queens wiki(en) -> 책 퀸즈 문제 풀이와 코드가 유사함.
-
N개 배치를 놓쳐서 며칠 동안 머리를 싸매고 있었다..ㅠㅠㅠㅠㅠ
-
예컨대, 4x4 체스판, 4개의 퀸을 놓을 수 있는 경우의 수는 4x4x4x4=256(완전탐색). 이를 유망함수를 추가해 탐색 대상을 줄여 해를 구할 수 있다. (4-퀸 문제의 해는 2개)


-
n-queens의 해
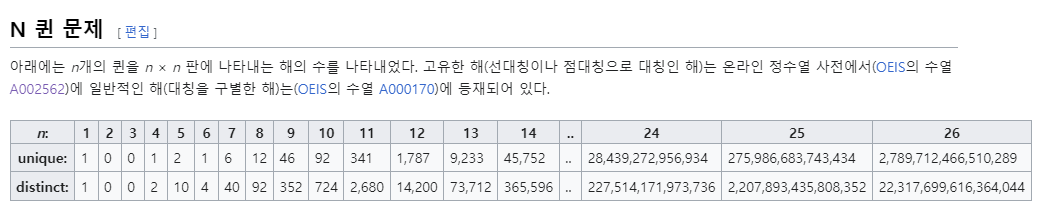
12-2 문제
1. 피로도
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/87946
def dfs(cur_k, cnt, dungeons, visited):
answer_max = cnt
for i in range(len(dungeons)):
if cur_k >= dungeons[i][0] and visited[i] == 0:
visited[i] = 1
answer_max = max(answer_max, dfs(cur_k - dungeons[i][1], cnt + 1, dungeons, visited))
visited[i] = 0
return answer_max
def solution(k, dungeons):
visited = [0] * len(dungeons)
answer_max = dfs(k, 0, dungeons, visited)
return answer_max순열로도.. (백트래킹은 아님)
import itertools
def solution(k, dungeons):
max_cnt = 0
for perm in itertools.permutations(dungeons, len(dungeons)):
cur_k = k
cnt = 0
for need, cost in perm:
if cur_k >= need:
cur_k -= cost
cnt += 1
else:
break
if cnt > max_cnt:
max_cnt = cnt
if max_cnt == len(dungeons):
return max_cnt
return max_cnt
2. N-퀸
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12952
def backtrack(col_positions, current_row, board_size):
total_solutions = 0
if current_row == board_size:
return 1
for col in range(board_size):
col_positions[current_row] = col
for prev_row in range(current_row):
same_col = (col_positions[prev_row] == col)
same_diag = abs(col_positions[prev_row] - col) == current_row - prev_row
if same_col or same_diag:
break
else:
total_solutions += backtrack(col_positions, current_row + 1, board_size)
return total_solutions
def solution(n):
return backtrack([0] * n, 0, n)3. 양궁대회
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/92342
from itertools import combinations_with_replacement
from collections import Counter
def solution(n, info):
maxdiff, max_comb = 0, {}
# 주어진 조합에서 각각의 점수 계산
def calculate_score(combi):
ryon, apeach = 0, 0
for score in range(1, 11):
arrows = cnt.get(score, 0)
if info[10 - score] < arrows:
ryon += score
elif info[10 - score] > 0:
apeach += score
return ryon, apeach
# 최대 차이와 조합 저장
def calculate_diff(diff, cnt):
nonlocal maxdiff, max_comb
if diff > maxdiff:
max_comb = cnt
maxdiff = diff
# 가능한 라이언의 과녁 점수 조합의 모든 경우에 대해서 체크
for combi in combinations_with_replacement(range(11), n):
cnt = Counter(combi)
score1, score2 = calculate_score(combi)
diff = score1 - score2
calculate_diff(diff, cnt)
# 최대 차이가 0이상이 경우, 조합 반환
if maxdiff > 0:
answer = [0] * 11
for n in max_comb:
answer[10 - n] = max_comb[n]
return answer
else:
return [-1]
4. 외벽점검(고난이도)
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/60062
5. 사라지는 발판(고난이도)
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/92345
# 어렵.....
def solution(board, aloc, bloc):
ROW, COL = len(board), len(board[0]) # 게임판의 행, 열 저장
DR, DC = [-1, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, -1]
# 주어진 위치가 유효한 위치인가?
def is_valid_pos(r, c):
return 0 <= r < ROW and 0 <= c < COL
# 재귀적 호출
def recursive_func(alpha_pos, beta_pos, visited, step):
# 현재 플레이어의 위치와 이동 가능 여부와
# 상대 플레이어가 이긴 경우를 저장하는 변수들
r, c = alpha_pos if step % 2 == 0 else beta_pos
can_move = False
is_opponent_winner = True
# 이긴 경우와 진 경우 저장하는 리스트
win_steps, lose_steps = [], []
# 현재 위치에서 이동할 수 있는 모든 방향으로 이동
for i in range(4):
nr, nc = r + DR[i], c + DC[i]
# 이동할 수 있다면
if is_valid_pos(nr, nc) and (nr, nc) not in visited and board[nr][nc]:
can_move = True
# 두 플레이어 위치가 같다면 A가 이김. True, step + 1 반환
if alpha_pos == beta_pos:
return True, step + 1
# 재귀적으로 호출하여 이긴 여부와 남은 툰수 가져오기
win, steps_left = (
recursive_func([nr, nc], beta_pos, visited | {(r, c)}, step + 1)
# 방문한 칸을 기록하는 visited 와 (r, c) 합집합
if step % 2 == 0
else recursive_func(
alpha_pos, [nr, nc], visited | {(r, c)}, step + 1
)
)
# 상대 플레이어가 이긴 경우만 True
# &= 비트 연산자 복합 대입. 논리적 AND
is_opponent_winner &= win
# 이긴 경우와 진 경우 저장
(win_steps if win else lose_steps).append(steps_left)
# 만약 이동할 수 있는 위치가 없다면
if not can_move:
return False, step
# 상대 플레이어가 이긴 경우
if is_opponent_winner:
return False, max(win_steps)
# 현재 플레이어가 이긴 경우
return True, min(lose_steps)
# A 플레이어가 이길 때까지 걸리는 최소 턴 수를 반환
# _ = 이 값은 사용하지 않을 것이다.
_, steps = recursive_func(aloc, bloc, set(), 0)
return steps
