하루 요약
천천히 하니까 할 수 있자나...!

✏️ 오늘의 한 일
- RB 트리 삽입
- GCC
- 메모리 누수
🌈 오늘의 성장
RB TREE 삽입
삽입하는 노드의 색깔은 항상 RED
삽입 절차
- 삽입 전 RB트리의 5가지 속성을 만족
- 삽입 방식은 일반적인 BST 방식과 동일
- 삽입 후 RB트리 위반 여부 확인
- RB트리 속성 위반시 재조정
- RB 트리 속성을 다시 만족
1. RED 삽입 후 2번 속성(root ⇒ Black)위반시
⇒ 루트를 블랙으로 변경
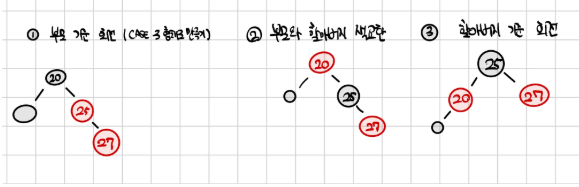
2. RED 삽입 후 4번 속성 위반 (Red⇒Black) 위반시
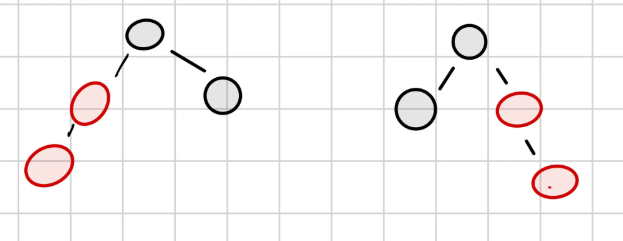
- CASE3 (일직선)
- 삽입된 RED가
- 부모의 왼쪽 자녀 or 오른쪽 자녀
- 부모도 RED
- 부모의 형제는 BLACK 인경우
부모와 할아버지의 색 교환 + 할아버지 기준 오른쪽 회전
- 삽입된 RED가
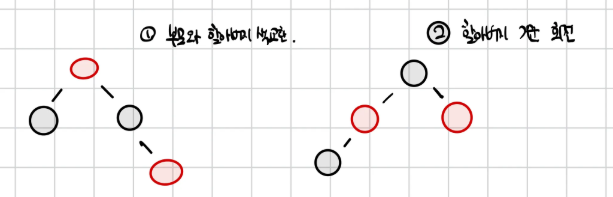
3. RED 삽입 후 4번 속성 위반(Red⇒Black)위반시
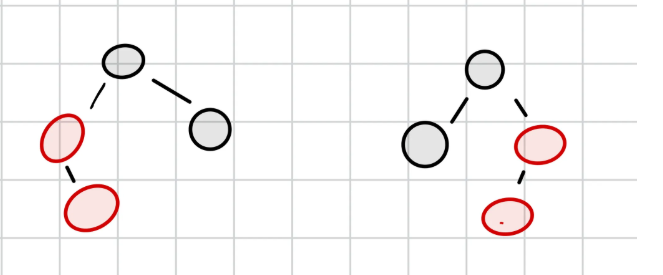
- CASE2 (꺾인 경우)
- 삽입된 RED가
- 부모의 오른쪽 자녀 or 왼쪽 자녀
- 부모도 RED
- 부모의 형제는 BLACK
부모 기준 왼쪽 회전+CASE3 방식
- 삽입된 RED가
4. RED 삽입 후 4번 속성 위반(Red⇒Black)위반시
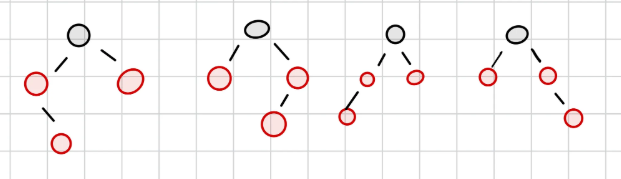
- CASE1
- 삽입된 RED의
- 부모의 형제가
RED - 부모도
RED
- 부모의 형제가
부모와 부모 형제 노드 색 변경 + 할아버지 색변경⇒ 할아버지 노드에서 다시 확인 시작- 5번 속성을 만족한다면, 부모와 두 자녀의 색을 바꾸어도 5번 속성을 만족한다는 원리를 이용
- 삽입된 RED의
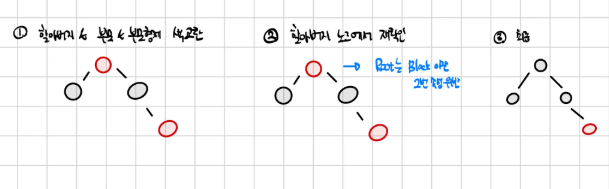
그럼 이걸 어떻게 코드화 하면 좋을까?
일단 삽입되었을 때, RB TREE의 속성을 깨는 경우를 분기처리 하면 다음 과 같다.
결국 RB트리의 삽입 함수는 삽입 위치 탐색 -> 삽입 -> RB트리 속성에 맞게 재조정
의 단계로 진행된다.
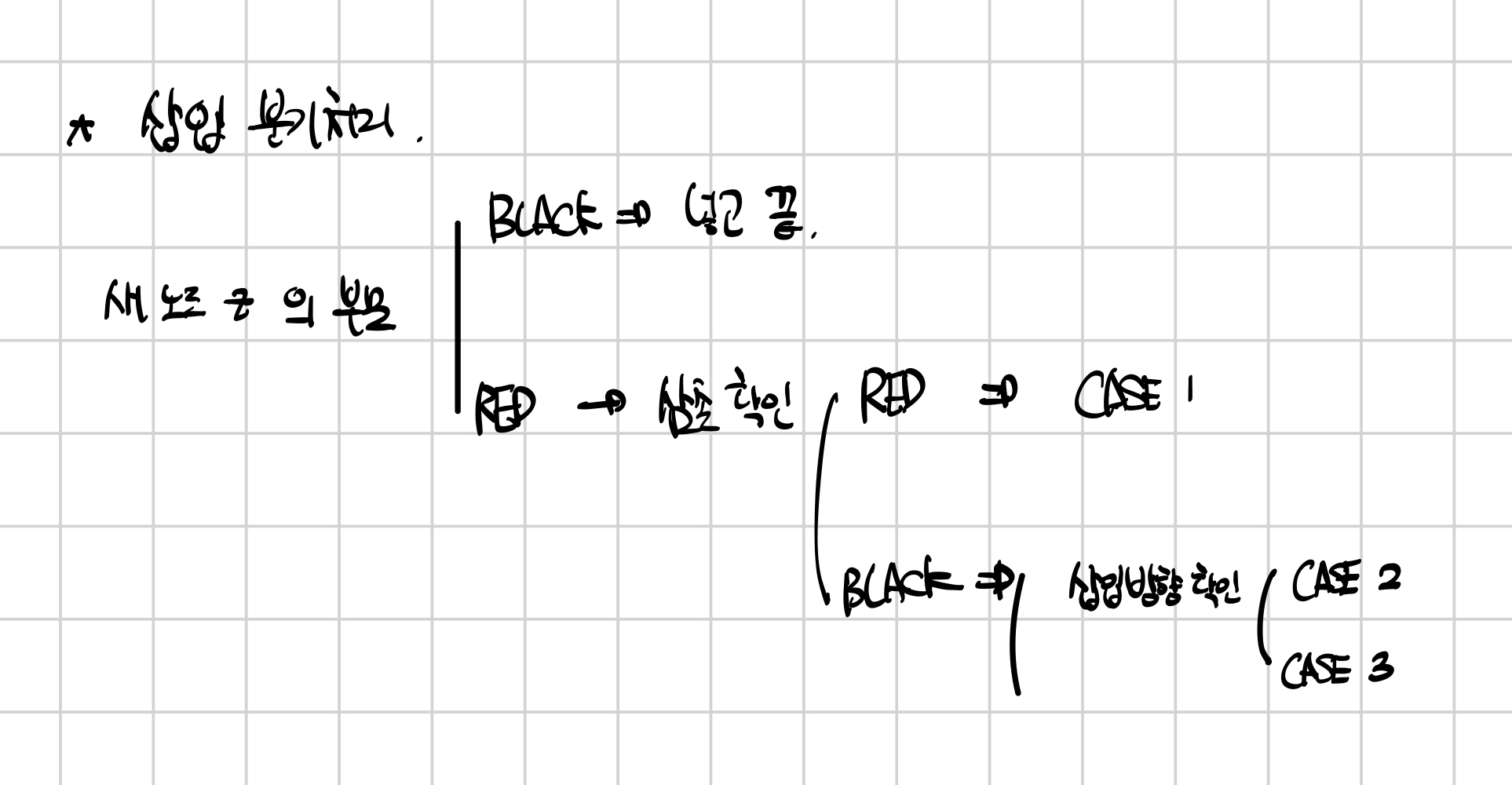
재조정 함수 Fixed-up 설계
1. 루트 노드 속성 위반
- 삽입된 노드가 트리의 첫 노드(= 루트)인 경우
- ⇒ 루트는 반드시 BLACK이어야 함
- 처리:
- 삽입 후
new_node->parent == t->nil이면 new_node->color = RBTREE_BLACK- 하고 RETURN
- 삽입 후
2. CASE 3: 일직선 구조 (Red 부모 + Black 삼촌)
- 삽입 노드의 부모가 RED일 경우 문제 발생
- 삽입 노드와 부모가 같은 방향 (왼↙️ or 오른↘)
- 조건 판단
- 부모의 형제(삼촌)가 BLACK이고
삽입 방향 == 부모 방향일 때 (예: 부모가 왼쪽 자식이고, 삽입된 노드도 왼쪽 자식)
-
부모와 조부모의 색 교환
color_t temp = parent->color; parent->color = grand_parent->color; grand_parent->color = temp; ``` -
회전 ⇒ 조부모노드 기준**
- 삽입 방향이 오른쪽이면 →
left_rotate - 삽입 방향이 왼쪽이면 →
right_rotate
- 삽입 방향이 오른쪽이면 →
3. CASE2. 꺾인 구조(RED 부모 + BLACK 삼촌)
- 삽입 노드의 부모가 RED
- 삽입 노드와 부모가 다른 방향(LEFT- RIGHT , RIGHT-LEFT)
- 조건 판단
- 부모의 형제(삼촌)가 BLACK이고
삽입 방향 != 부모 방향일 때
- 부모 기준 회전
- 삽입 방향이 오른쪽이면 →
left_rotate - 삽입 방향이 왼쪽이면 →
right_rotate
- 삽입 방향이 오른쪽이면 →
- CASE 3 방식을 활용
4. CASE 1. (RED 부모, + RED 삼촌)
- 삽입 노드의 부모가 RED
- 조건 판단
- 부모의 형제(삼촌)가 RED
-
삽입 노드 기준 부모&삼촌과 조부모 색깔 변경
- 그럼 조부모를 레드로
- 삼촌이랑 부모를 블랙으로
parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK; uncle->color = RBTREE_BLACK; grand_parent->color = RBTREE_RED; -
조부모 노드에서 다시 확인
- 조부모 노드를 다시 재귀적으로
Fix-up
- 조부모 노드를 다시 재귀적으로
이제 분기처리에 맞게 구조체의 포인터를 사용해서 구현하면 된다.
함수 구현에 필요한 변수 및 구조체 선언
void rbtree_fix_up(rbtree *t, node_t *z){
node_t *uncle;
node_t *parent = z->parent; // 새 노드의 부모
node_t *grand_parent = parent->parent; // 새 노드의 조부모
// int is_uncle_right = 0;
int is_straight_left = 0;
int is_straight_right = 0;예외 처리
// 예외처리
if (parent == t->nil || grand_parent == t->nil) return;
// 1. 루트 노드 속성 위반
if (t->root == z){
z->color = RBTREE_BLACK; // 루트노드로 들어간 z를 새 노드로 변경
return;
}삼촌이 조부모의 왼쪽 자식인지 오른쪽 자식인지 판별
// 0. 삼촌 노드 방향 Tracking
if (grand_parent->left == parent) {
uncle = grand_parent->right;
} else {
uncle = grand_parent->left;
}새로운 노드의 삽입 방향을 체크
// 삽입 방향 체크
if((parent->left == z) && (grand_parent->left == parent)){
is_straight_left = 1;
}
if((parent->right == z) && (grand_parent->right == parent)){
is_straight_right = 1;
}
새로운 노드 Z의 부모 색 확인
- 새로운 노드는 레드, 그때의 부모가 검정이라면 굳이 재조정 필요 없으니 RETURN
// 새노드 z의 부모 색깔 확인
if(parent->color == RBTREE_BLACK){ // 부모가 껌정이면 굳이 재조정 필요 없으니 return
return;
} CASE 1, CASE 3, CASE 2 확인
// CASE 1(부모 RED + 삼촌 RED)
if(uncle != t->nil && uncle->color == RBTREE_RED){
// parent & uncle와 grand_parent의 색 변경
parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
uncle->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
grand_parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
// 조부모 노드에서 다시 확인
rbtree_fix_up(t, grand_parent);
} else{ // (부모 RED + 삼촌 BLACK)
// CASE 3 (일직선)
if(is_straight_left){ // 왼쪽 일직선
// 1. 부모와 조부모 색 교환
color_t temp = parent->color;
parent->color = grand_parent->color;
grand_parent->color = temp;
// 2. 회전
right_rotate(t, grand_parent);
} else if(is_straight_right){
// 1. 부모와 조부모 색 교환
color_t temp = parent->color;
parent->color = grand_parent->color;
grand_parent->color = temp;
left_rotate(t, grand_parent);
} else {
// CASE 2 (꺾인 선)
if(parent->left == z){
// 왼쪽 삽입인 경우
right_rotate(t, parent);
z = z->left;
}
else
{ // 오른쪽 삽입
left_rotate(t, parent);
z = z->right;
}
// CASE 3 적용
parent = z->parent;
grand_parent = parent->parent;
color_t temp = parent->color;
parent->color = grand_parent->color;
grand_parent->color = temp;
if (z == parent->left) {
right_rotate(t, grand_parent);
} else {
left_rotate(t, grand_parent);
}
}
}
t->root->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
}GCC
GNU 컴파일러의 모음으로 GNU Compiler Collection의 약자이다.
결국 컴파일 도구인데,
컴파일 과정은 알다 시피 전처리 -> 컴파일 -> 어셈블 -> 링크 단계로 구성된다.
GCC 옵션
GCC컴파일러 역시 위 4단계를 다 거치기 때문에 옵션을 통해 조절이 가능하다
-o [파일명] [*.c]- 저장한 파일 명으로 실행 파일을 저장
gcc -o result.out main.c⇒ main.c 의 실행파일이 result.out에 저장
-E- 전처리 단계 수행한 후, 컴파일 과정을 거치지 않음, 결과는 standard output에 출력
-S- 컴파일 단계 수행 후, 어셈블 과정을 거치지 않음, 실행 결과로 어셈블리어로 바뀐
*.s가 생성
- 컴파일 단계 수행 후, 어셈블 과정을 거치지 않음, 실행 결과로 어셈블리어로 바뀐
-c[파일명][*. c]- 소스 코드를 컴파일 또는 어셈블, 링크 하지 않음, 파일명으로 오브젝트 파일 생성
gcc -c ft_isalnum.c
D [매크로상수명]=[값]:- 매크로 상수를 정의하기 위한 옵션이다.
ex)gcc -D BUFFER_SIZE=42 : BUFFER_SIZE라는 매크로 상수의 값을 42로 설정한다.
- 매크로 상수를 정의하기 위한 옵션이다.
여러 코드를 하나의 실행파일로 만들기
이번에 rbtree lab을 진행하면서 헤더파일과 여러개의 c 파일을 실행 파일로 만들어야 했다.
물론 MAKEFILE 이 제공되었지만, 이게 없었다면 어떻게 해야할까...? 라는 생각이 들었다.
- GCC 사용시
- 각각의 소스코드 파일들을 옵젝 파일로 변환
- 전처리 과정에서 헤더 파일은 합쳐짐(헤더는 필요 X)
- 여러개의 오브젝트 파일로 링크, 하나의 실행파일로 묶어주기
gcc -c rbtree.c
gcc -c driver.c
gcc -c test-rbtree.c
gcc -o test.out rbtree.o driver.o test-rbtree.o특히나 이 방식은 특정 파일이 수정되었다면, 다시 컴파일 해주어야 한다.
이걸 간편하게 만들어주는 것이 바로 Makefile
- Make 사용시
(make clean)
make testMAKEFILE 의 기능
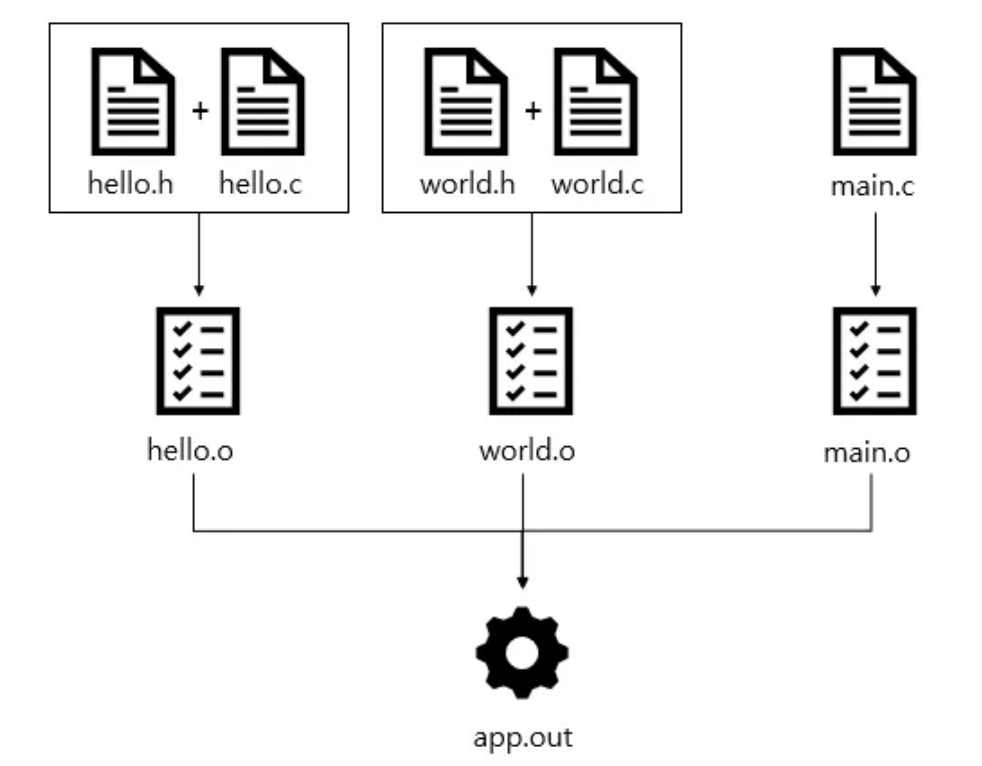
- incremental Build
- 컴파일 및 빌드 과정 자동화 + incremental build를 지원
- 변경된 파일에 의존성이 있는 대상들만 다시 빌드
- 위 사진 예시에서 hello.c 만 수정했다면
hello.o 와 app.out 만 다시 빌드
- 위 사진 예시에서 hello.c 만 수정했다면
- Built-in-rult
- 자주 사용되는 내장 규칙들을 자동 처리
- 소스파일(.c)를 목적 파일(.o)로 변환
- 자주 사용되는 내장 규칙들을 자동 처리
- make Clean
- make를 진행하면 쓸데없이 목적파일(.o) 들이 남는데, 이걸 일일히 지우기가 귀찮다
- 이걸 clean 명령어 하나로 쉽게 지울 수 있다.
메모리 누수 검사해보기
문제의 코드
void delete_rbtree(rbtree *t) {
// TODO: reclaim the tree nodes's memory
// 재귀적으로 진행?, 루트에서 양쪽 자식 확인후 있다면 재귀적으로 free?
if (t == NULL) return;
node_t *root = t->root;
if (root != t->nil) {
if (root->left != t->nil) { // 왼쪽 서브트리 있다면
t->root = root->left; // heap-use-after-free
delete_rbtree(t);
}
if (root->right != t->nil) { // 오른쪽 서브트리 있다면
t->root = root->right;
delete_rbtree(t);
}
free(root);
}
// 마지막 루트 기준 nil과 트리 해제
if (t->root == root) { // 가장 처음 들어온 루트일 때만
free(t->nil);
free(t);
}
}그 MacOS는 valgrind 지원이 종료되어, Clang/GCC 내장 기능인 AddressSanitizer를 사용했다.
clang -fsanitize=address -g -o rbtree test.c rbtree.c
./rbtree
결과값은
==7546==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-use-after-free on address 0x6020000000f8 at pc 0x000100e0a1c8 bp 0x00016eff6ab0 sp 0x00016eff6aa8
READ of size 8 at 0x6020000000f8 thread T0
#0 0x000100e0a1c4 in delete_rbtree rbtree.c:73
#1 0x000100e0a158 in delete_rbtree rbtree.c:71
#2 0x000100e09310 in main test.c:59
#3 0x000199ae4270 (<unknown module>)-
문제 상황
heap-use-after-free
free로 메모리할당 받은 것을 해제를 했는데, 이후에 그 메모리를 읽으려고 하고 있다. -
원인
t->root = root->left; , t->root = root->right;
지금 코드를 잘 보면,
root를 가리키던 트리를 root->left 또는 root->right로 갱신한 후, 다시 재귀적으로 delete_rbtree(t) 호출한다.
이 상태에서 마지막에 free(root)를 하게 되면 이미 헤제된 메모리를 재귀 도중 다시 접근하기 때문에 발생
- 해결
루트 변경 후 각 자식별 재귀를, 각 자식노드 먼저 재귀를 돌고 루트를 변경하고 현재 루트 노드를 해제하는 방식으로 수정void delete_node(rbtree *t, node_t *node) { if (node == t->nil) return; delete_node(t, node->left); delete_node(t, node->right); free(node); } void delete_rbtree(rbtree *t) { if (t == NULL) return; delete_node(t, t->root); free(t->nil); free(t); }
⛏ 오늘의 삽질
위 코드를 테스트 돌릴때 처음에 레드 노드 다음에 레드 노드가 오는 그런 결과가 등장
알고보니 CASE 3에서 회전을 조부모 노드를 넘겨준게 아니라 부모 노드를 넘겨주어 잘못된 결과가 등장
이를 조부모를 수정해서 완성했다.