알고리즘 분류: 구현
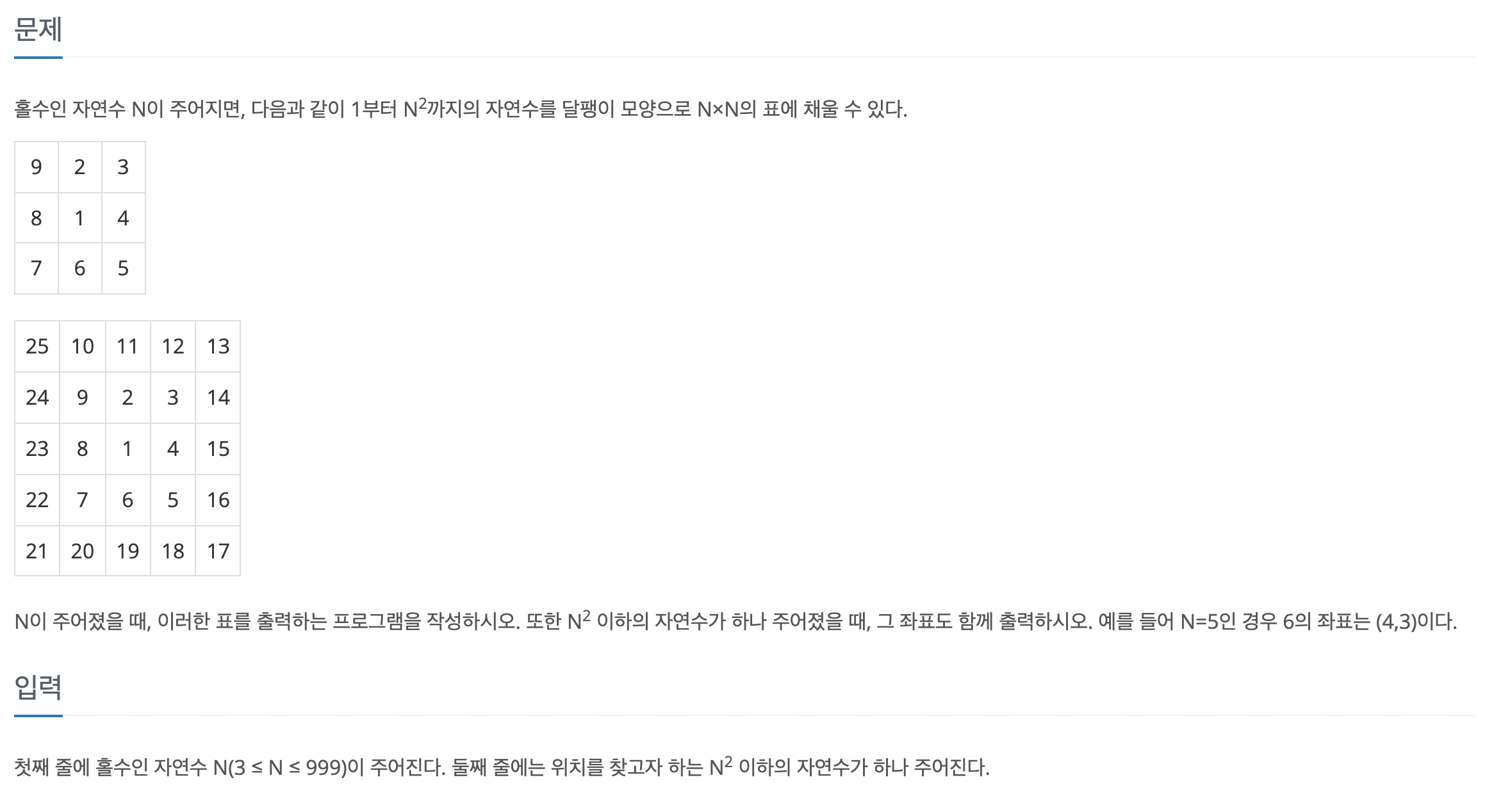
최종 제출 코드 (성공)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
static int[][] snail;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int where = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
// 달팽이 표 출력
printSnail(N, where);
br.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void printSnail(int N, int where) {
// N X N 배열 생성
snail = new int[N][N];
// 시작 위치
int x = N / 2;
int y = N / 2;
// 달팽이 표 생성 // U -> R -> D -> L
int num = 1;
int count = 1;
loop1:
while (true) {
// U
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
// 마지막은 U에서 끝남
if (x == 0 && y == 0) break loop1;
x--;
}
// R
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
y++;
}
count++;
// D
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
x++;
}
// L
for (int i = 0; i < count;i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
y--;
}
count++;
}
int wx = 0, wy = 0;
// 출력시간 줄이기 위해
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (where == snail[i][j]) {
wx = i;
wy = j;
}
sb.append(snail[i][j]).append(" ");
}
sb.append("\n");
}
System.out.print(sb);
System.out.println(++wx + " " + ++wy);
}
}
눈물 나는 도전기..😅
문제풀이
snail = new int[N][N];N X N 배열 생성
// 시작 위치
int x = N / 2;
int y = N / 2;배열의 가운데서 달팽이 수열이 시작하니까 인덱스 0부터 시작하는 걸 고려하면 2로 나눈 몫 지점부터 시작!
달팽이 수열은 상 -> 우 -> 하 -> 좌 순으로 움직이는데 각각의 길이가 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, ... 순으로 증가하는 걸 발견했다.
int count = 1;count 변수를 두어 위치가 두번 바뀔 때마다 1씩 증가하도록 구현한다.
증가하는 수 자체는 num 변수를 두어 배열에 들어간 다음 1씩 증가하도록 후위 연산자 ++을 이용하였다.
while (true) {
// U
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
// 마지막은 U에서 끝남
if (x == 0 && y == 0) break loop1;
x--;
}
// R
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
y++;
}
count++;
// D
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
x++;
}
// L
for (int i = 0; i < count;i++) {
snail[x][y] = num++;
y--;
}
count++;
}while문을 통해 상 -> 우 -> 하 -> 좌 순으로 count 횟수만큼 반복하여 수열을 생성한다.
이 때, 수열이 끝나는 지점은 0, 0 인데 항상 방향이 상일 때 끝나는 것을 보았고 상 방향에서 x, y위치를 확인하여 0, 0이면 while문을 빠져나오도록 구현하였다.
또 !
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(snail[i][j]).append(" ");처음에는 일일이 배열을 출력했지만 뛰어난 성능을 가진 StringBuilder를 이용하여 시간 초과를 해결하였다.
그리고 런타임에러(ArrayIndexOutOfBounds)
처음에는 아예 배열에서 숫자의 위치를 확인하여 출력시켜주는 메소드를 따로 만들어주었다.
private static void printWhere(int where, int N) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (where == snail[i][j]) System.out.println(++i + " " + ++j);
}
}
}어차피 snail 배열을 static으로 Main 클래스 안에서 선언해주었기 때문에 달팽이 수열을 구하고 출력한 뒤 그대로 다시 수를 찾아서 출력하면 될 줄 알았다. 메모리 측면에서도 더 효율적이라고 생각했다.
어차피 snail 배열은 static으로 똑같은 것을 사용하는 것인데 왜 배열 인덱스 범위가 벗어나 런타임에러가 발생할 수 있는지 알다가도 모를 일..
ㄴ이 부분 왜인지 아시는 분 있으면 알려주세요..😭
static 개념 다시 보다가 갑자기 싱글톤 패턴 개념도 다시 보기
싱글톤 패턴이란?
클래스를 통해 단 하나의 객체만 생성하게 강제하는 패턴
생성자를 private 키워드를 이용하여 다른 클래스에서 싱글톤 클래스의 생성자로의 접근을 막아 new를 이용하여 생성할 수 없게 한다.
싱글톤 패턴을 사용하는 이유?
객체를 생성할 때마다 메모리 할당을 받아야하는데 싱글톤 패턴을 통해 하나의 인스턴스 객체를 생성하여 메모리 낭비를 막을 수 있다. 또한 전역 객체로 공유가 가능하다.
혹시나... 싱글톤 패턴 적용해서 풀어봤는데 (제대로 맞게 한건지도 의문)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
class Snail {
private static Snail snail;
private static int[][] snailArr;
private Snail(int N) {
// N X N 배열 생성
snailArr = new int[N][N];
// 시작 위치
int x = N / 2;
int y = N / 2;
int num = 1;
int count = 1;
loop1:
while (true) {
// U
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snailArr[x][y] = num++;
// 마지막은 U에서 끝남
if (x == 0 && y == 0) break loop1;
x--;
}
// R
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snailArr[x][y] = num++;
y++;
}
count++;
// D
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
snailArr[x][y] = num++;
x++;
}
// L
for (int i = 0; i < count;i++) {
snailArr[x][y] = num++;
y--;
}
count++;
}
}
public static synchronized Snail getInstance(int N) {
if (snail == null) snail = new Snail(N);
return snail;
}
public void printSnail() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < snailArr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < snailArr.length; j++) {
sb.append(snailArr[i][j]).append(" ");
}
sb.append("\n");
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
public void printWhere(int where) {
for (int i = 0; i < snailArr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < snailArr.length; j++) {
if (snailArr[i][j] == where) {
System.out.println(++i + " " + ++j);
}
}
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int where = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
Snail snail = Snail.getInstance(N);
// 달팽이 표 출력
snail.printSnail();
snail.printWhere(where);
br.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}역시나 런타임 에러(ArrayIndexOutOfBounds) 발생...
다음에 다시 해결하러 와볼게.,, 안녕-😟
