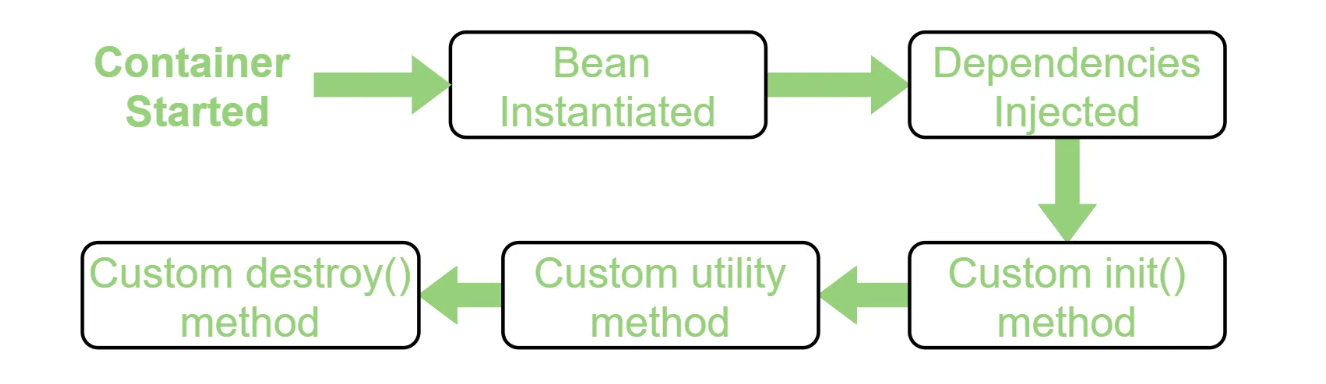
스프링 빈의 라이프사이클
스프링 빈의 라이프사이클은 크게 다음과 같은 단계로 나뉩니다.
- 객체 생성
- 의존성 주입
- 초기화(Initialization)
- 사용
- 소멸(Destruction)
스프링 IoC 컨테이너는 빈의 라이프사이클을 전적으로 관리하며, 필요한 메서드를 실행하거나 콜백을 호출하여 초기화 및 소멸 과정을 처리합니다.
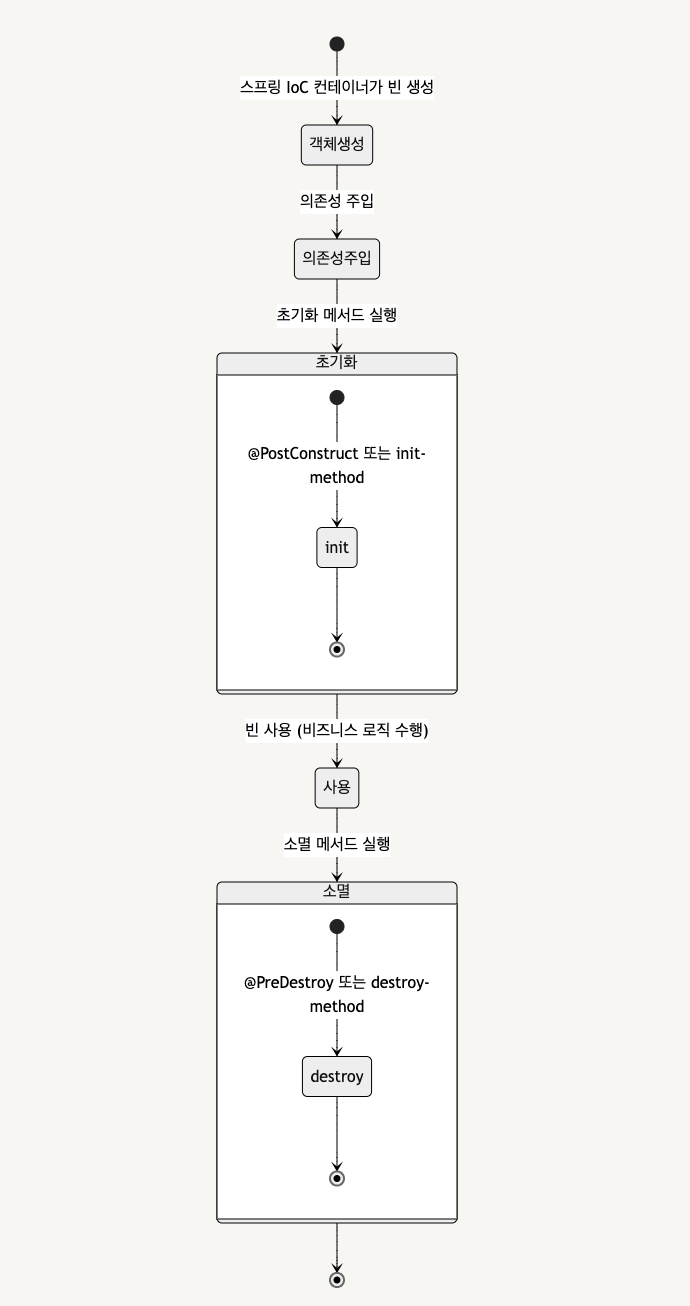
스프링 빈 라이프사이클의 각 단계
- 객체 생성: 스프링 컨테이너는 빈 정의에 따라 객체를 생성합니다. 이 단계에서는 빈의 생성자가 호출되어 객체가 메모리에 할당됩니다.
- 의존성 주입: 생성된 빈에 대해 의존성을 주입합니다. DI에 따라 필요한 의존성들이 생성자 주입, Setter 주입, 또는 필드 주입을 통해 주입됩니다.
- 초기화(Initialization): 빈이 설정되면 초기화 과정이 시작됩니다. 초기화 메서드는
@PostConstruct어노테이션이나init-method속성으로 지정할 수 있습니다. 이 단계에서 빈이 필요한 준비 작업을 수행하여 사용할 준비가 됩니다. - 사용: 빈은 사용 가능한 상태로 애플리케이션에서 제공하는 서비스를 수행합니다. 이 단계에서는 빈이 애플리케이션 내에서 비즈니스 로직을 처리하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 소멸(Destruction): 스프링 컨테이너가 종료되거나 빈이 더 이상 필요하지 않게 되면 소멸 단계로 이동합니다.
@PreDestroy어노테이션이나destroy-method속성을 통해 소멸 메서드를 지정할 수 있습니다. 소멸 메서드는 자원 해제 및 정리 작업을 수행합니다.
스프링 빈 라이프사이클 콜백 설정 방법
빈의 초기화와 소멸 과정에서 콜백 메서드를 설정할 수 있습니다. 스프링은 초기화와 소멸을 위해 다양한 방법을 제공합니다.
- InitializingBean과 DisposableBean 인터페이스 구현:
InitializingBean인터페이스의afterPropertiesSet()메서드를 통해 초기화 작업을 설정할 수 있습니다.DisposableBean인터페이스의destroy()메서드를 통해 소멸 작업을 설정할 수 있습니다.
@PostConstruct와@PreDestroy어노테이션 사용:@PostConstruct: 빈의 초기화 메서드를 지정합니다.@PreDestroy: 빈의 소멸 메서드를 지정합니다.
- XML 설정 파일의
init-method와destroy-method속성:- XML 설정에서
<bean>태그의init-method와destroy-method속성을 통해 초기화 및 소멸 메서드를 지정할 수 있습니다.
- XML 설정에서
빈 스코프와 객체 관리
스프링에서 빈은 싱글톤(Singleton)이 기본 스코프로 설정되지만, 여러 가지 스코프를 제공하여 객체 관리 방식을 다르게 할 수 있습니다.
- 싱글톤(Singleton): 스프링 컨테이너 내에서 빈을 한 번만 생성하여 모든 요청에서 같은 인스턴스를 사용합니다. 애플리케이션 내에서 공유가 필요한 빈에 적합합니다.
- 프로토타입(Prototype): 빈이 요청될 때마다 새 인스턴스를 생성합니다. 상태를 가지는 객체에 적합하며, 매번 다른 인스턴스가 필요할 때 사용합니다.
- Request/Session/GlobalSession: 웹 애플리케이션에서 HTTP 요청, 세션, 전역 세션별로 각각 다른 빈을 생성하는 스코프입니다. 일반적으로 웹 환경에서 사용됩니다.
예제: 빈 라이프사이클과 객체 관리 (애노테이션)
다음은 @PostConstruct와 @PreDestroy 어노테이션을 사용하여 초기화 및 소멸 과정을 지정하는 예제입니다.
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class ExampleBean {
public ExampleBean() {
System.out.println("ExampleBean 생성자 호출");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("ExampleBean 초기화 메서드 호출");
}
public void performTask() {
System.out.println("ExampleBean의 비즈니스 로직 수행");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("ExampleBean 소멸 메서드 호출");
}
}
XML 설정으로 초기화 및 소멸 메서드 지정
위의 예제를 XML 설정에서 초기화 및 소멸 메서드를 지정하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
<bean id="exampleBean" class="org.example.ExampleBean" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"/>
init-method="init":init메서드를 초기화 단계에서 호출합니다.destroy-method="destroy":destroy메서드를 소멸 단계에서 호출합니다.
이러한 설정을 통해 스프링은 빈의 생명 주기를 전적으로 관리하게 되며, 개발자는 객체 생성 및 소멸에 필요한 작업을 코드 수정 없이 설정할 수 있습니다.
관련 자료
예제 코드
package org.example.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
// 빈의 생성, 소멸 과정 InitializingBean, DisposableBean,
// 중간 설정 과정 ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware
public class WriteAction implements Action, InitializingBean, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware {
String writer;
public WriteAction() {
System.out.println("1. 생성자 호출");
}
public void setWriter(String writer) {
System.out.println("2. setWriter(String writer) 호출");
this.writer = writer;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("*. exectue() 호출");
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.out.println("4. setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) 호출");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("5. setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) 호출");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("3. setBeanName(String name) 호출");
// 빈 이름을 세팅
System.out.println("Bean name = " + name);
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("11. destroy() 호출");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("8. afterPropertiesSet() 호출");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("6. setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) 호출");
}
// 빈의 생성과 소멸에 추가 작동
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("9. initMethod() 호출 (개별 빈 커스팀 초기화 시)");
System.out.println("빈 커스텀 초기화");
}
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("12. destroyMethod 호출 (개별 빈 커스텀 소멸 시)");
System.out.println("빈 커스텀 소멸화");
}
}
package org.example.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class CustomBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("7. 초기화 전의 빈에 대한 처리 (전체)");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("10. 초기화 후의 빈에 대한 처리 (전체)");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
전체 라이프사이클과 단계별 호출되는 메서드
-
객체 생성 단계
- 생성자 호출: 스프링 컨테이너는 빈을 생성하기 위해 기본 생성자를 호출합니다.
1. 생성자 호출 -
프로퍼티 설정 단계
- Setter 메서드 호출: 스프링 컨테이너는 의존성을 주입하기 위해
setWriter(String writer)메서드를 호출합니다.
2. setWriter(String writer) 호출 - Setter 메서드 호출: 스프링 컨테이너는 의존성을 주입하기 위해
-
Aware 인터페이스를 통한 스프링 환경 정보 설정 단계
- 스프링 컨테이너는 빈에 스프링 컨텍스트와 관련된 여러 설정 정보를 주입하기 위해 다양한 Aware 인터페이스를 호출합니다.
- BeanNameAware: 빈의 이름을 주입받습니다.
3. setBeanName(String name) 호출 Bean name = writeAction - BeanClassLoaderAware: 빈의 클래스 로더를 설정합니다.
4. setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) 호출 - BeanFactoryAware: 빈의 생성 및 관리를 담당하는 BeanFactory를 설정합니다.
5. setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) 호출 - ApplicationContextAware: ApplicationContext 객체를 주입받습니다.
6. setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) 호출
-
초기화 전 빈에 대한 공통 처리 (BeanPostProcessor)
- CustomBeanPostProcessor 클래스의
postProcessBeforeInitialization메서드를 통해 빈 초기화 전 작업을 처리합니다. 이 메서드는 모든 빈에 대해 공통적인 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
7. 초기화 전의 빈에 대한 처리 (전체) - CustomBeanPostProcessor 클래스의
-
InitializingBean을 통한 초기화 (afterPropertiesSet)
- InitializingBean 인터페이스의
afterPropertiesSet()메서드가 호출됩니다. 이 메서드는 빈의 초기화 작업을 수행하며, 모든 속성 설정이 완료된 후에 호출됩니다.
8. afterPropertiesSet() 호출 - InitializingBean 인터페이스의
-
커스텀 초기화 메서드 (initMethod)
- init-method 속성으로 지정된
initMethod()가 호출됩니다. 이 메서드는 사용자 정의 초기화 메서드로, 초기화가 필요한 추가 작업을 지정할 수 있습니다.
9. initMethod() 호출 (개별 빈 커스팀 초기화 시) 빈 커스텀 초기화 - init-method 속성으로 지정된
-
초기화 후 빈에 대한 공통 처리 (BeanPostProcessor)
- CustomBeanPostProcessor 클래스의
postProcessAfterInitialization메서드를 통해 빈 초기화 후 작업을 수행합니다.
10. 초기화 후의 빈에 대한 처리 (전체) - CustomBeanPostProcessor 클래스의
-
빈 사용 단계
- 빈이 초기화된 후에는 실제 애플리케이션에서 사용됩니다. 여기서는
execute()메서드를 호출하여 빈의 기능을 수행할 수 있습니다.
*. execute() 호출 - 빈이 초기화된 후에는 실제 애플리케이션에서 사용됩니다. 여기서는
-
빈 소멸 단계 (destroy)
- DisposableBean 인터페이스의
destroy()메서드를 호출하여 빈의 소멸 작업을 수행합니다.
11. destroy() 호출 - DisposableBean 인터페이스의
-
커스텀 소멸 메서드 (destroyMethod)
- destroy-method 속성으로 지정된
destroyMethod()가 호출됩니다. 이 메서드는 빈이 소멸될 때 필요한 추가적인 정리 작업을 수행합니다.
12. destroyMethod 호출 (개별 빈 커스텀 소멸 시) 빈 커스텀 소멸화 - destroy-method 속성으로 지정된
빈 라이프사이클 전체 흐름 요약
위에서 설명한 단계들을 전체적으로 보면 다음과 같은 라이프사이클 흐름이 완성됩니다:
1. 생성자 호출
2. setWriter(String writer) 호출
3. setBeanName(String name) 호출
4. setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) 호출
5. setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) 호출
6. setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) 호출
7. 초기화 전의 빈에 대한 처리 (전체)
8. afterPropertiesSet() 호출
9. initMethod() 호출 (개별 빈 커스팀 초기화 시)
10. 초기화 후의 빈에 대한 처리 (전체)
*. execute() 호출 (빈 사용 단계)
11. destroy() 호출
12. destroyMethod 호출 (개별 빈 커스팀 소멸 시)
각 단계의 역할 및 중요성
- 생성 및 프로퍼티 설정: 빈이 스프링 컨테이너에서 인스턴스화되며 필요한 의존성이 주입됩니다.
- Aware 인터페이스 단계: 빈이 스프링 컨텍스트의 정보를 필요로 할 경우 Aware 인터페이스를 통해 설정됩니다.
- BeanPostProcessor: 초기화 전후에 모든 빈에 대해 공통적으로 수행될 작업을 지정할 수 있습니다.
- 초기화 및 커스텀 초기화: 모든 의존성이 주입된 후, 빈이 사용 준비를 위해 초기화됩니다.
- 빈 사용: 초기화가 완료된 빈은 실제 애플리케이션에서 비즈니스 로직을 수행하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 소멸 및 커스텀 소멸: 빈의 소멸 시점에 필요한 정리 작업이 수행됩니다.
이와 같은 단계적 생명주기 과정을 통해 스프링 프레임워크는 빈 객체의 생성부터 소멸까지 완전한 제어를 제공하여, 개발자가 빈의 라이프사이클을 효율적으로 관리할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
