PID 1 (Ancestor process)
프로세스 복제가 아닌 kernel에 의해 생성
시스템 기동 및 관련된 작업을 하는 최초의 프로세스
Background
init
SysV 유닉스에서 만들어짐
PID 1
부팅 시 초기화 담당
/etc/inittab 사용
초기화 후 runlevel 기능에게 제어 분할
upstart
init의 모든 기능을 그대로 둔채 runlevel관련 기능 대체
event-driven 방식으로 작동
서비스 dependency 해결
예상보다 부팅 속도 개선되지 않음
공용 서비스는 dependency에 의해서 복잡하게 꼬일 수 있음
모니터링 이상 작동
결국 systemd가 대세
systemd
Lennart Poettering 개발
시스템, 서비스, 자원 설정, 이벤트를 통합 관리
systemd
특징
unit 단위로 시스템 관리
service unit, target unit, device unit ..
동적 상태
unit의 현재 상태가 동적으로 관리되므로 외부 명령어에 의존하지 않음
병렬 처리
부팅 혹은 타겟 진입 시 프로세스 병렬 수행
종료
셧다운 시 실행 중인 unit만 중지하고 빠르게 종료
binaries
system configuration
hostnamectl, localectl, timedatectl ..
system monitoring/querying
systemd-analyze, journalctl, loginctl ..
system controlling
systemctl
Compatibility with SysV init scripts
systemd는 SysV init script와 일부 호환성을 제공
SysV에서 사용하는 명령어 제공
init, shutdown, reboot, halt ..
실제로는 symlink일 뿐
supported units
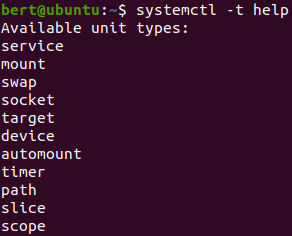
config files

unit config. dirs.
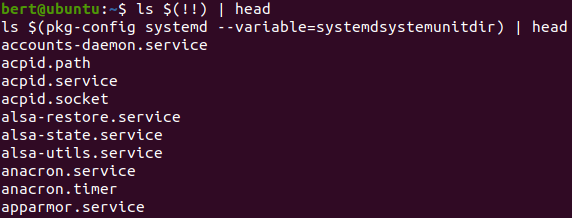
unut file
cat $(pkg-config systemd --variable=systemdsystemunitdir)/accounts-daemon.service
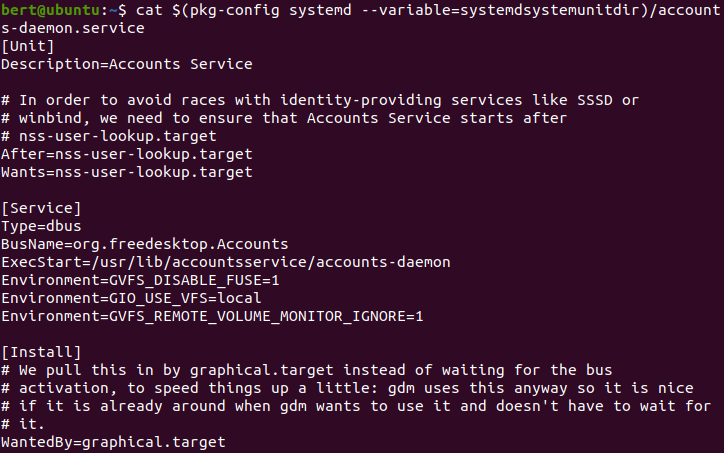
systemctl cat accounts-daemon
global config. dirs.
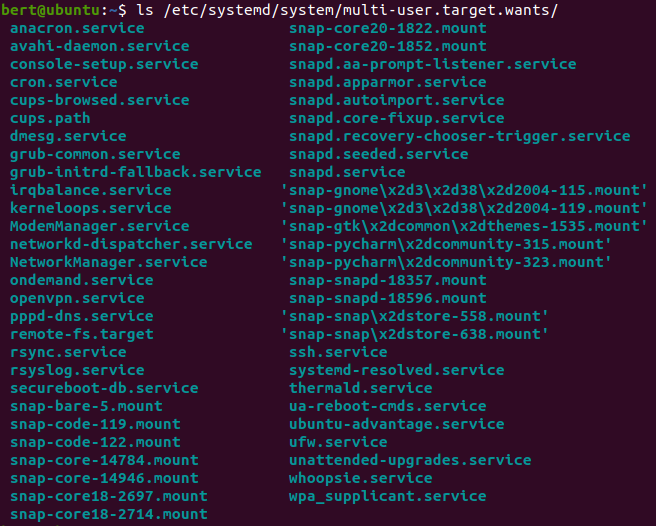

systemctl
systemctl
defaul로 list-units 명령 작동
방향키 로 오른쪽 내용 확인 가능
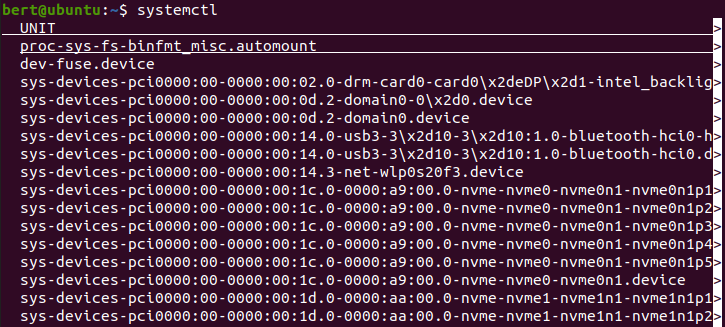
systemctl -a
\NetworkManager
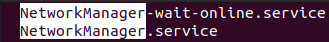
systemctl -a --state=dead

command
systemctl <command> [arg ...]
| command | 설명 |
|---|---|
| status | 유닛 상태 출력 |
| start | 유닛 시작 |
| stop | 유닛 정지 |
| is-active | active 상태 출력 |
| is-failed | failed 여부 출력 |
| kill | 시그널 보냄 |
실습을 위한 nginx 설치
sudo apt -y install nginx
상태 확인
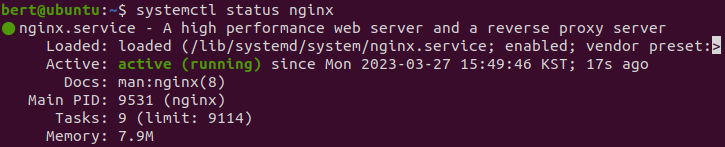
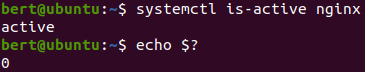
유닛 정지 후 상태 확인
sudo systemctl stop nginx
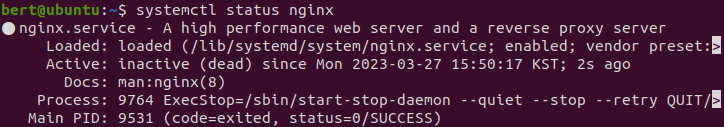
Abort signal 전송
systemctl kill nginx --signal=SIGABRT
서비스 재시작 시도
정지된 서비스인 경우 아무일도 하지 않음
systemctl try-restart nginx
| command | 설명 |
|---|---|
| is-enabled | 유닛 enabled 상태 확인 |
| disable | 유닛 비활성화 |
| enable | 유닛 활성화 --now 옵션 : enable&start |
| preset | 기본값으로 설정 |
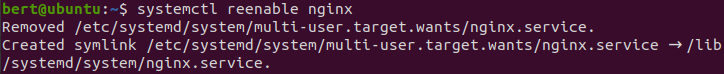
| reenable | 유닛 파일 재활성화 disable&enable |
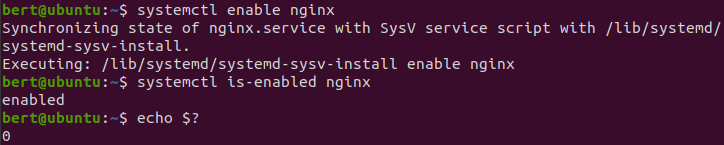
enable
reenable
target unit
유닛들을 논리적으로 묶은 그룹
- 시스템 시작 후 단계별로 기능을 묶음
- 과거 SysV runlevel 기능 대체
SysV runlevel의 문제점
- 정적 상태를 기준으로 함
- 런레벨 교체 시 의미없이 재시작되는 서비스들이 생김
- 스크립트 동작 순서가 serial하게 작동
- 일부 기능 그룹화 불가
systemd target
- 동적 상태를 기준
- 동작 순서 parallel하게 작동
target list
| command | 설명 |
|---|---|
| poweroff.target | 시스템 끄기 |
| rescue.target | 복구 모드 |
| multi-user.target | CLI 모드 |
| graphical.target | GUI 모드 |
| reboot.target | 리부팅 |
| shutdown.target | 시스템 끄기 |
| halt.target | 시스템 끄기 |
| emergency.target | 응급용 콘솔 |
change target
systemctl isolate <target>
default target
GUI로 로그인 환경 사용
systemctl set-default graphical.target
CLI로 로그인 환경 사용
systemctl set-default multi-user.target
default target 확인
systemctl get-default
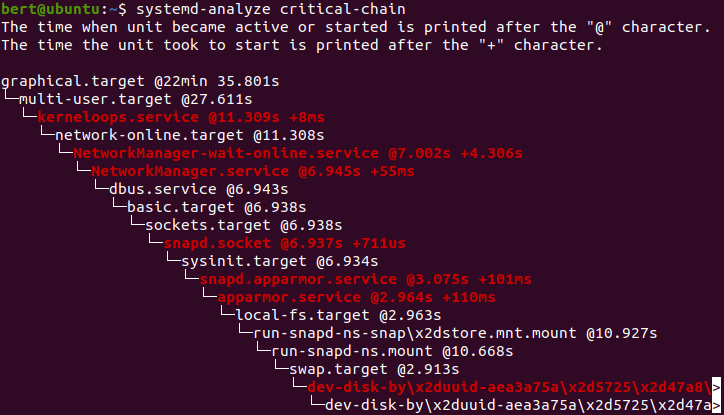
systemd analyzer
systemd-analyze [options] [command]
systemd의 구동 분석
| command | 설명 |
|---|---|
| blame | 서비스 작동에 걸린 시간 |
| critical-chain | 크리티컬 체인 출력 |
| plot, dot | 부팅 과정 출력 |
| dump | 시스템 정보 덤프 |
| verify | unit 파일 작성/변경 후 검증 |
systemd-analyze
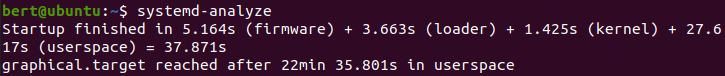
systemd-analyze blame
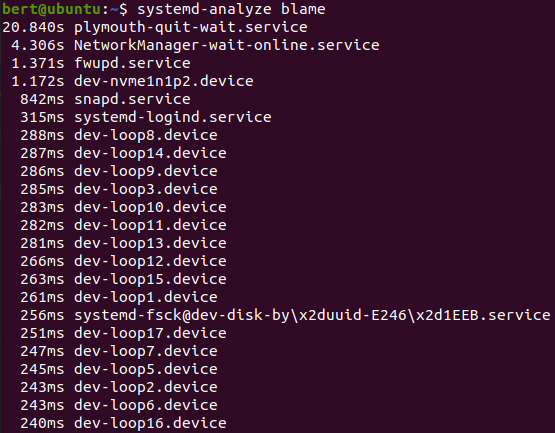
systemd-analyze critical-chain
systemd-analyze plot > svgfile.svg
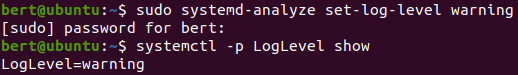
loglevel
loglevel = <emerg|alert|crit|err|warning|notice|info|debug>
default log level

current log level

change log level
systemd-journald
systemd는 로그 관리를 위해 systemd-journald daemon 사용
- kernel 및 userland 메시지를 통합 관리
syslog daemon으로부터 정보 수집 포함
binary data로 인덱싱하므로 빠른 검색과 출력 가능 - /run/log/journal
저널 디렉터리
journalctl
| -e | 출력 시 저널의 마지막 행으로 점프 |
| -f | 맨 끝 저널부터 시작하며 추가되는 부분 출력 |
| -n | 해당 라인 수 만큼 출력 |
| -a | 출력 불가능한 문자 필드까지 모두 포함 |
| -u | 특정 유닛 로그 출력 |
<binary path> | 특정 바이너리 로그 출력 |
| -x | catalog 출력 |
| -o | 출력 포멧 지정 |
| --since | 지정된 시각 이후부터 출력 |
| --until | 지정된 시각 이전까지 출력 |
| -r | 역순으로 출력 |
| -p | 특정 로그 우선 순위 지정 |
| --list-boots | 부트 ID |
journal-disk
journal은 기본적으로 메모리 기반으로 수집
/var/log/journal 생성 및 권한 설정
chown root:systemd-journal /var/log/journal
chmod g+s !$
systemctl restart systemd-journaldjournal.conf
cat /etc/systemd/journald.conf

disk usage
journal 차지 용량 확인
journalctl --disk-usage

30M에 근접하게 삭제
journalctl --vacuum-size=30M
priority
journalctl -p <priority>
loglevel = <emerg|alert|crit|err|warning|notice|info|debug>
terminal1 journalctl -f
terminal2 systemctl restart nginx
terminal1 journalctl -f -p notice
terminal2 su - 입력 후 passwd 오류 입력

period
30분 이내 건만 출력
journalctl -r --since -30m
