🖥️최소 신장 트리의 정의
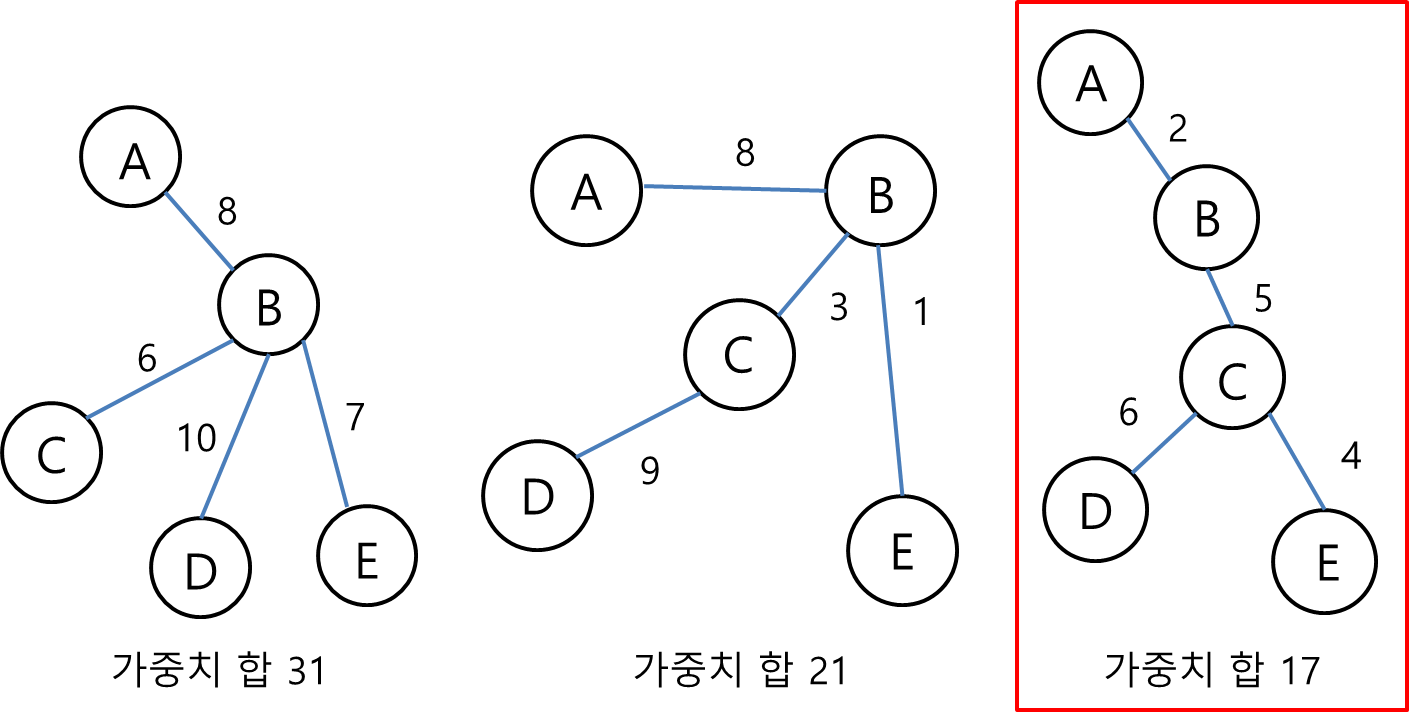
- 모든 노드를 연결 할 것
- 노드 전체를 한바퀴 도는 사이클이 없을 것
- 간선의 개수가 전체 노드의 개수보다 하나 적을 것
- 간선을 이동하는 거리를 합쳤을 때 가장 낮은 가중치를 가지는 것이 최소 신장 트리
최소 신장 트리 알고리즘
- 크루스칼 알고리즘
- 프림 알고리즘
크루스칼(Kruskal) 알고리즘
그래프의 간선을 하나씩 늘리며 MST를 만든다.
전체 그래프의 간선을 가중치에 따라 정렬한 후 사이클을 형성하지 않는 간선을 하나씩 추가하면서 MST를 만든다.
유니온 파인드 자료구조를 사용한다.
O(ElogV)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
간선이 적은 그래프에서 효율적이다.
import java.util.*;
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int src, dest, weight;
public Edge(int src, int dest, int weight) {
this.src = src;
this.dest = dest;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge other) {
return this.weight - other.weight;
}
}
class Subset {
int parent, rank;
}
public class KruskalAlgorithm {
int vertices, edges;
Edge[] edge;
KruskalAlgorithm(int vertices, int edges) {
this.vertices = vertices;
this.edges = edges;
edge = new Edge[edges];
for (int i = 0; i < edges; ++i)
edge[i] = new Edge(0, 0, 0);
}
int find(Subset[] subsets, int i) {
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent = find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
void union(Subset[] subsets, int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(subsets, x);
int rootY = find(subsets, y);
if (subsets[rootX].rank < subsets[rootY].rank) {
subsets[rootX].parent = rootY;
} else if (subsets[rootX].rank > subsets[rootY].rank) {
subsets[rootY].parent = rootX;
} else {
subsets[rootY].parent = rootX;
subsets[rootX].rank++;
}
}
void kruskalMST() {
Edge[] result = new Edge[vertices];
int e = 0; // Index used in result[]
int i = 0; // Index used to pick next edge
for (i = 0; i < vertices; ++i)
result[i] = new Edge(0, 0, 0);
Arrays.sort(edge);
Subset[] subsets = new Subset[vertices];
for (i = 0; i < vertices; ++i)
subsets[i] = new Subset();
for (int v = 0; v < vertices; ++v) {
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
i = 0;
while (e < vertices - 1) {
Edge nextEdge = edge[i++];
int x = find(subsets, nextEdge.src);
int y = find(subsets, nextEdge.dest);
if (x != y) {
result[e++] = nextEdge;
union(subsets, x, y);
}
}
System.out.println("Following are the edges in the constructed MST");
for (i = 0; i < e; ++i)
System.out.println(result[i].src + " -- " + result[i].dest + " == " + result[i].weight);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int vertices = 5; // Number of vertices in graph
int edges = 7; // Number of edges in graph
KruskalAlgorithm graph = new KruskalAlgorithm(vertices, edges);
// add edge 0-1
graph.edge[0] = new Edge(0, 1, 10);
// add edge 0-2
graph.edge[1] = new Edge(0, 2, 6);
// add edge 0-3
graph.edge[2] = new Edge(0, 3, 5);
// add edge 1-3
graph.edge[3] = new Edge(1, 3, 15);
// add edge 2-3
graph.edge[4] = new Edge(2, 3, 4);
// add edge 1-2
graph.edge[5] = new Edge(1, 2, 7);
// add edge 3-4
graph.edge[6] = new Edge(3, 4, 9);
graph.kruskalMST();
}
}
프림(Prim) 알고리즘
시작 정점에서 점진적으로 MST를 확장한다.
MST에서 연결된 정점들 중에서 가장 가중치가 적은 간선을 선택하여 새로운 정점을 추가한다.
모든 그래프에서 정점이 연결된 상태에서 작동한다.
우선순위 큐 사용한다.
O(E log V)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
간선이 많은 그래프에서 효율적이다.
import java.util.*;
class Graph {
private int vertices;
private LinkedList<Edge>[] adjacencyList;
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int dest, weight;
Edge(int dest, int weight) {
this.dest = dest;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge other) {
return this.weight - other.weight;
}
}
Graph(int vertices) {
this.vertices = vertices;
adjacencyList = new LinkedList[vertices];
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; ++i)
adjacencyList[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
void addEdge(int src, int dest, int weight) {
Edge edge1 = new Edge(dest, weight);
Edge edge2 = new Edge(src, weight);
adjacencyList[src].add(edge1);
adjacencyList[dest].add(edge2);
}
void primMST() {
boolean[] mstSet = new boolean[vertices];
Edge[] edgeTo = new Edge[vertices];
int[] key = new int[vertices];
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(vertices, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.weight));
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; ++i) {
key[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
edgeTo[i] = new Edge(-1, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
key[0] = 0;
pq.add(new Edge(0, key[0]));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Edge edge = pq.poll();
int u = edge.dest;
mstSet[u] = true;
for (Edge adj : adjacencyList[u]) {
int v = adj.dest;
int weight = adj.weight;
if (!mstSet[v] && weight < key[v]) {
key[v] = weight;
pq.add(new Edge(v, key[v]));
edgeTo[v] = new Edge(u, weight);
}
}
}
System.out.println("Following are the edges in the constructed MST");
for (int i = 1; i < vertices; ++i)
System.out.println(edgeTo[i].dest + " -- " + i + " == " + edgeTo[i].weight);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int vertices = 5;
Graph graph = new Graph(vertices);
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 2);
graph.addEdge(0, 3, 6);
graph.addEdge(1, 2, 3);
graph.addEdge(1, 3, 8);
graph.addEdge(1, 4, 5);
graph.addEdge(2, 4, 7);
graph.addEdge(3, 4, 9);
graph.primMST();
}
}