오늘은 원하는 섹션으로 화면이 스크롤되는 버튼과 페이지의 최상단으로 스크롤되는 버튼을 만들어보겠습니다
- 스크롤될 섹션별로 각각의 ref 값을 배열에 저장
제가 만든 프로젝트같은경우엔 섹션들이 map함수를 통해 렌더링되기때문에 따로 배열에 넣어주는 메소드가 필요했습니다

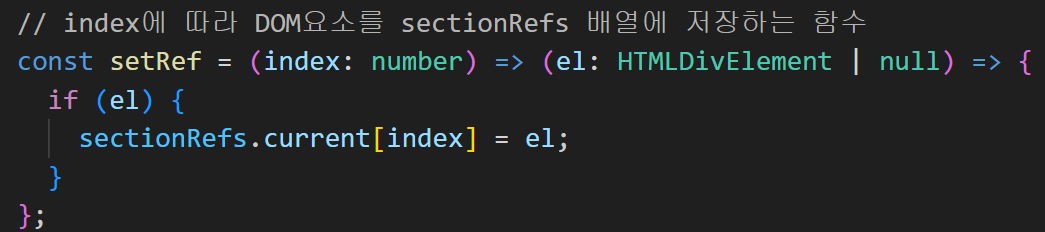
커링 방식 - 여러 개의 인자를 받는 함수가 있을 때, 이 인자를 한 번에 받지 않고, 각각 나눠서 받도록 변환하는 기법. 즉, 하나의 인자를 먼저 받고, 그 인자를 이용해 새로운 함수를 반환하는 방식
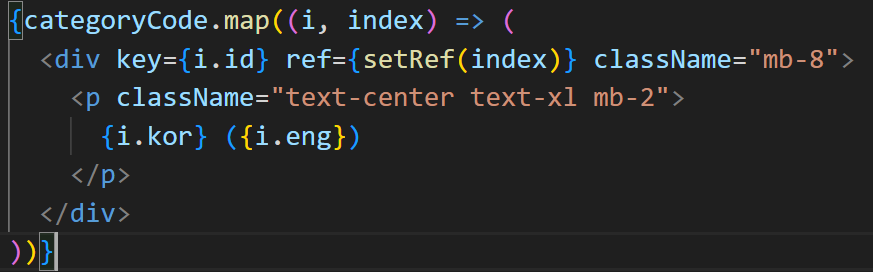
아래는 map함수를 통해 렌더링된 요소들의 상위 div태그를 섹션으로 잡고 sectionRefs에 배열로 넣어주는 setRef 메소드를 실행하는 코드입니다.
2. ref.current로 이동시켜줄 메소드 생성
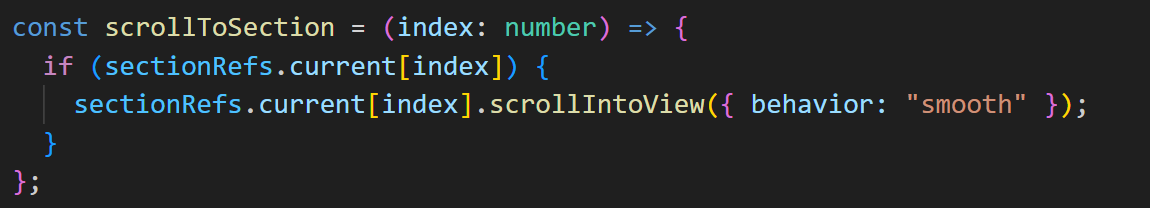
해당 메소드는 각 버튼으로부터 index를 받아와서 해당 index값의 섹션으로 scrollIntoView를 활용해서 이동을 시켜줍니다.
scrollIntoView
https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/API/Element/scrollIntoView
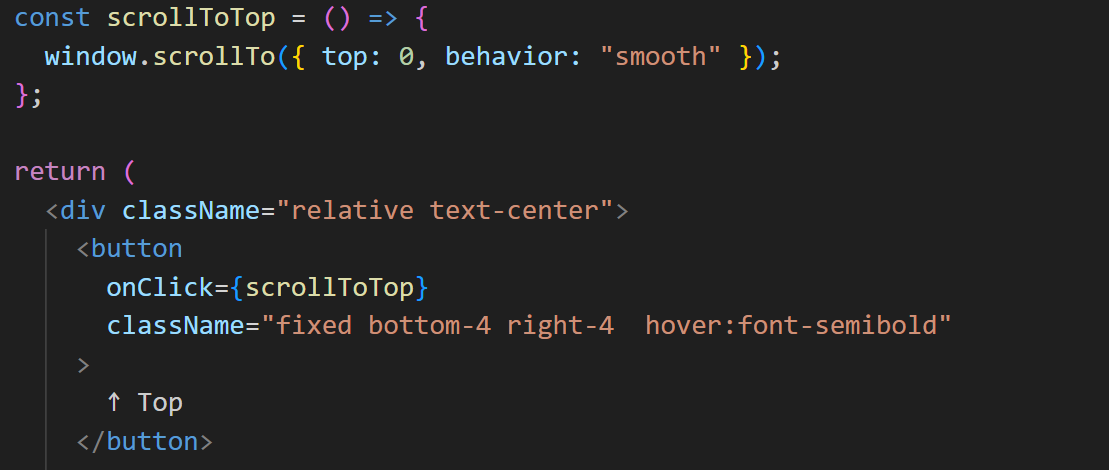
- 섹션으로 이동을 해줄 버튼 생성

- 화면의 최상단으로 보내줄 버튼
해당 버튼은 어떤 높이의 섹션에서도 항상 보여야하기때문에 fixed 속성을 활용했습니다
전체코드
"use client";
import React, { useEffect, useRef } from "react";
import { Faqs } from "@/types/type";
interface FaqListProps {
categoryCode: {
id: number;
kor: string;
eng: string;
}[];
sortData: {
[key: string]: Faqs[];
};
}
const FaqList = ({ categoryCode, sortData }: FaqListProps) => {
const sectionRefs = useRef<HTMLDivElement[]>([]);
// index에 따라 DOM요소를 sectionRefs 배열에 저장하는 함수
const setRef = (index: number) => (el: HTMLDivElement | null) => {
if (el) {
sectionRefs.current[index] = el;
}
};
const scrollToSection = (index: number) => {
if (sectionRefs.current[index]) {
sectionRefs.current[index].scrollIntoView({ behavior: "smooth" });
}
};
const scrollToTop = () => {
window.scrollTo({ top: 0, behavior: "smooth" });
};
return (
<div className="relative text-center">
<button
onClick={scrollToTop}
className="fixed bottom-4 right-4 hover:font-semibold"
>
↑ Top
</button>
<div className="mb-4">
{categoryCode.map((item, index) => (
<button
key={item.id}
onClick={() => scrollToSection(index)}
className="p-2 border rounded m-1 hover:bg-slate-200"
>
{item.kor}
</button>
))}
</div>
<div>
{categoryCode.map((i, index) => (
<div key={i.id} ref={setRef(index)} className="mb-8">
<p className="text-center text-xl mb-2">
{i.kor} ({i.eng})
</p>
{sortData[i.eng].map((item: Faqs) => (
<div key={item.id} className="border-2 rounded-lg mb-4 p-2">
<div>Q: {item.content.question}</div>
<div>A: {item.content.answer}</div>
</div>
))}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default FaqList;
