Learn JAVA Programming I
Part 1
Input is always read as a string
"string literal"
String message = scanner.nextLine();
Variable's Type Persists
(but, int➡️double OK. not the other way around)
Boolean.valueOf("true" and "TRue")
System.out.println("Four: " + (2 + 2));
int / int = int
type casting : (double) int / int = double
{code block}
< 0 / 0-49 / 50-59 등 범위 다룰 때 : 0-49는 언뜻 봐서 comparison 2개가 요구되는 것처럼 보이지만, else if 앞뒤로 이미 처리한게 있는지 확인하면 깔끔해짐!
comparison is affected by how much information a variable can hold : String ∞ 🆚 int, double, 유한
Conditional : find the most demanding condition!!!!!
else문 : 한 줄이라고 {} 생략 안 됨!!!
Part2
Math.sqrt의 결과는 항상 double
Break == Exit the Loop
Continue == return to the beginning of the Loop
Clarity : One part, One Task
본질(원형 먼저), 그 뒤에 조건 덧붙임! 🗯️"clac avg? get the sum & count ready!"
Execution simulate : at each point the condition i < 4 is evaluated.
PROGRAM : one piece at a time.
기능(Task)에 맞게 구조(Structure)를 짜라.
Methods cannot be defined e.g. inside other methods.
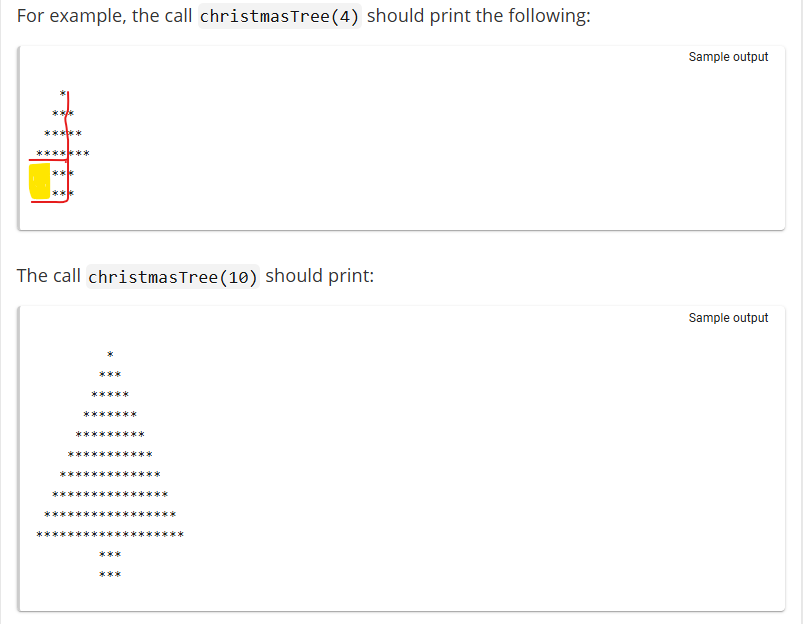
Part3 : csv를 split(",")해서 Array를 거쳐서 ArrayList에 add()한 뒤, for Each : 로 iterate하여 필요한 결과값을 도출한다.
Array, ArrayList, String 모두 Reference type
Variables in Java : 1️⃣value type (actual val, limited amount) 2️⃣ Reference type
ArrayList assumes that all the variables contained in it are reference types.
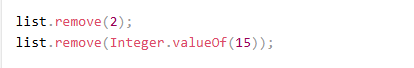
remove(index) value type할꺼면 명시해라
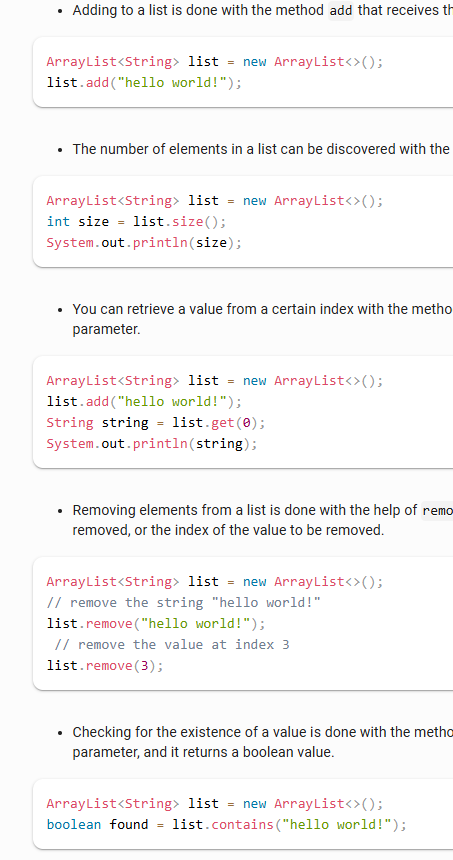
Part4

If a method receives as parameters all the variables whose values it uses, it can have a static modifier.
Part5 : OOP is Abstracting; a program is built from small and distinct objects that work together
Object-oriented programming is primarily about isolating concepts into their own entities or, in other words, creating abstractions.
Constructor Overloading : 2 (or more) constructors in a class
a special case (특수/보편 관계?) ➡️ Call!
🛑 If a constructor calls another constructor, the constructor call must be the first command in the constructor.
Private variable can be accessed from all the methods contained by that class. (diff Object 👌)
.equals의 디폴트값: 그냥 ==처럼 refer val 끼리 비교함.
Every Class inherits the class Object (그래서 누구나 equals, toString 쓸 수 있는 거)
The contains() method of a list uses the equals method of the object type
equals(Object) always!!!
const === final : cannot be modified after they have been set in the constructor.
Part 6
잘 변하지 않는 특징들을 field로, 상황에 따라 변하는 값은 그냥 getCalcVal() method로!
set of words??
The set is a clear distinct "concept"/ abstraction. ➡️ potential objects ➡️separating the concept into a class of its own.
1️⃣Proceed with small steps
- Try to separate the program into several sub-problems and work on only one sub-problem at a time
- Always test 과정중에, test solution to the sub-problem
- Recognize the conditions that require the program to work differently. (핵심 조건 뽑아내기)
2️⃣ Write as "clean" code as possible
- Indent your code
- Use descriptive method and variable names
- Don't make your methods too long, not even the main method
- Do only one thing inside one method
- Remove all copy-paste code
- Replace the "bad" and unclean parts of your code with clean code
As a corollary, a program that's broken is rarely fixed by adding more code to it.
String의 반댓말은 null이다.
stringTest tells it's a test class.
each method tests an individual unit.
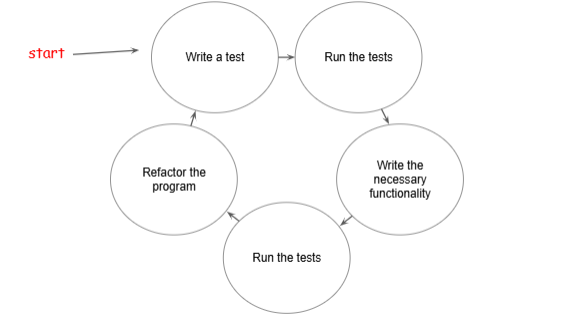
Only checked existence of wanted functionality ? narrow view !!
CHECK that UNWANTED behavior doesn’t occur.
Gather together the things that change for the same reasons. Separate those things that change for different reasons.
Part 7
OOP - structure formed by the data(자체)
Procedural - formed by functionality(기능)
Methods without the static modifier are instance methods. Methods with the static modifier are class methods

