
문제
- 추상 클래스와 상속을 사용하여 다형성 예제를 만들어보시오
- 추상 클래스와 상속의 개념을 이해하고 이를 활용하여 다형성 구현하기
코드 구현
- 추상 클래스 생성
abstract class Car{
abstract void run();
}
// 자식 클래스
class Ambulance extends Car{
void run() {System.out.println("앰블런스 지나가요~삐뽀삐뽀~");}
}
class Cultivator extends Car{
void run() {System.out.println("경운기 지나가요~덜컹덜컹~");}
}
class SportsCar extends Car{
void run() {System.out.println("스포츠카 지나가요~ 씽~");}
}- 메서드 호출
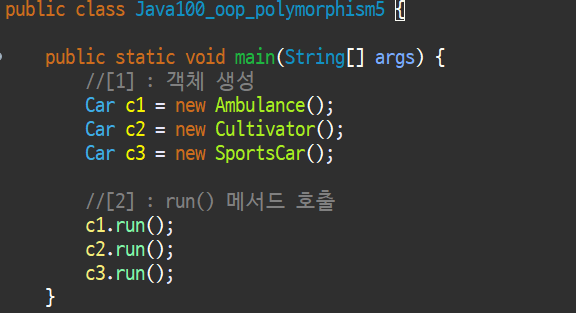
ex1) 배열과 반목문을 사용하여 객체 생성해보기
- 배열 선언
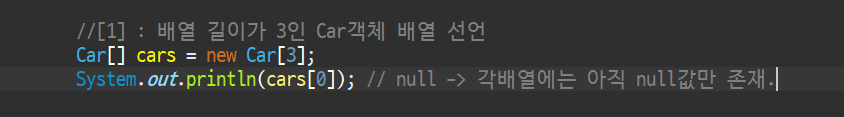
2-1 . 배열 초기화
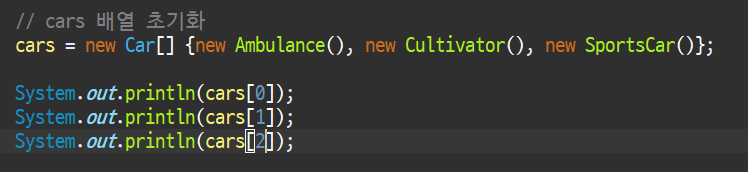
결과물 - 주소값이 나온다( 각 객체가 생성된 메모리 공간의 주소값)
com.study.Ambulance@3b6eb2ec
com.study.Cultivator@1e643faf
com.study.SportsCar@6e8dacdf
2-2. 부모타입의 자식 클래스 객체들로 바로 배열 초기화 하려면 아래와 같이 하면됨!
Car[] cars = {new Ambulance(), new Cultivator(), new SportsCar()};- 반복문 돌면서 각 객체의 run() 메서드 호출
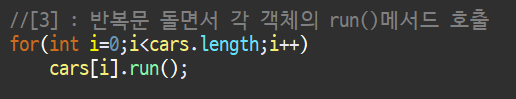
결과물
앰블런스 지나가요~삐뽀삐뽀~
경운기 지나가요~덜컹덜컹~
스포츠카 지나가요~ 씽~
3-2. 향상된 for문 사용해보기
for(Car obj : cars) obj.run();결과물 - 동일하다
앰블런스 지나가요~삐뽀삐뽀~
경운기 지나가요~덜컹덜컹~
스포츠카 지나가요~ 씽~
ex2) 다형성을 사용하면서 배열이나 매개변수를 활용해보기
- 아래와 같이 클래스들이 있다고 하자
class Person_1{}
class Batman extends Person_1{}
class Human {}
class Superman extends Human{}- 배열에서 다형성을 사용할 수 없다면?
배열은 동일한 타입의 데이터를 하나로 묶어서 관리하는 자료구조인데 다형성이 없다면
각 객체별로 관리를 해야한다.
즉 아래와 같이 부모 클래스로 객체를 생성했을 때 부모클래스 객체만 배열에 초기화 할 수 있다.
Person_1[] persons = new Person_1[10]; // 이건 Person 전용
persons[0] = new Person_1();
persons[1] = new Person_1();
자식 클래스도 똑같다.
Batman[] batmans = new Batman[10]; // 이건 Batman 전용
batmans[0] = new Batman();
batmans[1] = new Batman();- 다형성을 사용할 수 있을 때
Human[] humans = new Human[10];
humans[0] = new Humans(); - 이건 당연히 되고
humans[1] = new Superman(); - 자식클래스로도 부모타입으로 받아 객체 생성을 할 수 있다.
- 매개 변수의 다형성
프로그래밍 언어에서 함수나 메서드를 호출할 때는 그에 맞는 적절한 파라미터를 보내줘야한다.
- System.out.println() 메서드의 경우
-어떤 타입, 객체를 매개변수로 받더라도 에러없이 해당 객체의 값을 출력해준다.
-그것이 가능한 이유 --> 바로 다형성을 활용하고 있기 때문이다.
-실제 메서드의 API를 보면 public void println(Object x)로 파라미터(최상의타입)가 되어 있기에 어떤 객체 타입이 전달되더라도 에러없이 출력이 되는것이다.
결론적으로, Object는 가장 최상위 조상(단군 할아버지,창조주)이므로 어떤 객체를 보내도 그 보다 상위 타입이 된다.
System.out.println(new Person_1());
System.out.println(new Batman());
System.out.println(new Human());
System.out.println(new Superman());
강의가 맥락없이 갑자기 뚝 끊겼다 ㅋㅋㅋ 다형성 개념을 끝으로 oop파트는 끝났다. 자바의 신을 사서 자바 공부를 더 해야 할 것 같다. 그다음 알고리즘 파트 기대되는데 너무 기대하면 안될것 같다.ㅎㅎ