1. Multithreading
Why?
process가 가지고 있던 두가지 특징은 1) Unit of resource ownership 2) Unit of dispatching 이다. 이 둘을 separate하여 process가 1번, thread가 2번을 수행하도록 한다.
Basics
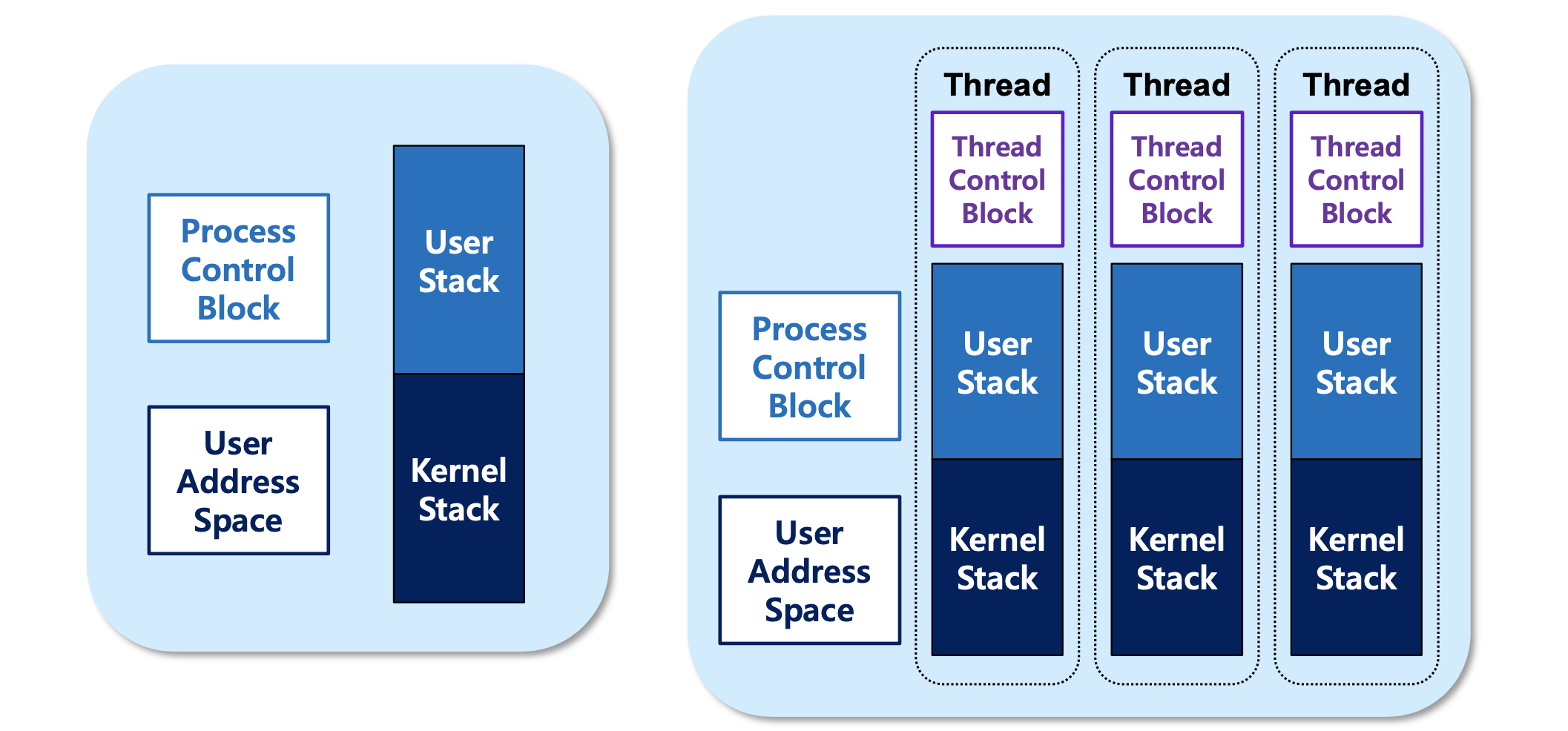
- running, ready, stopped 세가지 state을 가진다.
- 각 thread는 TCB와 stack을 가지고, process의 PCB와 memory를 공유한다.
Pros
- Effective concurrent programming
- Resource sharing
- Economy - cheap to implement compared to process
- Agility in responses
ex) web server with worker threads
2. Pthreads Programming Model
Pthreads : POSIX standard for threads
pthread_create() // create a new thread
pthread_exit() // terminate the calling thread
pthread_join() // wait for a specific thread to exit
pthread_yield() // release CPUint main(void)
{
pthread_t threads[NUM_THREADS];
int thread_args[NUM_THREADS];
int rc, i;
/* create all threads */
for (i=0; i<NUM_THREADS; ++i) {
thread_args[i] = i;
printf("In main: creating thread %d\n", i);
rc = pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, ThreadCode, (void *)&thread_args[i]);
assert(0 == rc);
}
/* wait for all threads to complete */
for (i=0; i<NUM_THREADS; ++i) {
rc = pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
assert(0 == rc);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}3. Implementation
User-Level Threads
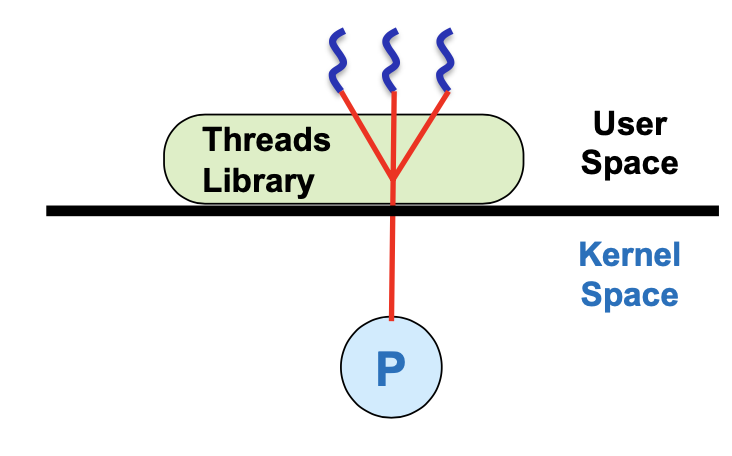
user level에서 thread간 scheduling
Pros) thread switching할 때 mode switching 필요 x → overhead 줄어듬
Cons) HW interrupt가 발생했을 때 어느 thread에 전달할 지 kernel이 알 수 없어 preemptive scheduling 불가능
하나의 thread가 block되면 전체 process가 block됨
Kernel-Level Threads
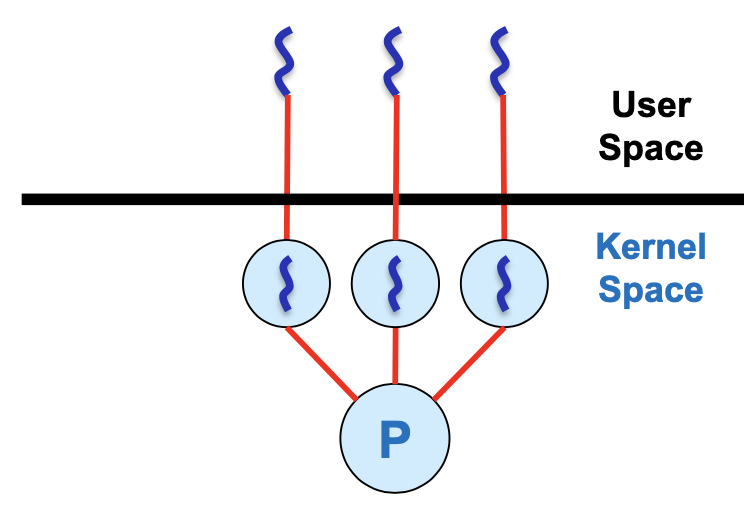
kernel level에서 thread간 scheduling
thread 단위로 blocking이라는 장점이 있지만 mode switching 필요하다는 단점
UL/KL Threads
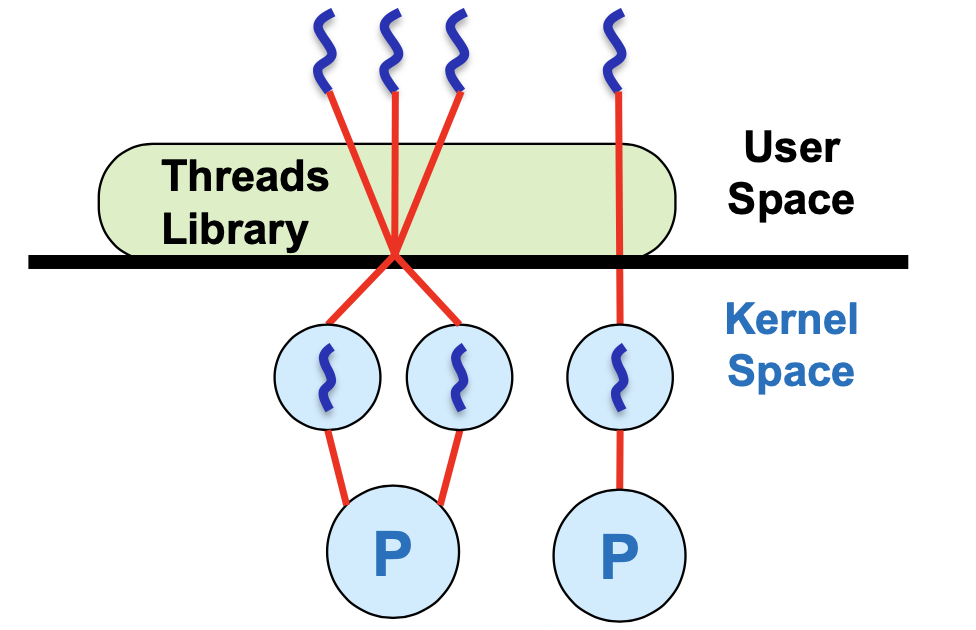
lightweight process(LWP)가 접착제 역할