문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1697
풀이
문제 분석
- 처음에는 dfs로 접근했으나, 각 초별로 방문할 수 있는 위치를 고려하는게 아닌 경우의 수를 모두 만들어본 후에 최소값을 도출하는 방식이기에 시간초과가 났다
- 이에 따라 bfs로 접근하도록 문제 풀이를 다음과 같이 수정하여 통과할 수 있었다
- index out of bounds 에러를 만났었는데 그 이유는 TIL에서 정리하도록 하겠다
- 초 별로 방문할 수 있는 위치를 true로 설정한다는 것이 가장 중요한 포인트였다
- 다음 그림을 참고하면 좀 더 이해가 수월하지 않을까 싶다
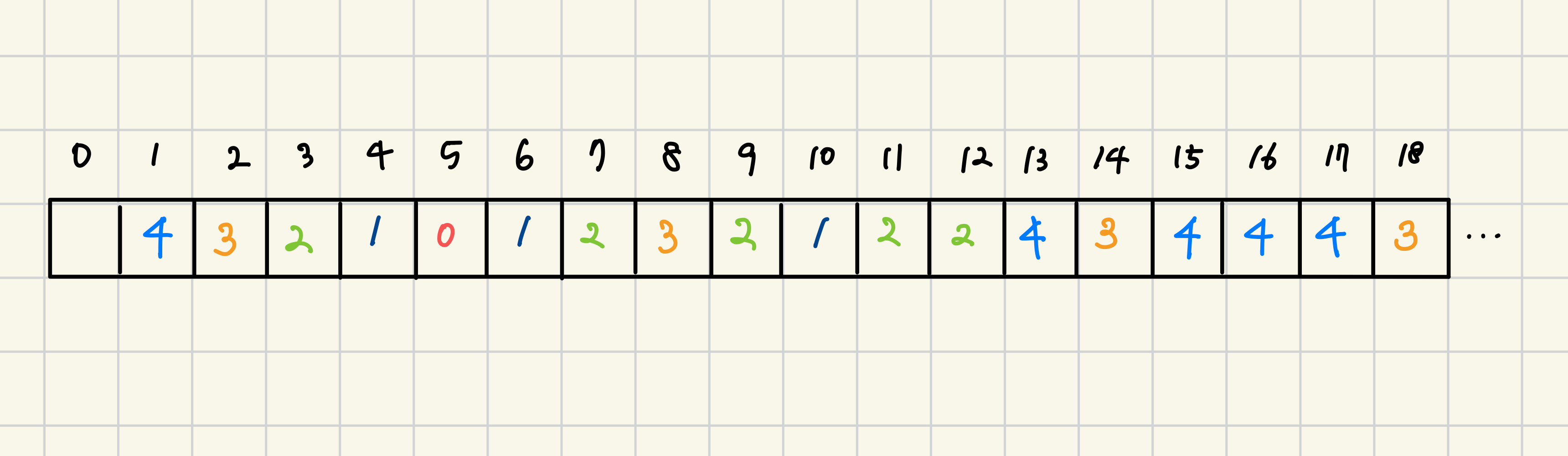
- 다음 그림에서는 이해를 돕기 위해 해당 위치를 방문한 "초"를 써두었지만 실제로는 방문 여부(true/false)를 visited 배열에 저장하여 한 번 방문한 위치는 다시 방문하지 않도록 처리한다
1. 초기에는 시작 위치를 큐에 담고 방문한 배열로 체크한다
2. 큐가 비지 않는다면 다음을 반복한다
2.1 큐의 사이즈만큼 반복문을 돈다
- 큐에서 하나의 값을 꺼내어 동생의 위치(K)와 같은지 확인한다
- 같지 않다면 다음에 방문할 수 있는 위치들을 큐에 삽입한다
- 더하거나 빼거나 곱하거나 연산을 진행하고, 이때 배열의 범위를 벗어나지 않도록 if문으로 처리가 필요하다
2.2 반복문을 한 번 수행할 때마다 count를 통해 초를 증가시킨다코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static int N = 0;
private static int K = 0;
private static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] token = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = Integer.parseInt(token[0]);
K = Integer.parseInt(token[1]);
visited = new boolean[100001];
int answer = bfs();
System.out.println(answer);
}
private static int bfs() {
int count = 0;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int[] num = {-1, 1, 2};
queue.add(N);
visited[N] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for(int i=0 ; i<size ; i++) {
int idx = queue.poll();
if(idx == K) {
return count;
}
for(int j=0; j<3 ; j++) {
int nextIdx;
if(j < 2) {
nextIdx = idx + num[j];
}
else {
nextIdx = idx * num[j];
}
if(nextIdx < 0 || nextIdx > 100000 || visited[nextIdx]) {
continue;
}
queue.add(nextIdx);
visited[nextIdx] = true;
}
}
count++;
}
return count;
}
}TIL
-
연산자 순서로 인해 index out of bound를 만나 이를 기록하려한다
-
더하거나 빼거나 곱하거나 연산을 진행하고, 이때 배열의 범위를 벗어나지 않도록 if문으로 처리가 필요하다 라고 위의 설명에 써 두었는데, 다음에 방문할 위치의 index를 구했을 때 내가 정의해둔 visited 배열의 범위를 벗어날 수 있을 것이다
-
그래서 if(nextIdx < 0 || nextIdx> 100000 || visited[nextIdx])라는 조건문을 사용하고 있다
-
그러나 처음에는 다음과 같이 nextIdx > 100000보다 visited[nextIdx]를 먼저 작성했다
if(nextIdx < 0 || visited[nextIdx] || nextIdx> 100000)- || 연산자의 경우 각 순서대로 작성된 수식을 계산하기 때문에 nextIdx > 100000 조건이 배열에 접근하는 수식보다 뒤에 위치하고 있어 visited[nextIdx]를 검사하는 과정에서 index out of bound 가 발생했던 것이었다
- 이와 비슷하게 && 연산자를 사용할 때에 계산식이 포함되는 경우 앞의 수식이 false이면 뒤의 수식은 계산하지 않고 바로 넘어간다는 특징이 있다
- 관계 연산자를 사용할 때 조금 더 주의를 기울여야겠다는 생각이 들었다
