Emotion 은 JS 로 css 스타일을 작성하도록 설계된 라이브러리다.
Emotion은 프레임워크에 구애 받지 않고 사용이 가능하며, React와 함께 사용할 수도 있다.
1. 패키지 소개
@emotion/css 패키지
npm i @emotion/cssimport { css } from '@emotion/css'
const color = 'white'
render(
<div
className={css`
padding: 32px;
background-color: hotpink;
font-size: 24px;
border-radius: 4px;
&:hover {
color: ${color};
}
`}
>
Hover to change color.
</div>
) @emotion/css 패키지는 프레임워크에 구애받지 않으며 Emotion 을 사용할수 있는 방법이다.
바벨 플러그인, config 변경 같은 다른 추가 셋팅이 필요하지 않는다.
자동으로 벤더프리픽스를 지원하고, 중첩 선택자, 미디어 쿼리를 지원한다.
css 클래스 이름을 생성하고 cx 구성하는 기능을 사용하는 것을 선호한다.
@emotion/react 패키지
npm i @emotion/react@emotion/react 패키지는 리액트가 필요하며 리액트 사용자에게 권장된다.
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const color = 'white'
render(
<div
css={css`
padding: 32px;
background-color: hotpink;
font-size: 24px;
border-radius: 4px;
&:hover {
color: ${color};
}
`}
>
Hover to change color.
</div>
)빌드환경이 React를 사용할때 가장 좋다.
css 속성 지원
-
style 속성과 유사함, 그러나 벤더프리픽스를 지원하고, nested 선택자, 미디어 쿼리를 지원
-
css 속성은 theme 와 함께 호출되는 인수를 허용해서 개발자가 공통 및 사용자 정의 가능한 값에 쉽게 접근할 수 있도록 한다.
-
적절한 패넡과 구성이 설정되도록 ESLint 플러그인을 사용할 수 있다.
css() 함수 특징
-
css() 함수는 css 스타일 선언 내용을 인자로 받는데 객체형으로 넘겨도 되고 문자형으로 넘겨도 된다.
[객체형]
import { css } from "@emotion/react";
function MyComponent() {
return (
<div
css={css({
color: "green",
})}
>
객체형
</div>
);
}[문자형]
import { css } from "@emotion/react";
function MyComponent() {
return (
<div
css={css`
color: blue;
`}
>
문자형
</div>
);
}
Emotion 문서에는 스타일을 객체로 선언해서 css() 함수에 넘기라고 권장하는데, 이 방법은 css() 함수 호출을 생략하고 css prop 에 바로 객체를 넘길수 있으며 타입스크립트를 사용하면 타입체킹을 통해 오타를 줄여줄 수 있기 때문이다.
@emotion/styled 패키지
npm i @emoiton/styled @emotion/react@emotion/styled 패키지는 style 을 가진 Component 를 만들고 싶을 사람들에게 선호된다.
import styled from '@emotion/styled'
const Button = styled.button`
padding: 32px;
background-color: hotpink;
font-size: 24px;
border-radius: 4px;
color: black;
font-weight: bold;
&:hover {
color: white;
}
`
render(<Button>This my button component.</Button>)2. 설치
Emotion 을 사용하는 방법은 여러가지가 있는데, 만약 리액트를 사용한다면 가장 쉽게 사용할 수 있는 방법은 @emotion/react package 를 설치하는 것이다. React 를 사용하지 않는다면 @emotion/css 를 사용한다.
yarn add @emotion/react 스타일을 압축 및 호이스팅 하여 최적화하고 souce map 및 label 로 더 나은 개발자 경험을 생성하는 플러그인이 있다. (선택)
yarn add@emotion/babel-plugin3. CSS props
이모션으로 요소를 style 링 하는 주된 방법은 css props 를 사용하는 것이다.
JSX Pragma
jsx pragma 를 css props 을 사용하는 소스 파일의 가장 상단에 둬야한다.
이 option 은 css prop 기능을 테스트 하거나 babel 구성을 구성할 수 없는 프로젝트(create-react-app, codesandbox 등)에서 가장 잘 작동한다.
React v16 이하의 버전을 사용하는 곳에서는 아래와 같이 써야하고, jsx() 함수도 불러와야한다.
/** @jsx jsx */
import {css, jsx} from '@emotion/react";이것은 React.createElement 대신 jsx 함수를 사용하도록 jsx babel 플러그인을 구성하는 것이다.
그 이상의 버전에서는
/** @jsxImportSource @emotion/react */위와 같이 상단에 쓰면, React 의 jsx() g함수를 사용하지 말고 Emotion 의 jsx() 함수를 사용하라는 뜻이다.
써주지 않으면 css prop 에 넘어간 스타일이 제대로 반영이 안될 수 있다.
스타일 우선순위
className 속성의 이모션 스타일을 포함하는 className 이 css 속성 스타일을 재정의한다.
이모션 외의 소스에서 가져온 클래스 이름은 무시되고 계산된 이모션 클래스 이름에 추가된다.
우선순위 순서는 직관적이지 않은 것처럼 보일 수 있지만, 부모로 부터 전달된 className prop 을 통해 css prop에 정의된 스타일을 가진 구성 요소를 커스텀 할 수 있다.
const P = props => (
<p
css={{
margin: 0,
fontSize: 12,
lineHeight: '1.5',
fontFamily: 'Sans-Serif',
color: 'black'
}}
{...props} // <- props contains the `className` prop
/>
)
const ArticleText = props => (
<P
css={{
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Georgia, serif',
color: 'darkgray'
}}
{...props} // <- props contains the `className` prop
/>
)위 예제의 경우 p 요소의 css 가 정의되어 있는데, ArticleText 요소가 p를 재정의 함으로써
중복된 css 가 덮어 씌워진다.
fontSize, fontFamily, color 는 ArticleText 에 정의된 것이 우선한다.
4.Composition
Composition 은 이모션에서 가장 강력하고 유용한 기능이다. CSS에서 반환된 값을 다른 스타일 블록에 보간하여 스타일을 함께 구성할 수 있다.
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const base = css`
color: hotpink;
`
render(
<div
css={css`
${base};
background-color: #eee;
`}
>
This is hotpink.
</div>
)일반적으로 css 는 여러 클래스를 사용하여 스타일을 함께 구성할 수 있지만, 정의된 순서에 따라 나중에 정의된 것이 우선된다.
그런데 Emotion 을 사용하면 스타일을 만들고 결합할 수 있다.
이모션의 Compositon 을 사용하면 스타일이 사용 순서대로 병합되므로 스타일이 생성된 순서를 생각할 필요가 없다.
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const danger = css`
color: red;
`
const base = css`
background-color: yellow;
color: turquoise;
`
render(
<div>
<div css={base}>This will be turquoise</div>
<div css={[danger, base]}>
This will be also be turquoise since the base styles overwrite the danger
styles.
</div>
<div css={[base, danger]}>This will be red</div>
</div>
)5.중첩 선택자
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const paragraph = css`
color: turquoise;
a {
border-bottom: 1px solid currentColor;
cursor: pointer;
}
`
render(
<p css={paragraph}>
Some text. <a>A link with a bottom border.</a>
</p>
)paragraph 안의 a 태그에 대한 style 은 위와 같이 줄 수 있다.
또한 & 를 사용해서 다른요소에 중첩된 현재 클래스를 선택할 수 있다.
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const paragraph = css`
color: turquoise;
header & {
color: green;
}
`
render(
<div>
<header>
<p css={paragraph}>This is green since it's inside a header</p>
</header>
<p css={paragraph}>This is turquoise since it's not inside a header.</p>
</div>
)paragraph 중 header 에 중첩된 요소는 color 가 green 으로 표시된다.
6.미디어쿼리
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
render(
<p
css={css`
font-size: 30px;
@media (min-width: 420px) {
font-size: 50px;
}
`}
>
Some text!
</p>
)재사용 가능한 미디어쿼리
미디어쿼리를 사용할때, 해상도를 변수로 설정해서 실수를 방지하며 반복을 줄일 수 있다.
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const breakpoints = [576, 768, 992, 1200]
const mq = breakpoints.map(bp => `@media (min-width: ${bp}px)`)
render(
<div>
<div
css={{
color: 'green',
[mq[0]]: {
color: 'gray'
},
[mq[1]]: {
color: 'hotpink'
},
[mq[2]]: {
color: 'yellow'
},
[mq[3]]: {
color: 'red'
},
}}
>
Some text!
</div>
</div>
)facepaint - 미디어 쿼리를 좀더 편리하게 쓰자
facepaint 라이브러리를 설치하면 미디어쿼리를 좀 더 편하게 쓸수있다.
facepaint 는 오직 객체 styles 에서만 쓸 수 있다.
yarn add facepaintimport facepaint from 'facepaint'
const breakpoints = [576, 768, 992, 1200]
const mq = facepaint(breakpoints.map(bp => `@media (min-width: ${bp}px)`))
render(
<div
css={mq({
color: ['green', 'gray', 'hotpink', 'red']
})}
>
Some text.
</div>
)576 이하에서는 green
576~768 사이에서는 gray
768~922 사이에서는 hotpink
922 이상에서는 red
Global Styles
종종 reset css 나 fontface 와 같이 글로벌 css 가 필요할 수 있다.
그때 Global 컴포넌트를 사용할 수 있다. 글로벌 컴포넌트는 styles prop을 포함하고 있다.
import { Global, css } from '@emotion/react'
render(
<div>
<Global
styles={css`
.some-class {
color: hotpink !important;
}
`}
/>
<Global
styles={{
'.some-class': {
fontSize: 50,
textAlign: 'center',
color: 'red !important',
}
}}
/>
<div className="some-class">This is hotpink now!</div>
</div>
)style 을 공유하는 방법
1) CSS 개체 내보내기
스타일을 공유하는 가장 간단한 방법은 공유파일에서 CSS 를 내보낸 다음 여러 위치에서 해당 CSS 를 가져오는 것이다.
export const errorCss = css({
color: 'red',
fontWeight : 'bold'
})
//Use arrays to compose styles
export const largeErrorCss = css([errorCss, {fontSize: '1.5rem'}])그리고 구성요소에 가서 import 해서 쓰면 된다.
import {errorCss} from '...'
return <p css={errorCss}> Failed to fizzle the frozzle.</p>이 방법은 css 만 공유하려는 경우에 유용하다.
2) 컴포넌트 재사용을 통한 스타일 공유
이 방법은 약간 더 복잡하지만 강력하다.
export function ErrorMessage({className, children}) {
return (
<p css={{color:'red', fontWeight: 'bold'}} className={className}>{children}</p>
)
}
export function LargeErrorMessage({className, children}) {
return (
<ErrorMessage css={{fontSize: '1.5rem'}} className={className}>{children}</ErrorMessage>
)
}참고) 'fontSize: '1.5rem'은 className prop을 통해 ErrorMessage 구성 요소로 전달되므로 ErrorMessage에서 className prop을 받아야 작동합니다!
그리고 컴포넌트 중 하나에서
import {ErrorMessage} from '...'
return <ErrorMessage>Failed to fizzle the frozzle.</ErrorMessage>동적 스타일에 style prop 을 사용해라
css 변수를 쓰지 않을 경우 각각 다른 아바타 이미지를 주기 위해 아래와 같이 css 를 작성해야한다.
<style>
.css-1udhswa {
border-radius: 50%;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-style: url(https://i.pravatar.cc/150?u=0);
}
.css-1cpwmbr {
border-radius: 50%;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-style: url(https://i.pravatar.cc/150?u=1);
}
.css-am987o {
border-radius: 50%;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-style: url(https://i.pravatar.cc/150?u=2);
}
</style>스타일을 가진 css 변수
.avatar {
border-radius: 50%;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-style: var(--background-style);
}function Avatar({ imageUrl }) {
return <div className="avatar" style={{ '--background-style': imageUrl }} />
}타입스크립트로 쓴다면
style={{ ['--background-style' as any]: imageUrl }}컴포넌트 외부에서 style 정의
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const cardCss = {
self: css({
backgroundColor: 'white',
border: '1px solid #eee',
borderRadius: '0.5rem',
padding: '1rem'
}),
title: css({
fontSize: '1.25rem'
})
}
export function Card({ title, children }) {
return (
<div css={cardCss.self}>
<h5 css={cardCss.title}>{title}</h5>
{children}
</div>
)
}색상 및 기타 스타일 상수를 js 변수로 정의.
앱 전체에서 색상, 패딩, 테두리 반경 등을 사용하는 경우 테마에 추가하거나 다음과 같이 js 상수로 정의한다.
export const colors = {
primary: '#0d6efd',
success: '#198754',
danger: '#dc3545'
}Keyframse
import { css, keyframes } from '@emotion/react'
const bounce = keyframes`
from, 20%, 53%, 80%, to {
transform: translate3d(0,0,0);
}
40%, 43% {
transform: translate3d(0, -30px, 0);
}
70% {
transform: translate3d(0, -15px, 0);
}
90% {
transform: translate3d(0,-4px,0);
}
`
render(
<div
css={css`
animation: ${bounce} 1s ease infinite;
`}
>
some bouncing text!
</div>
)Attaching props
css 가 props 를 통해 전달되면 컴포넌트 요소의 css 보다 우선한다.
import { css } from '@emotion/react'
const pinkInput = css`
background-color: pink;
`
const RedPasswordInput = props => (
<input
type="password"
css={css`
background-color: red;
display: block;
`}
{...props}
/>
)
render(
<div>
<RedPasswordInput placeholder="red" />
<RedPasswordInput placeholder="pink" css={pinkInput} />
</div>
)
Labels
Emotion 은 임의로 className 을 변형한다. 그런데, 커스터마이징을 할 수있다.
label 이라 하는 css의 속성을 추가하면 그 값은 클래스 이름 끝에 추가되므로 읽기 쉬워진다.
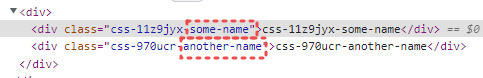
@emotion/babel-plugin 는 변수 이름 및 기타 정보를 기반으로 이런 라벨을 자동으로 추가하기 때문에 수동으로 지정할 필요는 없다.
가변 스타일링
Emotion 을 사용하면 React 컴포넌트에서 넘어온 props 에 따라 다른 스타일을 적용할 수 있다. 바꾸고 싶은 css 속성 값에 상수 대신 prop에 따라 변하는 변수를 할당해주면 된다.
/** @jsxImportSource @emotion/react */
const fontSize = {
small: "14px",
medium: "16px",
large: "18px",
};
function Button({ children, variant = "medium" }) {
return (
<button
css={{
borderRadius: "6px",
fontSize: fontSize[variant],
}}
>
{children}
</button>
);
}
export default Button;import Button from "./Button";
function App() {
return (
<>
<Button variant="small">small</Button>
<Button variant="medium">medium</Button>
<Button variant="large">large</Button>
</>
);
}props 에 따라 바꾸고 싶은 css 속성이 여러개일 때
/** @jsxImportSource @emotion/react */
const colors = {
default: "rgb(36, 41, 47)",
danger: "rgb(207, 34, 46)",
outline: "rgb(9, 105, 218)",
};
const sizeStyles = {
small: {
fontSize: "12px",
color: "red",
},
medium: {
fontSize: "14px",
color: "blue",
},
large: {
fontSize: "16px",
color: "yellow",
},
};
function Button({ children, size = "medium"}) {
return (
<button
css={{
fontWeight: "600",
...sizeStyles[size],
cursor: "pointer",
}}
>
{children}
</button>
);
}
export default Button;