[TIL] java 반복문의 continue, continue label

문제1
- 홀수, 짝수 구하기 문제를 While반복문과 continue를 사용하여 구현해보시오.
- 1~30까지의 수에서 짝수만 출력하시오.
[출력결과]
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28
풀이
public class Java100_license_CosPattern2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// [1] : 변수 선언
int num=1;
// [2] : 반복문 돌면서 홀수 인지 체크--> 홀수면 Pass(continue)
while(num<=30) {
if(num%2!=0) {
num++;
continue;
}
System.out.print(num+" ");
num++;
}
}
}- continue를 만나면 그 다음 명령을 실행하지 않고 바로 while조건으로 올라간다.
문제2
- 중첩 반복문 구조에 대해서 구현해보시오.
- continue label이란 무엇인지 설명해보고 관련된 예제를 코드로 구현해보시오.
0 2 4 6 8
10 12 14 16 18
20 22 24 26 28
30 32 34 36 38
- 중첩 반복문으로 풀기
public class Java100_license_CosPattern3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// [1] : 이중 반복문
for(int i=0;i<=3;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
// 출력값
int output = i*10+ j*2;
System.out.print(output+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}- continue 추가해서 풀기
public class Java100_license_CosPattern1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// [1] : 이중 반복문
for(int i=0;i<=3;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<10;j++) {
// 출력값
int output = i*10+ j;
// 짝수만 출력
if(output%2!=0)
continue;
else
System.out.print(output+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}-첫 for문은 0~3 세번 돌면서 행 3개를 만들어 준다.
-두번째 for문은 1~9 9번 돌면서 정수를 9까지의 수를 만든다.
-출력값 변수를 만들어 행(i)이 증가할수록(3번) 정수의 십의 자리수가 증가하도록 연산해준다.
-조건문 if를 통해 출력값이 짝수일때 continue명령에 의해 다음 반복문(j++)으로 넘어가도록 조건(연산)을 걸어준다.
문제3
- COS Pro 2급,1급에서 자주 나오는 패턴인 중첩 반복문 구조에 대해서 구현해보시오.
- 중첩 반복문으로 만든 배열 중 첫번째 열만 출력해보기
<출력결과>
0
10
20
30
Continue label
: 여러개의 중첩된 반복문을 한번에 빠져나와야 할때 쓰인다.
- 반복문 앞에 라벨을 붙여 사용한다.
라벨명: for(조건){문장} - 빠져나와야 하는 조건에서 continue 또는 break 뒷 부분에 빠져나갈 반복문 라벨 이름을 붙인다.
if(조건){continue 라벨명;}
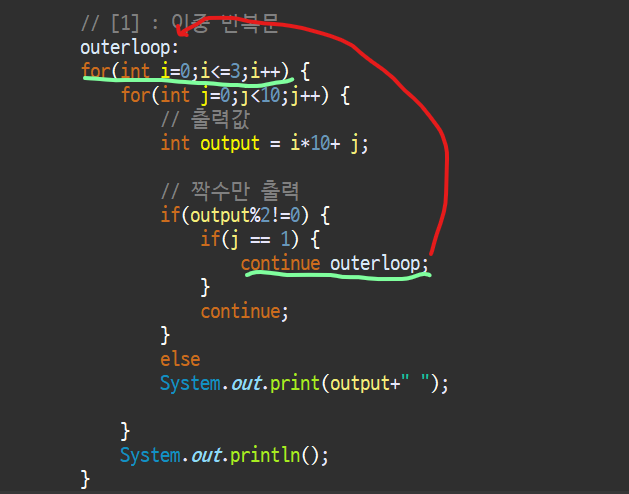
-j가 1이면 outerloop label이 선언된 바깥쪽 for문으로 분기하여 그 다음 단계부터 다시 수행
코드
public class Java100_license_CosPattern4 {
public static void main(String[] args){
// [1] : 이중 반복문
outerloop:
for(int i=0;i<=3;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<10;j++) {
// 출력값
int output = i*10+ j;
// 짝수만 출력
if(output%2!=0) {
if(j == 1) {
System.out.println();
continue outerloop;
}
continue;
}
else
System.out.print(output+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}-j가 0일때 else로 넘어가서 0를 출력한 후 다음 루프로 넘어가 j가 1이 된다.
-j가 홀수 1이므로 첫번째 if문에서 먼저 개행를 해준 뒤 continue에 의해 outerloop, 즉 가장 첫번째 for문으로 넘어가서 i가 1이된다.
-다시 j가 0부터 초기화되어 루프를 돌고 출력값 ouput이 10으로 연산되어 출력된다.
-위 과정이 i가 3이 될때 반복되어 0 10 20 30이 차례대로 개행되어 출력된다.