💡 시간 초과 발생 방지를 위해서 시작전 시간 계산을 간략하게 진행하고 들어가자!!

< 시간초과 발생 코드 >
import sys
while(1):
m = int(sys.stdin.readline())
if m == 0:
break
sentence = list(sys.stdin.readline())
result = [0] * (len(sentence) - m)
for i in range(len(sentence)-m):
word = [None] * m
idx = 0
num = 0
for j in range(i,len(sentence)):
if num == m and sentence[j] not in word:
# append는 시간을 많이 잡아먹기 때문에, 배열의 크기를 알면 배열의 크기를 정해두고 받아보자
# result.append(j-i)
result[i] = j-i
break
if sentence[j] in word:
continue
else:
word[idx] = sentence[j]
idx += 1
num += 1
print(max(result))- 시간 제한이 1초이고, 입력값이 최대 100만 글자이므로, for문을 2번쓰면 시간초과가 당연히 발생하는 것을 고려하지 못하였습니다.
- 결국 "완전탐색"의 방식은 불가능 하였습니다.
💡 도무지 생각 나지 않아서, 예시 답안을 참고
=> "투포인터" or "슬라이딩 윈도우" 사용 필요
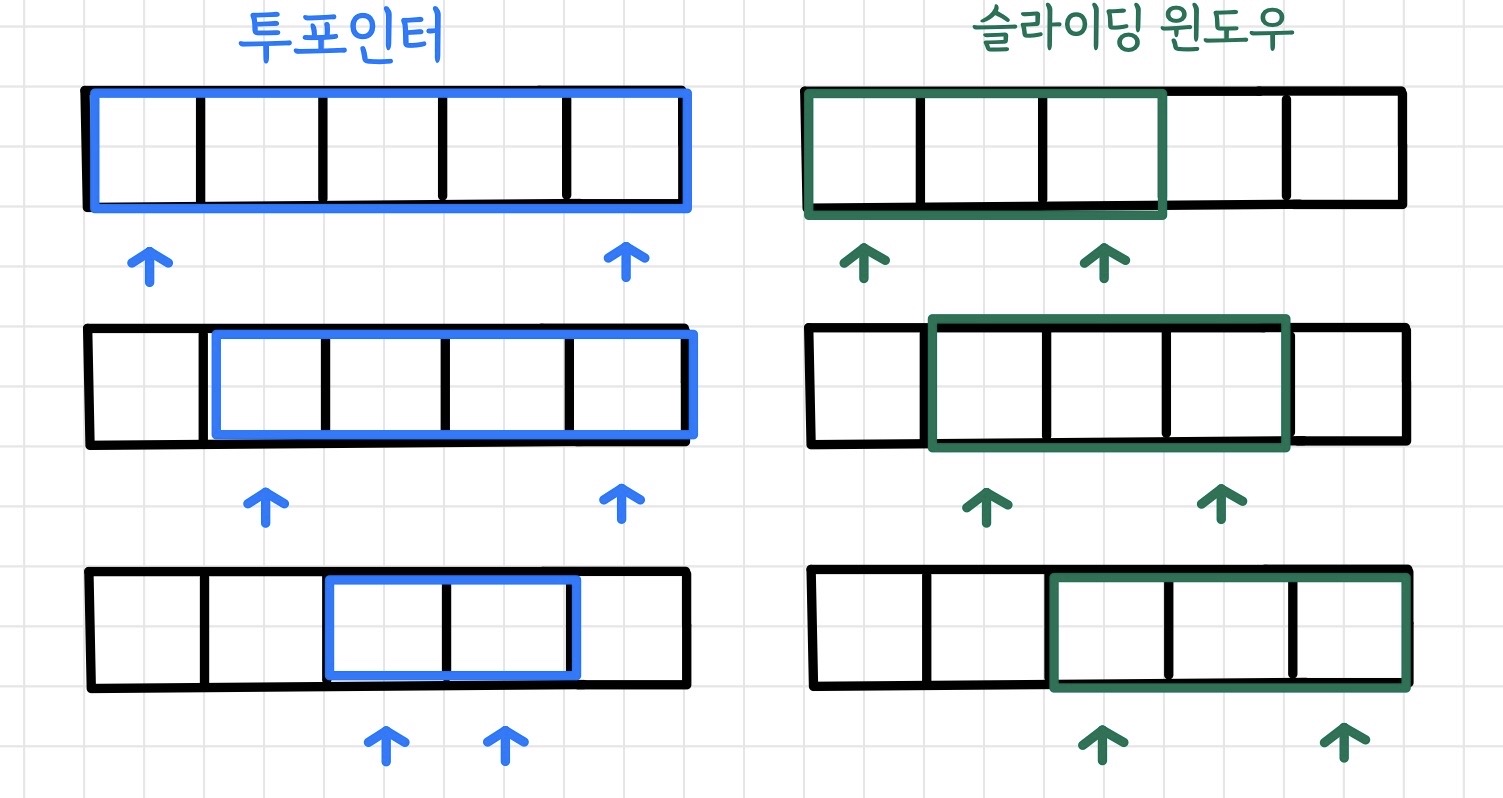
투포인터
- 리스트에 담겨 있는 데이터를 "처음"과 "끝"에 포인터를 두어, 접근할 데이터의 범주를 표현할 수 있다.
- "특정한 합을 가지는 부분 연속 수열 찾기"와 같은 문제를 선형시간(O(N))안에 풀어야 할 경우 사용한다.
- 범주가 변경이 가능할 경우 사용
슬라이딩 윈도우
- 리스트에 담겨 있는 데이터를 "고정된 크기"의 윈도우가 움직이면서 윈도우 내의 크기를 비교할 수 있다.
- 고정된 범주에서 사용 가능
< 해결코드 >
import sys
from collections import defaultdict
while(True):
m = int(sys.stdin.readline().rstrip())
if m == 0:
break
# 투포인터의 시작과 끝점
start = 0
end = 0
# 총 갯수
cnt = 0
# 범주 내에 문자의 개수를 저장
# dic = dict()
dic = defaultdict(int)
sentence = list(sys.stdin.readline().rstrip())
while(end < len(sentence)):
if len(dic) < m:
# dic[sentence[end]] = dic.get(sentence[end], 0) + 1
# dict가 defaultdict로 선언될 경우 없으면 자동으로 0으로 채워줌
dic[sentence[end]] += 1
end += 1
else:
if sentence[end] in dic:
dic[sentence[end]] += 1
end += 1
else:
dic[sentence[start]] -= 1
if dic[sentence[start]] == 0:
del dic[sentence[start]]
start += 1
if len(dic) <= m:
cnt = max(cnt, end-start)
print(cnt)- 우선 투포인터를 사용해야하며, 문자의 갯수를 저장하기 위해 해쉬맵(딕셔너리)를 사용해야한다.
- end가 입력받은 문장의 끝부분을 가르킬때 까지 반복하며, 기존에 dic의 크기가 m보다 작으면 새로운 딕셔너리를 생성해서 추가하다.
(+ defaultdict(int)로 선언해주면 선언하면서 해당 자료형으로 초기화까지 해준다)
(+ dict의 get함수를 사용하면 해당하는 key의 value값을 받아올 수 있으며, default값 설정도 가능하다) - end를 이동하면서 다음에 들어오는 값이 dic내부에 있는지 없는지 여부로 dict의 문자들을 삭제시켜주면서 변경시킨다.
- 만약 end가 달라서 새로운 문자가 들어왔을때, 이전의 end-start값과 현재의 end-start값을 비교해서 max값을 찾는다.
